Gravitational Gradients
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Terminology
Definitions
Distribution of disease not a random process but end result of interaction between pathologic process with its environment
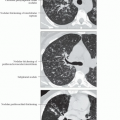
Gravity alters pulmonary physiology and creates differing regional environments, especially in upright lung
Ventilation (V) upright lung
Normal 3x difference from top to bottom of lung due to effect of gravity on intrapleural pressure, transpulmonary gradients, and alveolar size
Branching pattern of airways important in distribution of particulate material suspended in inhaled air
Turbulent airflow in large upper airways (1st 6 generations) directs particles > 5 µm in diameter against ciliated airways where they can be removed from lung
Particles < 5 µm in diameter can deposit in respiratory bronchioles within centrilobular portion of lobule
Particles tend to follow straightest pathway through lung, which is to lung periphery
Determines distribution of inhaled insults, which acutely affect lung
Perfusion (Q) upright lung
Normal 18x difference from top to bottom of lung due to effect of gravity on low pressure pulmonary arterial system
Main pulmonary artery inclined toward left upper lung; jet effect across pulmonic valve increases blood flow 10% above similar regions in right upper lobe
Zonal blood flow (according to West model)
Blow flow determined by pulmonary arterial (pa), pulmonary venous (pv), and alveolar pressure (pA)
Zone 1: pA > pa > pv, capillaries collapsed, no blood flow, does not occur in normal lung but in hypotensive patient on mechanical ventilation and PEEP may develop zone I conditions in nondependent lung
Zone 2: pa > pA > pv, blood flow not determined by gradient between arterial and venous pressure but gradient between arterial and alveolar pressure and may produce erroneous clinical pressure readings from wedged Swan-Ganz catheter
Zone 3: pa > pv > pA, blood flow determined by arterial venous pressure gradient
Determines distribution of hydrostatic (cardiogenic edema) and blood borne insults (hematogenous metastases)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree