Groin Hernia
KEY FACTS
Terminology
Imaging
IMAGING
General Features
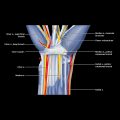
 Inguinal canal
Inguinal canal
 Femoral canal
Femoral canal
 Indirect inguinal hernia
Indirect inguinal hernia
 Direct inguinal hernia
Direct inguinal hernia
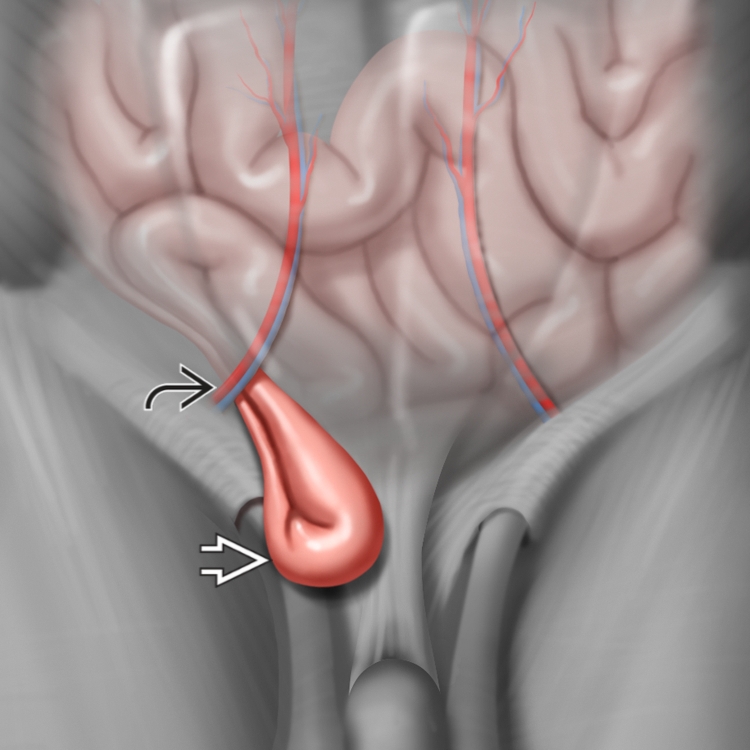
 Femoral hernia
Femoral hernia
 Double hernia (a.k.a. saddlebag hernia)
Double hernia (a.k.a. saddlebag hernia)
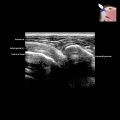
Ultrasonographic Findings




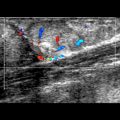
 . Note that the neck of a direct inguinal hernia is medial to the inferior epigastric vessels
. Note that the neck of a direct inguinal hernia is medial to the inferior epigastric vessels  . A direct inguinal hernia passes through the transversalis fascial defect in the Hesselbach triangle.
. A direct inguinal hernia passes through the transversalis fascial defect in the Hesselbach triangle.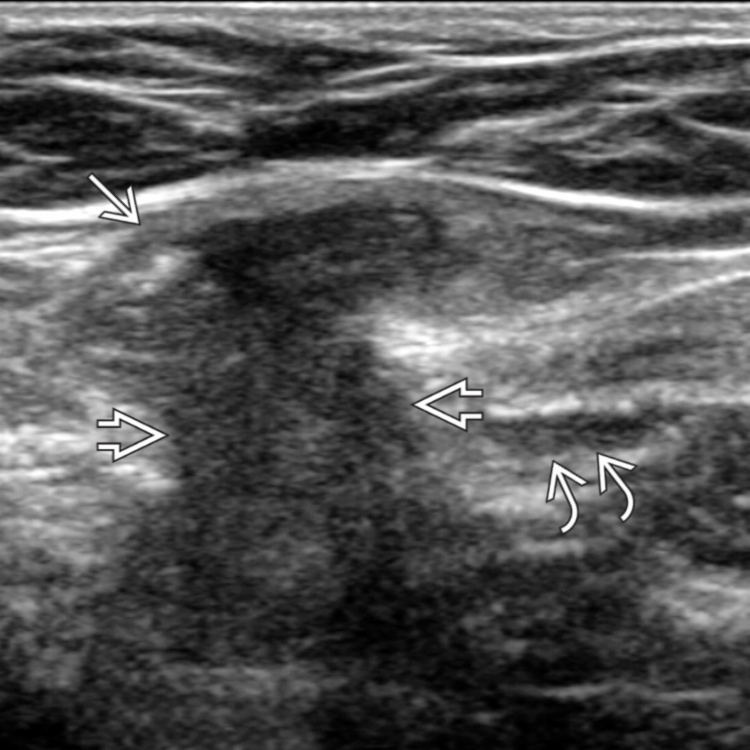
 containing hypoechoic mesenteric fat. The neck
containing hypoechoic mesenteric fat. The neck  of the hernia lies medial to the inferior epigastric vessels
of the hernia lies medial to the inferior epigastric vessels  .
.
 containing bowel
containing bowel  . The neck
. The neck  of the hernia is wide and lies medial to the inferior epigastric vessels
of the hernia is wide and lies medial to the inferior epigastric vessels  . Obstruction is rare in direct inguinal hernias, as they usually have a wide neck.
. Obstruction is rare in direct inguinal hernias, as they usually have a wide neck.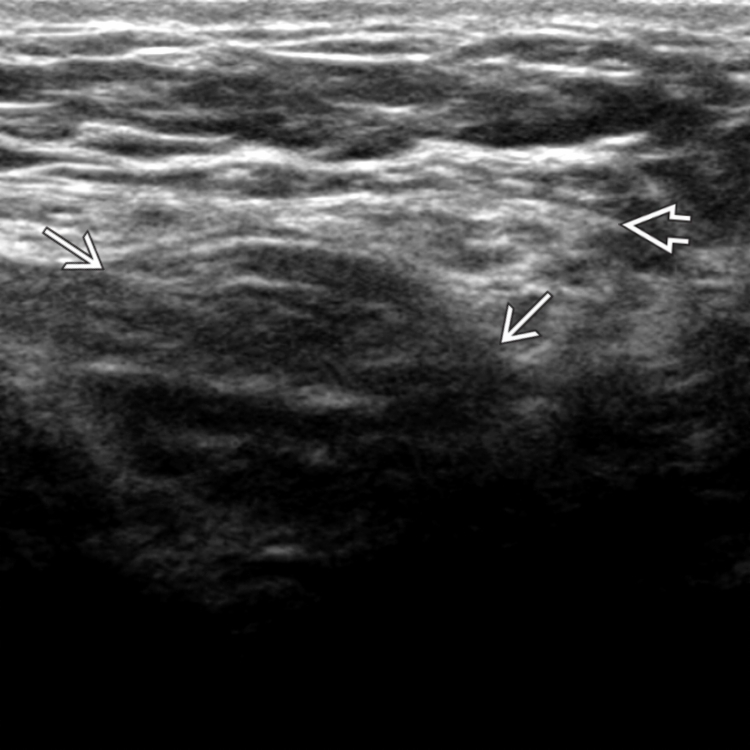
 that arises cephalad to the inguinal ligament
that arises cephalad to the inguinal ligament  . The inguinal ligament is difficult to appreciate on still images but is more readily appreciable in real time.
. The inguinal ligament is difficult to appreciate on still images but is more readily appreciable in real time.