• Causes include infiltration by fibrosis (interstitial fibrosis), abnormal cells (lymphangitis carcinomatosa), or fluid (pulmonary oedema) • Smooth interlobular septal thickening: pulmonary oedema or alveolar proteinosis • Irregular interlobular septal thickening: lymphangitic spread of tumour or the nodular septal thickening seen in sarcoidosis • A fine reticular pattern (most commonly seen with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis) • A coarse reticular pattern: this occurs with severe fibrosis and is characterized by interlacing irregular linear opacities • Ground-glass opacification (if the septal thickening is very fine) • Progressive fibrosis and end-stage lung destruction of unknown cause • It is also known as cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis (CFA) or usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) • A clinicopathological entity of an isolated organizing pneumonia seen in patients without an identifiable associated disease (e.g. infection, malignancy or connective tissue disease) • COP was previously known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) • This is characterized by alveolar space filling with macrophages and a strong association with cigarette smoking • RB–ILD and DIP are part of the same disease spectrum, with DIP the more severe form • RB–ILD: areas of patchy ground-glass opacification (due to macrophage accumulation within the alveolar spaces and ducts) • DIP: ground-glass opacification is also the dominant feature • A multisystem non-caseating granulomatous disorder of unknown aetiology • The lungs, hilar and mediastinal nodes are the most commonly affected organ system • Lung granulomas have a characteristic distribution along the lymphatics within the bronchovascular sheath, interlobular septa and subpleural regions • Lymph nodes appear lobulated with a well-demarcated outline (they can be massive) • Garland’s triad: bilateral symmetrical hilar and paratracheal lymphadenopathy • 40% of patients with nodal enlargement will develop parenchymal opacities within 1 year – of these ⅓ will develop persistent fibrotic shadowing (± traction bronchiectasis) • Parenchymal changes appear as any nodal enlargement subsides (these tend to progress in unison in lymphoma) Causes of eggshell nodal calcification* Sarcoidosis • The most common pattern: rounded or irregular moderately well-defined nodules (2–4mm) • The second most common pattern: peribronchovascular patchy airspace consolidation • Complications: cor pulmonale • Perilymphatic nodular opacities (1–5mm) within the subpleural regions and along the bronchovascular bundles and interlobular septae (generating irregular and beaded interfaces) • Pleural thickening and effusions are unusual (any effusion seen is usually unilateral and small) • Intrinsic mural sarcoidosis can rarely cause airway narrowing (with single or multiple lesions seen down to a segmental level) • Sarcoidosis is the most common cause of intrathoracic lymph node enlargement • 67Gallium accumulation is a sensitive but non-specific indicator of active inflammation in sarcoidosis • Diagnosis: transbronchial biopsy
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT)
HRCT PATTERNS OF DIFFUSE LUNG DISEASE
RETICULAR PATTERN
Definition
HRCT
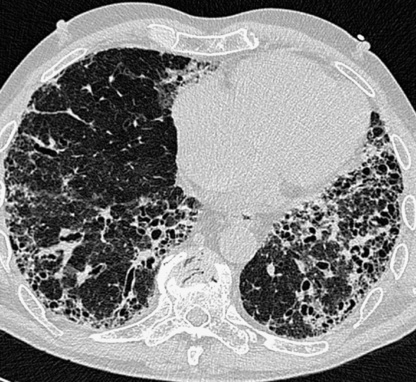
 an end-stage fibrotic (honeycomb) lung is characterized by cystic airspaces surrounded by irregular walls
an end-stage fibrotic (honeycomb) lung is characterized by cystic airspaces surrounded by irregular walls
 Traction bronchiectasis/bronchiolectasis: extensive fibrosis can distort the lung morphology resulting in irregular segmental or subsegmental airway dilatation
Traction bronchiectasis/bronchiolectasis: extensive fibrosis can distort the lung morphology resulting in irregular segmental or subsegmental airway dilatation
IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS
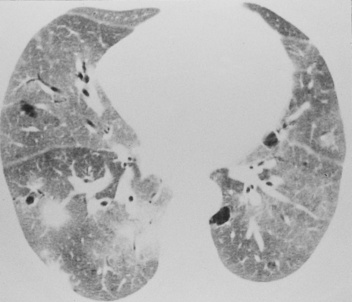
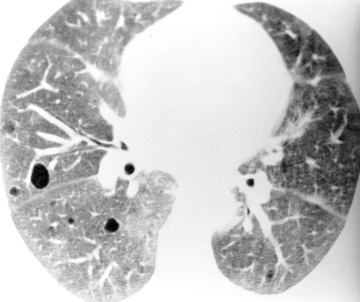
IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS (IPF)
DEFINITION
 UIP specifically refers to the histopathological pattern seen in patients with the clinical presentation of CFA or IPF
UIP specifically refers to the histopathological pattern seen in patients with the clinical presentation of CFA or IPF
CRYPTOGENIC ORGANIZING PNEUMONIA (COP)
DEFINITION
IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS
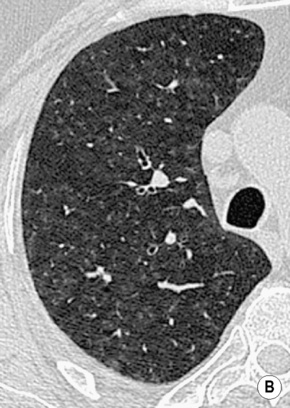
RESPIRATORY BRONCHIOLITIS–INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE (RB–ILD) AND DESQUAMATIVE INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIA (DIP)
DEFINITION
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
HRCT
 poorly defined low attenuation centrilobular nodules
poorly defined low attenuation centrilobular nodules  upper lobe centrilobular emphysema and areas of air trapping (usually to a limited extent and reflecting the bronchiolitic element)
upper lobe centrilobular emphysema and areas of air trapping (usually to a limited extent and reflecting the bronchiolitic element)
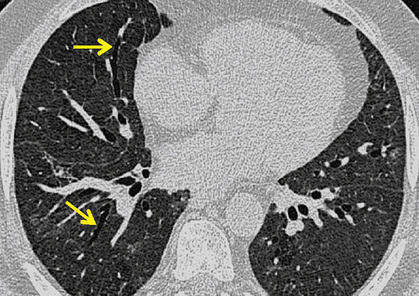
 this typically affects the peripheral lower zones and may be patchy
this typically affects the peripheral lower zones and may be patchy  occasionally there are features of established fibrosis (which is usually to a limited extent)
occasionally there are features of established fibrosis (which is usually to a limited extent)
Clinico–radiological–pathological criteria
Histological pattern
HRCT features*
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Usual interstitial pneumonia
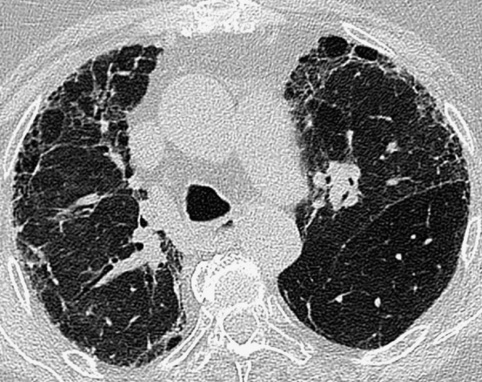
Peripheral (subpleural) and basal reticular opacities  honeycombing
honeycombing  areas of ground-glass opacity (associated with traction bronchiectasis)
areas of ground-glass opacity (associated with traction bronchiectasis)
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia
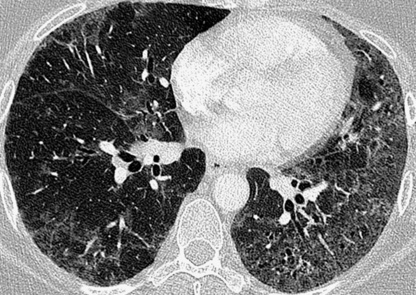
Areas of ground-glass opacity ± traction bronchiectasis  minimal honeycombing
minimal honeycombing
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Organizing pneumonia
Peripheral or peribronchial consolidation  areas of ground-glass opacity
areas of ground-glass opacity  a perilobular pattern is increasingly recognized
a perilobular pattern is increasingly recognized
Acute interstitial pneumonia
Diffuse alveolar damage
Consolidation (within the dependent lung)  areas of ground-glass opacity
areas of ground-glass opacity  traction bronchiectasis (organizing phase)
traction bronchiectasis (organizing phase)
Respiratory bronchiolitis–interstitial lung (RB–ILD)
RB–ILD
Poorly defined centrilobular nodules  areas of ground-glass opacity
areas of ground-glass opacity  bronchial wall thickening
bronchial wall thickening  limited emphysema
limited emphysema
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
DIP
Areas of ground-glass opacity  features of interstitial fibrosis
features of interstitial fibrosis
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
LIP
Areas of ground-glass opacity  poorly defined centrilobular nodules
poorly defined centrilobular nodules  thickened interlobular septa
thickened interlobular septa  thin-walled discrete cysts
thin-walled discrete cysts  air trapping
air trapping
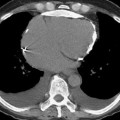
SARCOIDOSIS
SARCOIDOSIS
DEFINITION
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
CXR (lymphadenopathy)
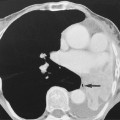
 they can calcify in a characteristic ‘eggshell’ fashion
they can calcify in a characteristic ‘eggshell’ fashion  airway or vascular compression is unusual
airway or vascular compression is unusual
 The lymphadenopathy can occasionally (1–5%) be asymmetrical or unilateral – marked asymmetry should bring the diagnosis into question
The lymphadenopathy can occasionally (1–5%) be asymmetrical or unilateral – marked asymmetry should bring the diagnosis into question  unilateral paratracheal lymphadenopathy is usually right-sided (left-sided lymphadenopathy causes enlargement of the aortopulmonary window nodes)
unilateral paratracheal lymphadenopathy is usually right-sided (left-sided lymphadenopathy causes enlargement of the aortopulmonary window nodes)
CXR (parenchymal changes)
Silicosis
Histoplasmosis
Lymphoma (post-irradiation)
Blastomycosis
Amyloidosis
 very small aggregated opacities can give a ground-glass appearance
very small aggregated opacities can give a ground-glass appearance
 this usually demonstrates a nodular pattern but can also contain air bronchograms and have ill-defined margins
this usually demonstrates a nodular pattern but can also contain air bronchograms and have ill-defined margins  a conglomerate opacity resembling progressive massive fibrosis can develop
a conglomerate opacity resembling progressive massive fibrosis can develop
 bullous disease (± mycetoma formation)
bullous disease (± mycetoma formation)  pneumothorax
pneumothorax
HRCT
 larger ill-defined nodules can develop – these rarely cavitate but can demonstrate air bronchograms
larger ill-defined nodules can develop – these rarely cavitate but can demonstrate air bronchograms  patchy ground-glass opacification
patchy ground-glass opacification  air trapping is commonly seen
air trapping is commonly seen
Other thoracic findings
 there is a potential for significant airflow obstruction or atelectasis (particularly involving the middle lobe)
there is a potential for significant airflow obstruction or atelectasis (particularly involving the middle lobe)
PEARLS
 symmetry is the important diagnostic feature
symmetry is the important diagnostic feature
 The anterior mediastinal nodes are occasionally enlarged – posterior mediastinal nodal enlargement is unusual
The anterior mediastinal nodes are occasionally enlarged – posterior mediastinal nodal enlargement is unusual

 it almost always represents significant interstitial lung disease (ILD)
it almost always represents significant interstitial lung disease (ILD)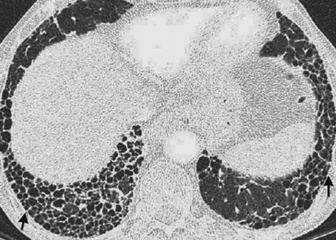
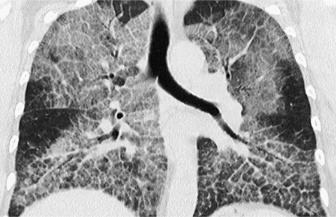
 nodules can be < 5mm from the pleural surface
nodules can be < 5mm from the pleural surface lymphangitis carcinomatosa
lymphangitis carcinomatosa most peripheral nodules are > 5mm from the pleural surface
most peripheral nodules are > 5mm from the pleural surface  a ‘tree-in-bud’ appearance suggests endobronchial disease
a ‘tree-in-bud’ appearance suggests endobronchial disease respiratory bronchiolitis–interstitial lung disease (RB–ILD)
respiratory bronchiolitis–interstitial lung disease (RB–ILD)  diffuse panbroncholitis
diffuse panbroncholitis  endobronchial spread of TB
endobronchial spread of TB  cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
cryptogenic organizing pneumonia pulmonary metastases
pulmonary metastases  pneumoconiosis
pneumoconiosis  sarcoidosis (rare)
sarcoidosis (rare)
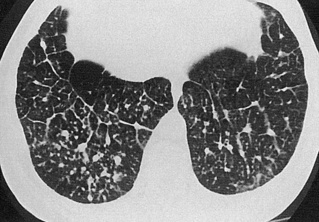
 it represents a combination of partial airspace filling, interstitial thickening and displacement of air from the lung
it represents a combination of partial airspace filling, interstitial thickening and displacement of air from the lung acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)  acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)  non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)  diffuse pneumonias (particularly Pneumocystis jiroveci (P. carinii) pneumonia in AIDS patients)
diffuse pneumonias (particularly Pneumocystis jiroveci (P. carinii) pneumonia in AIDS patients)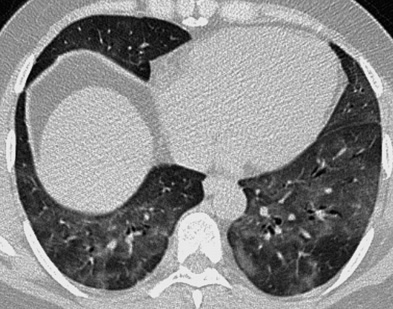


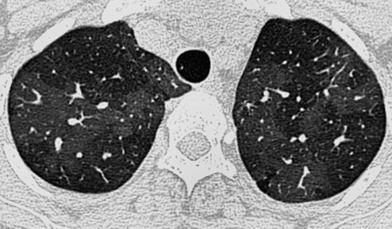
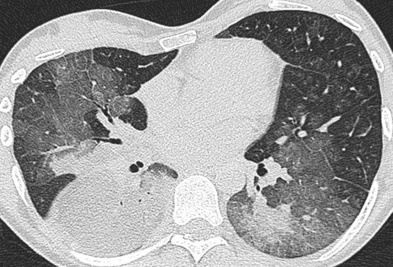
 dyspnoea
dyspnoea  weight loss
weight loss  clubbing
clubbing  it commonly affects patients who are 40–70 years old (M>F)
it commonly affects patients who are 40–70 years old (M>F) these are most profuse at the lung bases
these are most profuse at the lung bases  although there is associated volume loss, the lung volumes may be preserved or increased if there is coexisting emphysema
although there is associated volume loss, the lung volumes may be preserved or increased if there is coexisting emphysema mediastinal adenopathy is frequently seen (up to 2cm and unrelated to infection or malignancy)
mediastinal adenopathy is frequently seen (up to 2cm and unrelated to infection or malignancy)  pleural effusions are uncommon
pleural effusions are uncommon  pulmonary hypertension can be seen with severe disease
pulmonary hypertension can be seen with severe disease asbestosis
asbestosis  connective tissue disease
connective tissue disease  rarely drugs
rarely drugs it commonly affects patients who are aged between 40 and 50 years (M = F)
it commonly affects patients who are aged between 40 and 50 years (M = F) a reticular pattern is common
a reticular pattern is common  there may be significant fibrosis (with a uniform temporality in comparison with UIP) but honeycombing is sparse
there may be significant fibrosis (with a uniform temporality in comparison with UIP) but honeycombing is sparse dyspnoea
dyspnoea  malaise
malaise  weight loss
weight loss  it commonly affects patients during the 6th decade (M = F)
it commonly affects patients during the 6th decade (M = F) there is lung volume preservation
there is lung volume preservation ground-glass opacification, subpleural linear opacities and a distinctive perilobular pattern is commonly seen
ground-glass opacification, subpleural linear opacities and a distinctive perilobular pattern is commonly seen  the lung architecture is generally well preserved with cavitation rarely seen
the lung architecture is generally well preserved with cavitation rarely seen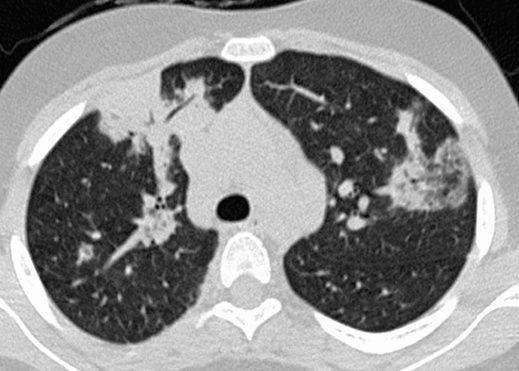
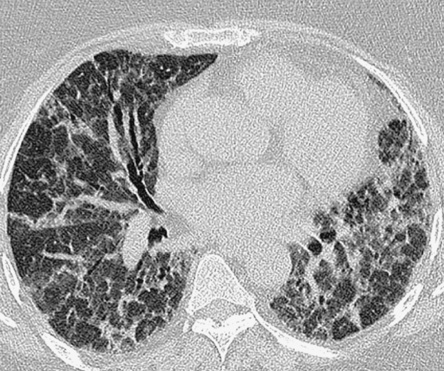
 cough
cough
 it resembles lymphoma but its clinical course is more akin to a chronic interstitial pneumonia
it resembles lymphoma but its clinical course is more akin to a chronic interstitial pneumonia ground-glass opacification
ground-glass opacification  thickened bronchovascular bundles and interlobular septal thickening
thickened bronchovascular bundles and interlobular septal thickening  discrete thin-walled cysts lying deep within the lung parenchyma (measuring up to 3cm)
discrete thin-walled cysts lying deep within the lung parenchyma (measuring up to 3cm) bronchial dilatation and architectural distortion (fibrotic phase)
bronchial dilatation and architectural distortion (fibrotic phase)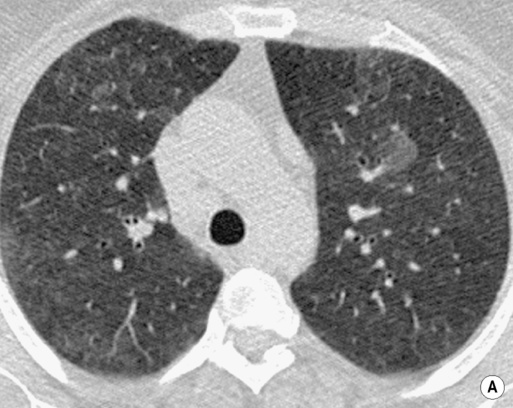

 malaise
malaise  weight loss
weight loss  fever and night sweats
fever and night sweats  dyspnoea
dyspnoea  erythema nodosum
erythema nodosum  arthralgia
arthralgia  30% of patients are asymptomatic
30% of patients are asymptomatic