Hypoechoic Subcutaneous Mass
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
 Comprises both vascular tumor (hemangioma) and vascular malformation
Comprises both vascular tumor (hemangioma) and vascular malformation
 Variable US appearances
Variable US appearances
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
 Benign, solitary smooth muscle neoplasm most commonly occurs in subcutaneous soft tissues of lower limb
Benign, solitary smooth muscle neoplasm most commonly occurs in subcutaneous soft tissues of lower limb
 Usually round or ovoid in shape with long axis parallel to extremity axis
Usually round or ovoid in shape with long axis parallel to extremity axis
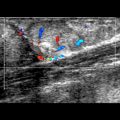
 Smooth-bordered, homogeneous, hypoechoic mass without perceivable capsule
Smooth-bordered, homogeneous, hypoechoic mass without perceivable capsule
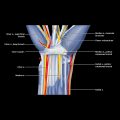
 Occurs in close proximity to artery or vein
Occurs in close proximity to artery or vein
 Often hypervascular ± vascular convergence
Often hypervascular ± vascular convergence
 Benign skin tumor arising from cells of hair matrix; more commonly seen in children
Benign skin tumor arising from cells of hair matrix; more commonly seen in children
 Well-circumscribed, ovoid, heterogeneous, solid subdermal mass containing matrix calcification, intrinsic vascularity, and peripheral hypoechoic rim (due to connective tissue capsule)
Well-circumscribed, ovoid, heterogeneous, solid subdermal mass containing matrix calcification, intrinsic vascularity, and peripheral hypoechoic rim (due to connective tissue capsule)
 Intrinsic vascularity may be peripheral, central, or mixed
Intrinsic vascularity may be peripheral, central, or mixed
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Hypoechoic Subcutaneous Mass