| SKULL BASE REGION | Trigeminal cistern |
| HISTOPATHOLOGY | N/A |
| PRIOR SURGICAL RESECTION | N/A |
| PERTINENT LABORATORY FINDINGS | N/A |
Case description
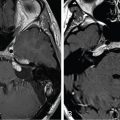
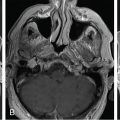
The patient is a 74-year-old male with essential trigeminal neuralgia (TN) of the right V2-V3 territory. TN started 5 years before, and the clinical presentation was very typical. The pain was initially sensitive to carbamazepine, and then progressively became resistant to several drugs. High-quality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed an absence of any visible neurovascular conflict and a wide trigeminal cistern. Both percutaneous approaches and stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) were proposed to the patient, who opted for SRS ( Figure 9.43.1 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | Gamma Knife – Icon |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) | 90 at the 100% isodose line |
| Number of Fractions | 1 |

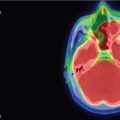
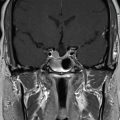
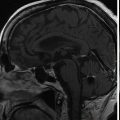
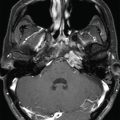
Imaging of the treatment plan. The dose planning is displayed in axial CISS images fused with computed tomography (CT) bony window ( A ), axial CT bony window ( B ), coronal CISS images fused with CT bony window ( C ), and sagittal CISS images fused with CT bony window ( D ). Following Leksell G frame application under local anesthesia, an MRI and a CT scan were performed for stereotactic purposes. The MRI included a high-resolution, 0.5 mm 3 T2 CISS sequence and a 3D T1 MPR sequence on a 1.5 T Siemens MR machine. A single 4-mm isocenter was positioned 7–8 mm anterior to the nerve emergence from the pons (retrogasserian target) on the cisternal portion of the right trigeminal nerve. A dose of 90 Gy was prescribed at the 100% isodose point. The treatment time was 55 minutes, which translates to a biologically effective dose (BED) of 2390 Gy2.47. CISS, Constructive interference in steady state; MPR, multiplanar reformation.
| Critical Structure | Dose Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Brainstem | < 0.01 cc > 15 Gy |
| Basilar artery | Very tolerant |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree