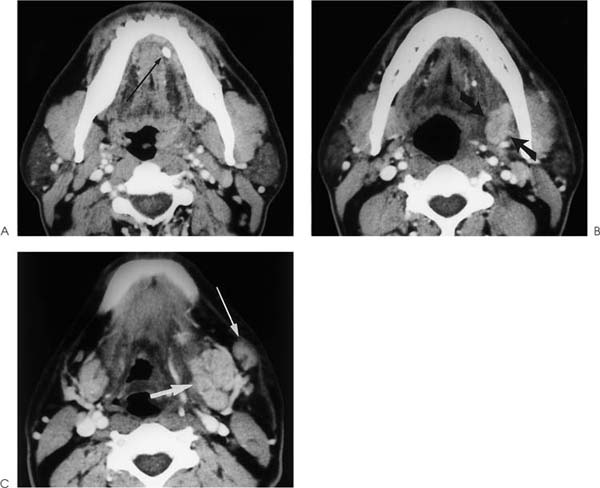
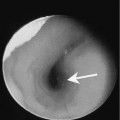
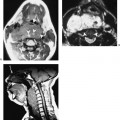
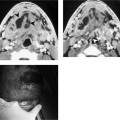
Chapter 202 Submandibular space (SMS) abscess, or cellulitis, is usually secondary to infections involving the submandibular nodes, submandibular gland, teeth, or mandible. Submandibular gland abscesses are frequently associated with ductal stenosis or calculi (Fig. 202–1). Submandibular duct calculi are relatively common and account for 85% of all salivary gland stones. Odontogenic infections occur in patients with poor oral hygiene. There is no known sex predilection for SMS infection, and this condition is seen mainly in the adult population. Patients usually present with unilateral pain and tenderness in the SMS. In patients with underlying calculus disease, a history of salivary colic or submandibular gland swelling following meals may be elicited. SMS abscess arising from dental infection may produce trismus if the adjacent medial pterygoid muscle is also involved.
Infection
Epidemiology
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree