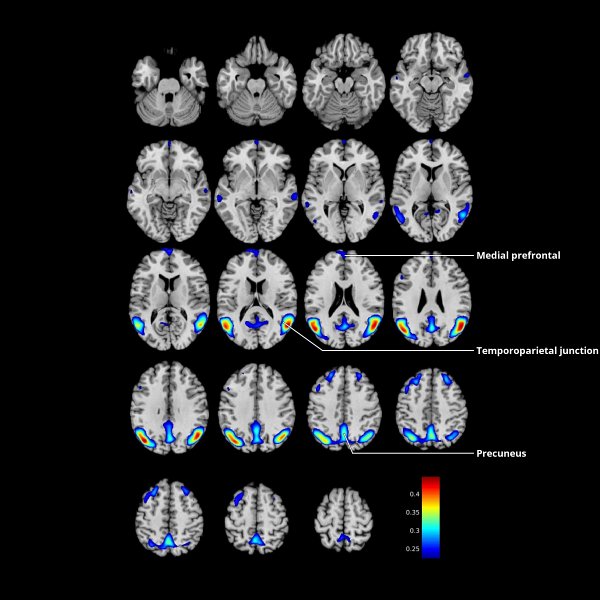
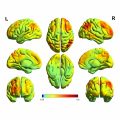
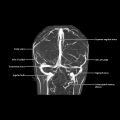
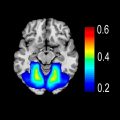
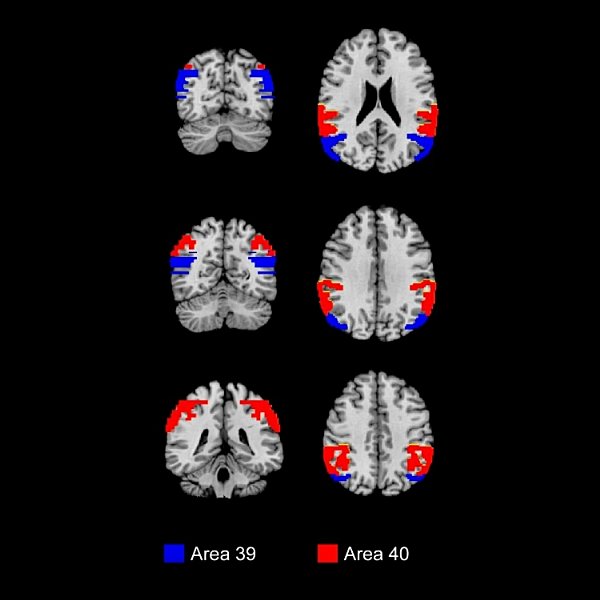
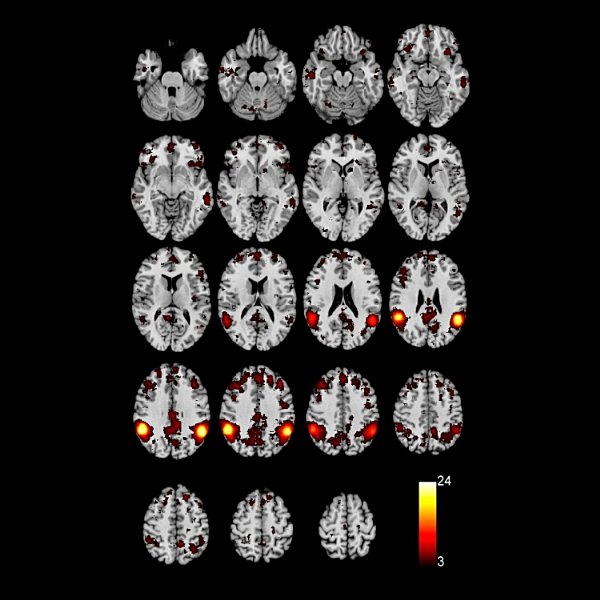
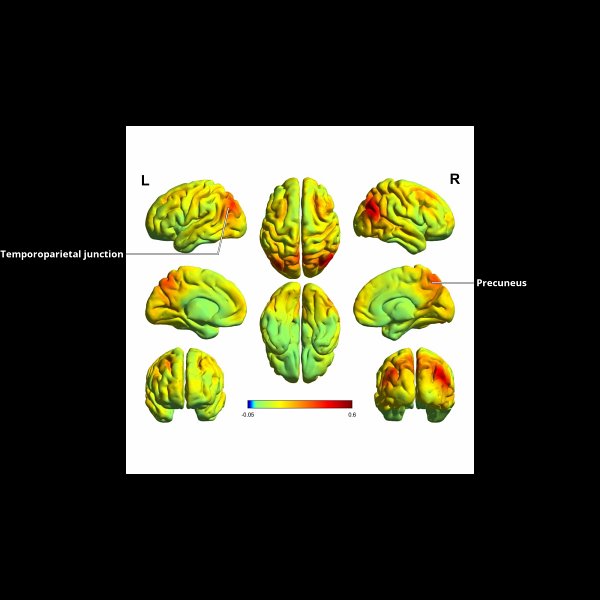
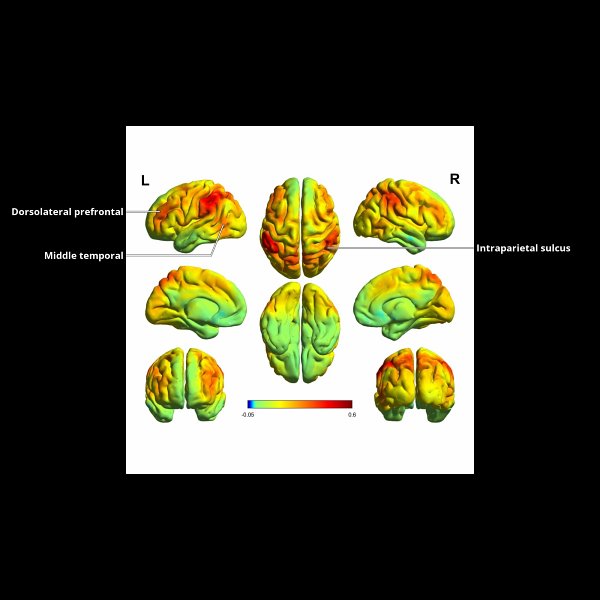
div style=”display:none;”> INFERIOR PARIETAL LOBULE: LOCATION AND COACTIVATION AREA 39: FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY AREA 40: FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY
Inferior Parietal Lobule (Areas 39, 40)
Image Gallery
Print Images
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine