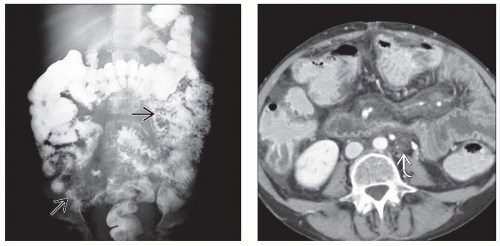
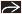Intestinal Lymphangiectasia
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Rare disease or syndrome characterized by hypoproteinemia, peripheral edema, and lymphocytopenia resulting from loss of lymphatic fluid into intestine
Important cause of protein-losing enteropathy
Imaging
Diffuse small bowel wall thickening with submucosal edema
Infiltration of small bowel mesentery
± mesenteric and retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy
± short segment, nonobstructing SB intussusceptions
For secondary form of lymphangiectasia
May see signs of cardiac failure, retroperitoneal fibrosis or tumor, tuberculosis, etc.
Top Differential Diagnoses
Whipple disease
Lymphoma
Intestinal opportunistic infections
Pathology
Primary form
Congenital abnormality of lymphatic development
Secondary form
Lymphatic obstruction of lacteals draining the small intestine
Both forms result in abnormal (deficient) absorption of chylomicrons and fat-soluble vitamins, excessive leakage of lymph into bowel lumen, and excessive loss of protein
Diagnosis is made by intestinal biopsy
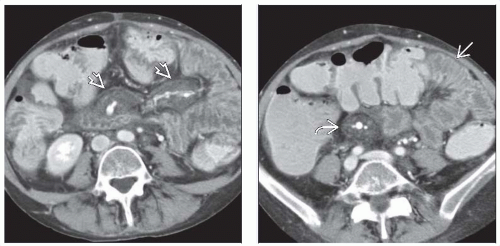 (Left) In the same patient, note the striking edema in the root and leaves of mesentery
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree


|