• This can assess tumour blood vessel density (an indirect measure of tumour neovascularity malignancy) • DSC imaging differs from contrast enhancement, which is an indicator of vascular endothelial (blood–brain barrier) integrity • Useful in identifying acute infarcts or abscesses (which can mimic brain tumours) • ADC measurements correlate inversely with the histological glioma cell count • Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) provides additional information about the direction of water diffusion • Children: primary tumours usually occur infratentorially and within the posterior fossa between the ages of 2 and 10 years (e.g. pilocytic astrocytoma, pontine glioma, ependymoma and medulloblastoma) Features distinguishing an extra- from an intra-axial tumour • Adults: 70% of intracranial tumours are primary (30% are metastases) Common calcified and haemorrhagic lesions* Primary cerebral tumours and age groups† The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system (abridged) Differentiating between an infarct and tumour ©12 • A benign or malignant tumour arising from an astrocyte • Astrocyte: a structural or supporting cell type within the brain • This is the largest group of primary brain neoplasms (75% of all glial tumours) • Location: supratentorial (50%) (the majority will eventually progress to a more malignant type over time): • Grade I (benign pilocytic astrocytoma): this is potentially resectable with a low proliferative potential (up to 40% of all paediatric intracranial tumours) • Grade II (diffuse astrocyoma): an infiltrating (rather than destroying) low-grade tumour • Grade III (anaplastic astrocytoma): although there is increased mitotic activity and anaplasia there is no necrosis • Grade IV (glioblastoma multiforme): this is the commonest primary adult intracranial neoplasm • Differential: lymphomatosis cerebri *It is typically cystic with a mural nodule and located within the posterior fossa – it tends to be solid or lobulated when seen elsewhere. • A relatively benign slow-growing neoplasm arising from the oligodendrocyte • It is classified as a WHO grade II (well-differentiated, low-grade) or WHO grade III (anaplastic high-grade) tumour • It occurs predominantly in adults (during the 4th decade) and accounts for 5–10% of all intracranial neoplasms • A low-grade tumour arising from the ependyma • It accounts for 5% of all intracranial tumours (a higher incidence is seen in the paediatric population) • A benign tumour of endothelial origin that is composed of thin-walled blood vessels • It usually presents in young adults (M>F) • Common symptoms include headache, ataxia, nausea, vomiting and vertigo • 20% are associated with von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) disease – these generally present at an earlier age • Multiple haemangioblastomas are only seen with von Hippel–Lindau disease A vascular nodule within an avascular mass Differentiating between a haemangioblastoma and a juvenile pilocystic astriocytoma • This accounts for up to 30% of all paediatric infratentorial tumours (they may occur in adults) • This is an aggressive tumour, accounting for 30-40% of all posterior fossa tumours • It classically arises from the roof of the 4th ventricle and is therefore usually a midline cerebellar mass (a lateral cerebellar location is more common in older children and adults)
Intracranial tumours in adults
IMAGING TECHNIQUES AND GENERAL FEATURES
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
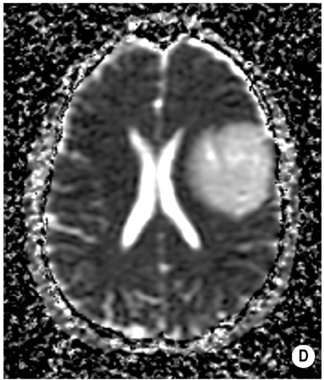
Dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced (DSC) MR perfusion imaging
 rCBV measurements correlate closely with markers of tumour vascularity and angiogenesis
rCBV measurements correlate closely with markers of tumour vascularity and angiogenesis
 Higher rCBV values with high-grade tumours
Higher rCBV values with high-grade tumours
 rCBV maps can aid stereotactic tumour biopsies
rCBV maps can aid stereotactic tumour biopsies
 In radiation necrosis the residual enhancing lesion has a low rCBV (higher with tumour recurrence due to new vessel formation)
In radiation necrosis the residual enhancing lesion has a low rCBV (higher with tumour recurrence due to new vessel formation)
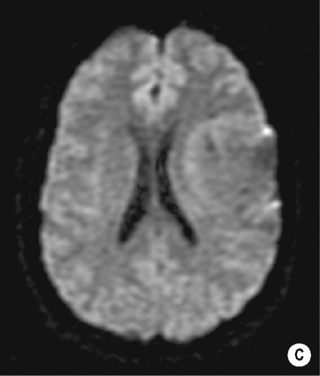
MR diffusion imaging
 ADC measurements of any enhancing components in radiation necrosis are significantly higher than with recurrent tumour (mirroring the higher cellular density with a recurrent neoplasm)
ADC measurements of any enhancing components in radiation necrosis are significantly higher than with recurrent tumour (mirroring the higher cellular density with a recurrent neoplasm)
 the normally high anisotropy within white matter tracts can be lost if infiltrated by tumour
the normally high anisotropy within white matter tracts can be lost if infiltrated by tumour
CLASSIFICATION OF INTRACRANIAL TUMOURS
Extra-axial tumours
Patient age and tumour site are useful indicators to the likely tumour type
 below 2 and above 10 years of age supratentorial tumours are more common (paediatric supratentorial tumours will preferentially affect the midline structures)
below 2 and above 10 years of age supratentorial tumours are more common (paediatric supratentorial tumours will preferentially affect the midline structures)  intracranial metastases are rare
intracranial metastases are rare
Extra-axial tumour
Intra-axial tumour
‘Buckling’ and medial displacement of the grey–white matter interface
Yes
No
CSF cleft separating the base of the mass from adjacent brain
Yes
No
Broad base along a dural or calvarial surface
Yes
No
Associated bone changes
• Meningioma: hyperostotic bone reaction
• Dermoid cyst/schwannoma: bone thinning (with enlargement of the middle cranial fossa or internal auditory meatus)
Rare
Grey–white matter junction
Preserved
Destroyed
 Astrocytoma: this is the most common primary childhood brain tumour (the majority are pilocytic astrocytomas and characteristically occur within the cerebellum, hypothalamus and optic nerves)
Astrocytoma: this is the most common primary childhood brain tumour (the majority are pilocytic astrocytomas and characteristically occur within the cerebellum, hypothalamus and optic nerves)
 the vast majority of tumours are supratentorial – the posterior fossa is rarely affected by a primary tumour (a metastasis is more likely at this location)
the vast majority of tumours are supratentorial – the posterior fossa is rarely affected by a primary tumour (a metastasis is more likely at this location)
Tumour
Typical site
Colloid cyst
Foramen of Monro/third ventricle
Meningioma
Trigone of lateral ventricle
Choroid
Fourth ventricle
Ependymoma
Lateral ventricle (more common in children) and fourth ventricle
Neurocytoma
Lateral ventricles (involving septum pellucidum)
Metastases
Lateral ventricles, ependyma and choroid plexus
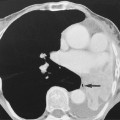
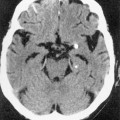
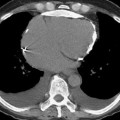
Common calcified lesions
Common haemorrhagic lesions
Oligodendrogliomas (90%)
Choroid plexus tumours
Ependymoma
Central neurocytoma
Meningioma
Craniopharyngioma
Teratoma
Chordoma
GBM (grade IV glioma)
Oligodendroglioma
Metastases
– Melanoma
– Lung
– Breast
Tumour
Age group
Brainstem glioma, optic nerve glioma
0–5
Medulloblastoma, cerebellar astrocytoma, papilloma choroid plexus, pinealoma, craniopharyngioma
5–15
Ependymoma
15–30
Glioma, meningioma, acoustic neuroma, pituitary tumour, hemangioblastoma
30–65
Meningioma, acoustic tumour, glioblastoma
65+
TUMOURS OF NEUROEPITHELIAL TISSUE
Astrocytic tumours
Anaplastic astrocytoma
Diffuse astrocytoma
Glioblastoma
Gliomatosis cerebri
Pilocytic astrocytoma
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
Oligodendroglial tumours
Oligodendroglioma
Anaplastic oligodendroglioma
Oligoastrocytic tumours
Oligoastrocytoma
Anaplastic oligoastrocytoma
Ependymal tumours
Ependymoma
Subependymoma
Anaplastic ependymoma
Myxopapillary ependymoma
Choroid plexus tumours
Choroid plexus papilloma
Choroid plexus carcinoma
Other neuroepithelial tumours
Astroblastoma
Chordoid glioma of the third ventricle
Angiocentric glioma
Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumours
Ganglioglioma and gangliocytoma
Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour
Central neurocytoma and extraventricular neurocytic tumours
Tumours of the pineal region
Pineoblastoma
Pineocytoma
Embryonal tumours
Medulloblastoma
CNS primitive neuroectodermal tumour
Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour
TUMOURS OF CRANIAL AND PARASPINAL NERVES
Schwannoma (neurilemoma, neurinoma)
Neurofibroma
Perineurioma
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour (MPNST)
TUMOURS OF THE MENINGES
Tumours of meningothelial cells
Meningioma
Mesenchymal tumours
Primary melanocytic lesions
Other neoplasms related to the meninges
Haemangioblastoma
LYMPHOMAS AND HAEMATOPOIETIC NEOPLASMS
Malignant lymphomas
Plasmacytoma
Granulocytic sarcoma
GERM CELL TUMOURS
Germinoma
Embryonal carcinoma
Yolk sac tumour
Choriocarcinoma
Teratoma
Mixed germ cell tumour
TUMOURS OF THE SELLAR REGION
Craniopharyngioma
Granular cell tumour
Pituicytoma
Spindle cell oncocytoma of the adenohypophysis
METASTATIC TUMOURS
Tumour
Infarct
Grey matter changes
This is usually centred on the cerebral white matter and spares the overlying grey matter
This often simultaneously involves the cerebral cortex and juxtacortical white matter
Shape
Spherical or ovoid
Wedge or box shaped (with its base towards the brain surface)
Distribution
Not confined to a vascular territory
Confined to a vascular territory
Contrast enhancement
Gyriform enhancement is rare
Gyriform enhancement can be present
GLIOMAS
ASTROCYTOMA
DEFINITION
 cerebellum (35%)
cerebellum (35%)  brainstem (15%)
brainstem (15%)
WHO classification
 It characteristically occurs within the cerebellum in children
It characteristically occurs within the cerebellum in children  it can also occur within the hypothalamus and optic nerves (optic nerve involvement is a feature of NF-1)
it can also occur within the hypothalamus and optic nerves (optic nerve involvement is a feature of NF-1)
 it results in a relatively mild neurological deficit and a generally good prognosis
it results in a relatively mild neurological deficit and a generally good prognosis
 it is very malignant (with the worst prognosis)
it is very malignant (with the worst prognosis)  tumour necrosis is a hallmark
tumour necrosis is a hallmark
PEARLS
MRI
 viral encephalitis
viral encephalitis  acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)
acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)  vasculitis
vasculitis
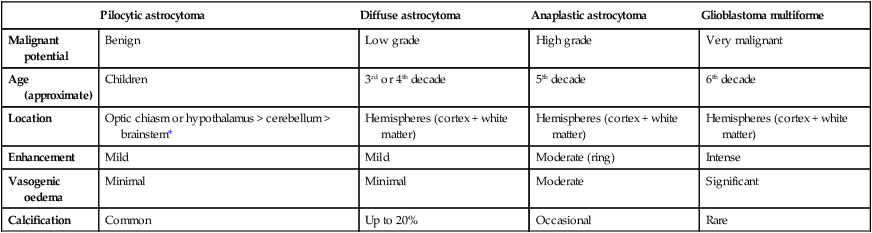
Pilocytic astrocytoma
Diffuse astrocytoma
Anaplastic astrocytoma
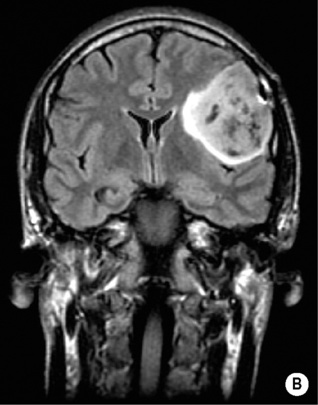
Glioblastoma multiforme
Malignant potential
Benign
Low grade
High grade
Very malignant
Age (approximate)
Children
3rd or 4th decade
5th decade
6th decade
Location
Optic chiasm or hypothalamus > cerebellum > brainstem*
Hemispheres (cortex + white matter)
Hemispheres (cortex + white matter)
Hemispheres (cortex + white matter)
Enhancement
Mild
Mild
Moderate (ring)
Intense
Vasogenic oedema
Minimal
Minimal
Moderate
Significant
Calcification
Common
Up to 20%
Occasional
Rare
GLIOMAS
OLIGODENDROGLIOMA
DEFINITION
 Oligodendrocyte: a cell that insulates the central nervous system axons and which is equivalent to a Schwann cell within the peripheral nervous system
Oligodendrocyte: a cell that insulates the central nervous system axons and which is equivalent to a Schwann cell within the peripheral nervous system
 it is chemosensitive
it is chemosensitive
EPENDYMOMA
DEFINITION
 Ependyma: this forms the epithelial lining of the ventricular system, cerebral hemispheres, brainstem and cerebellum, central canal of the spinal cord, and tip of the filum terminale
Ependyma: this forms the epithelial lining of the ventricular system, cerebral hemispheres, brainstem and cerebellum, central canal of the spinal cord, and tip of the filum terminale
INFRATENTORIAL TUMOURS
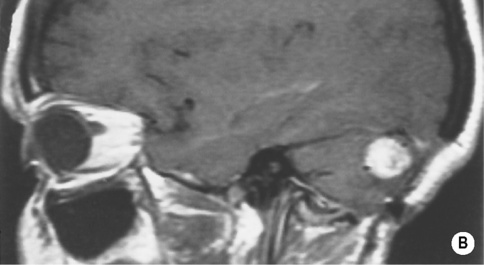
CEREBELLAR HAEMANGIOBLASTOMA
DEFINITION
 it is predominantly found within the posterior fossa (supratentorial lesions are rare) and is the commonest primary intra-axial and infratentorial adult tumour
it is predominantly found within the posterior fossa (supratentorial lesions are rare) and is the commonest primary intra-axial and infratentorial adult tumour
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 it is an unusual paediatric tumour unless in the context of von Hippel–Lindau disease
it is an unusual paediatric tumour unless in the context of von Hippel–Lindau disease
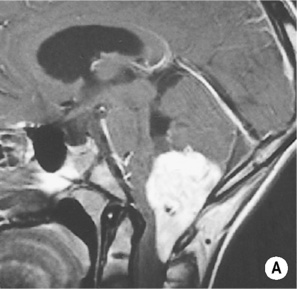
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
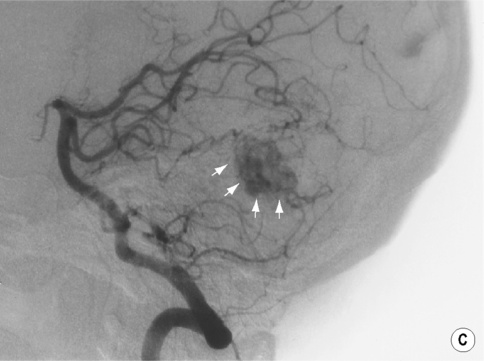
Angiography
 there may be draining veins present
there may be draining veins present
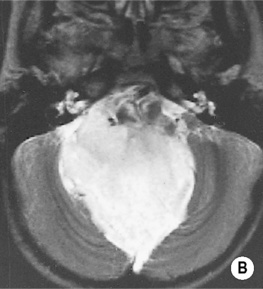
Haemangioblastoma
Juvenile pilocystic astrocytoma
Age
30–40 years
5–15 years
Pial attachment
Yes
No
A tiny nodule with a huge cystic component
More likely
Less likely
Arteriogram
Hypervascular nodule
Hypovascular nodule
Multiplicity and association with VHL disease
More likely
Less likely
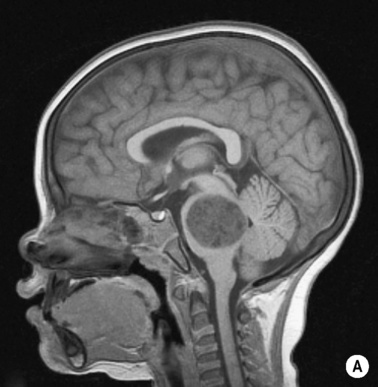
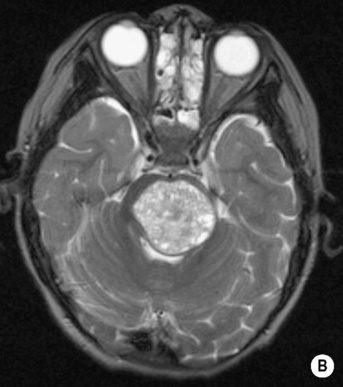
BRAINSTEM GLIOMA
DEFINITION
 80% of tumours are high grade, but symptoms occur late as the tumour infiltrates rather than destroys adjacent tissues (hydrocephalus is a late feature)
80% of tumours are high grade, but symptoms occur late as the tumour infiltrates rather than destroys adjacent tissues (hydrocephalus is a late feature)
MEDULLOBLASTOMA
DEFINITION
 it is also known as the PNET of the posterior fossa
it is also known as the PNET of the posterior fossa
 subsequent hydrocephalus is common
subsequent hydrocephalus is common

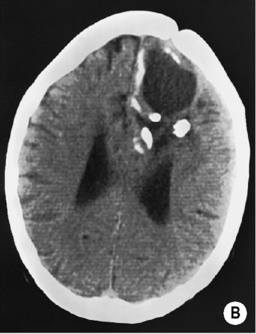
 high attenuation areas within a tumour indicate tumour calcification or recent intratumoural haemorrhage
high attenuation areas within a tumour indicate tumour calcification or recent intratumoural haemorrhage it provides a limited area of coverage (compared with MRI)
it provides a limited area of coverage (compared with MRI)  unlike MRI it can provide a direct relationship between the CT attenuation value and tissue contrast material concentration
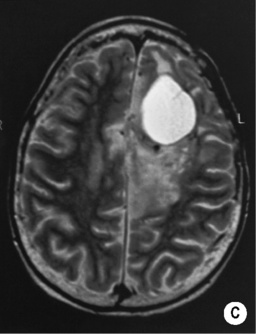
unlike MRI it can provide a direct relationship between the CT attenuation value and tissue contrast material concentration T2WI/FLAIR: high SI
T2WI/FLAIR: high SI signal loss is seen within any cystic tumour components
signal loss is seen within any cystic tumour components it may also be seen with certain low-grade tumours (e.g. pilocytic astrocytomas)
it may also be seen with certain low-grade tumours (e.g. pilocytic astrocytomas) this is more conspicuous on T2*WI (stronger magnetic susceptibility effects)
this is more conspicuous on T2*WI (stronger magnetic susceptibility effects)

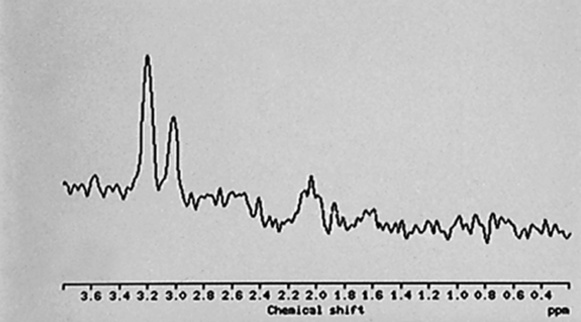
 these occur much more frequently in adults than children (accounting for the majority of the primary infratentorial adult tumours)
these occur much more frequently in adults than children (accounting for the majority of the primary infratentorial adult tumours)





 predominantly cystic (70%) or solid (30%)
predominantly cystic (70%) or solid (30%)  an associated strongly enhancing mural nodule when cystic
an associated strongly enhancing mural nodule when cystic  calcification is rare
calcification is rare  no adjacent oedema
no adjacent oedema T2WI: high SI
T2WI: high SI  T1WI + Gad: avid homogeneous enhancement of any solid component
T1WI + Gad: avid homogeneous enhancement of any solid component hypothalamic or chiasmatic tumours may be more aggressive
hypothalamic or chiasmatic tumours may be more aggressive often large and lobulated when at the chiasm and can extend into the hypothalamus
often large and lobulated when at the chiasm and can extend into the hypothalamus  haemorrhage and necrosis is uncommon
haemorrhage and necrosis is uncommon T1WI: low SI
T1WI: low SI  T2WI: high SI
T2WI: high SI poor enhancement (there is an intact blood–brain barrier)
poor enhancement (there is an intact blood–brain barrier) T2WI/FLAIR: high SI
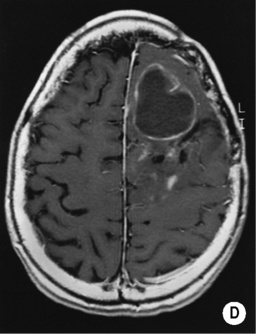
T2WI/FLAIR: high SI  T1WI + Gad: enhancement suggests progression to a higher histological grade
T1WI + Gad: enhancement suggests progression to a higher histological grade although tumours may appear well-defined they are always infiltrative (commonly extending along the white matter tracts)
although tumours may appear well-defined they are always infiltrative (commonly extending along the white matter tracts) T1WI + Gad: an irregularly thick enhancing peripheral ‘ring’ (active mitosis)
T1WI + Gad: an irregularly thick enhancing peripheral ‘ring’ (active mitosis)  a multicentric tumour with seeding via the CSF space (5%)
a multicentric tumour with seeding via the CSF space (5%)  a lower ADC than with a low-grade glioma
a lower ADC than with a low-grade glioma it typically involves the hemispheric white matter
it typically involves the hemispheric white matter  it presents between the 2nd and 4th decades (M = F)
it presents between the 2nd and 4th decades (M = F) T1WI: a homogeneous intermediate-to-low SI infiltrating mass
T1WI: a homogeneous intermediate-to-low SI infiltrating mass  T2WI/FLAIR: a homogeneous high SI infiltrating mass
T2WI/FLAIR: a homogeneous high SI infiltrating mass  T1WI + Gad: no or minimal enhancement
T1WI + Gad: no or minimal enhancement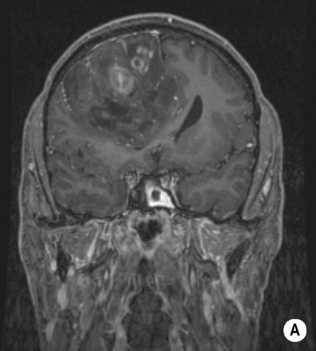
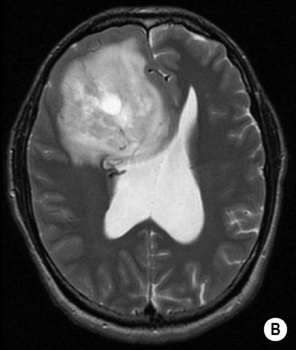
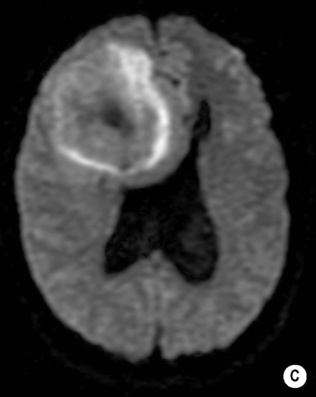
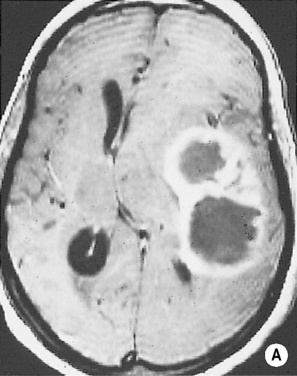
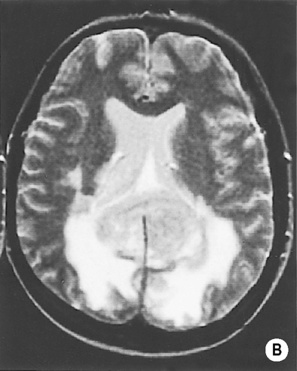
 it may erode the calvarium
it may erode the calvarium cysts or haemorrhage can be seen in 20% but necrosis and oedema is rare
cysts or haemorrhage can be seen in 20% but necrosis and oedema is rare T2WI/FLAIR: heterogeneous high SI
T2WI/FLAIR: heterogeneous high SI 25% are supratentorial (arising from white matter ependymal cells)
25% are supratentorial (arising from white matter ependymal cells)  10% arise within the spinal cord
10% arise within the spinal cord
 they predominantly affect young adults
they predominantly affect young adults
 there are two age peaks at 5 and 35 years of age
there are two age peaks at 5 and 35 years of age calcification is seen in > 50% of cases and cystic elements can also be demonstrated
calcification is seen in > 50% of cases and cystic elements can also be demonstrated  there can be an associated obstructive hydrocephalus
there can be an associated obstructive hydrocephalus it is more frequently calcified or cystic than an infratentorial tumour
it is more frequently calcified or cystic than an infratentorial tumour T1WI: normal-to-low SI
T1WI: normal-to-low SI  T2WI: predominantly high SI
T2WI: predominantly high SI  T1WI + Gad: mild-to-moderate enhancement (which is often heterogeneous)
T1WI + Gad: mild-to-moderate enhancement (which is often heterogeneous) it occurs mainly in elderly males and presents as an intraventricular mass in the lateral or 4th ventricle
it occurs mainly in elderly males and presents as an intraventricular mass in the lateral or 4th ventricle  it is relatively benign and does not disseminate
it is relatively benign and does not disseminate it arises from the roof of the 4th ventricle
it arises from the roof of the 4th ventricle  it demonstrates a rounded shape compared with an ependymoma (that moulds to the ventricular margins)
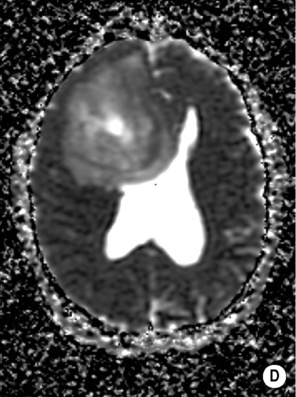
it demonstrates a rounded shape compared with an ependymoma (that moulds to the ventricular margins)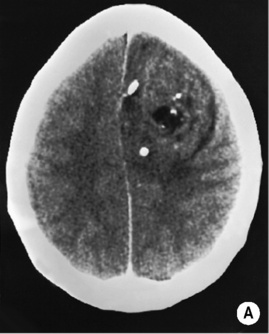
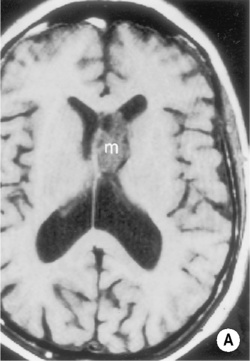
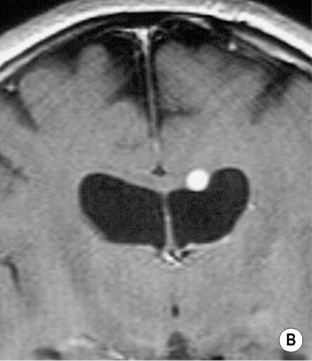
 there is little surrounding oedema
there is little surrounding oedema  cyst wall enhancement indicates tumour extension (as for a pilocytic astrocytoma)
cyst wall enhancement indicates tumour extension (as for a pilocytic astrocytoma)
 there is poor enhancement
there is poor enhancement  it can encase the basilar artery
it can encase the basilar artery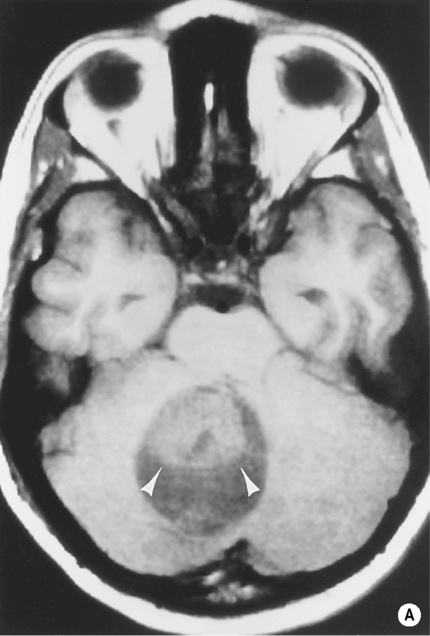
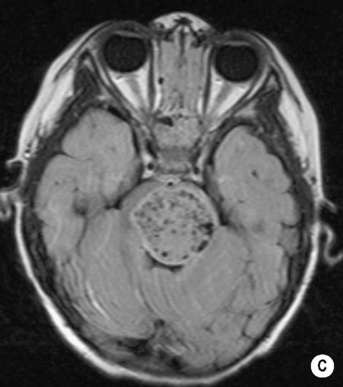
 a 2nd peak is seen in young adults who present with a ‘desmoplastic’ and less aggressive form
a 2nd peak is seen in young adults who present with a ‘desmoplastic’ and less aggressive form