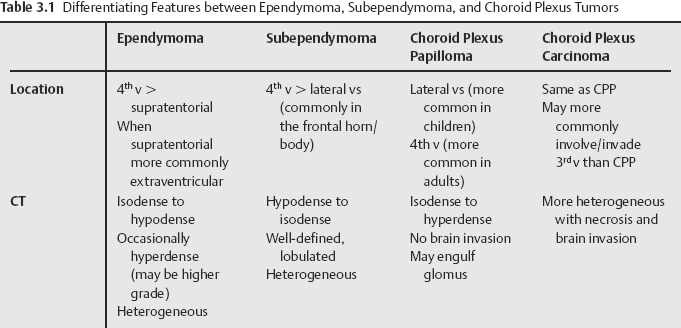
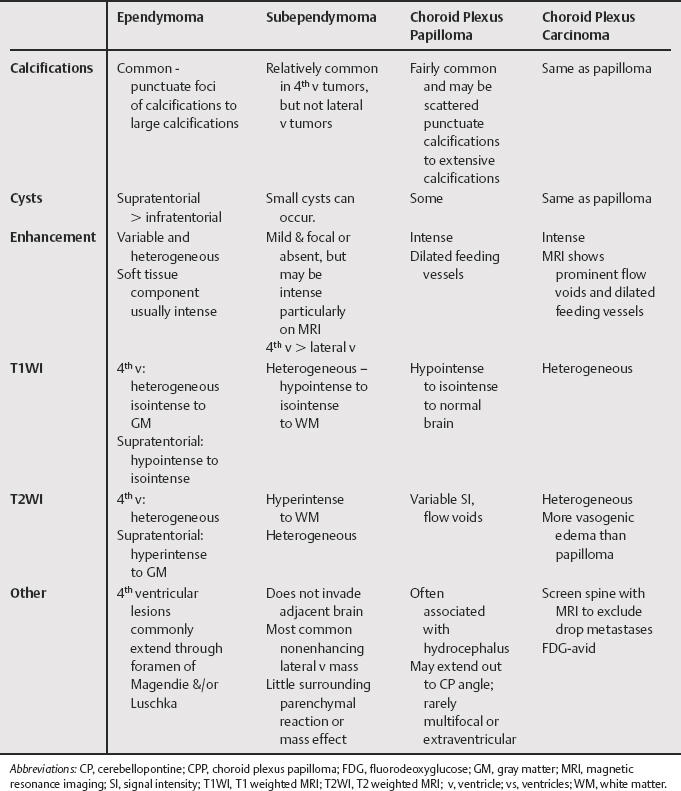
3 Overall, intraventricular neoplasms are more common in children than they are in adults, where they are relatively uncommon. There are differences in the presentation and etiology of these lesions between the adult and pediatric population. For example, ependymomas constitute almost one third of all brain tumors in patients younger than 3 years and are more common in the 4th ventricle in pediatric patients, whereas they are frequently extraventricular and supratentorial within the adult population. However, choroid plexus papillomas present more commonly in children’s lateral ventricles, but in the 4th ventricle in adults. Choroid plexus carcinomas, which represent 26 to 35% of choroid plexus tumors, are more common in children, but are rare brain neoplasms. Both papillomas and carcinomas can seed the subarachnoid space. Subependymomas are rarely seen in children; they occur in middle-aged and older adults, and are more commonly found in the 4th ventricle as opposed to the lateral ventricle. In the lateral ventricles, they usually have no or little enhancement, which when present is heterogeneous. In the 4th ventricle, they can enhance more intensely and calcify more commonly. Differentiating features for these tumors can be found in Table 3.1. Central neurocytomas are rare tumors, generally found in young adults. They usually occur in the bodies of the lateral ventricles either arising from the septum or from the superolateral wall of the ventricle, where they may present with symptoms related to obstruction. They can extend into the 3rd ventricle, but very rarely arise within the 3rd or 4th ventricle. Intraventricular meningiomas account for 0.5 to 3% of intracranial meningiomas and are generally located at the trigone, with most presenting in individuals from 40 to 60 years of age with a gender predilection reported as 1:1 or with a female predominance of 2:1. Less commonly, they can arise in the 3rd ventricle, and only rarely arise from the 4th (77.8% lateral, 15.6% 3rd, 6.6% 4th). Meningioma is the most common atrial mass in the adult population. Differentiating features for these neoplasms can be found in Table 3.2.
Intraventricular Neoplasms
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree