(1)
Department of Nuclear Medicine, INHS, Asvini, Mumbai, India
Abstract
Nuclear medicine is boon of technological advancement which uses safe, painless, and cost-effective techniques to image the body and treat disease. It involves application of radioactive substances in very tiny amount to human body by injection, ingestion, or inhalation. In nuclear medicine procedures, a chemical compound labeled with (mixed in a specific manner) radioactive material, called radiopharmaceuticals or tracer, is administered into the human bodies that can target and localize in specific organs or cellular receptors. Because of its inherent chemical properties, similar to the body, they mimic certain physiological mechanism of the body. Once localized, the radiopharmaceutical is detected by special types of cameras that work with computers to provide precise pictures about the area of interest of the body. For example, some images are depicted in Figs. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5.
Nuclear Medicine is boon of technological advancement which uses safe, painless, and cost-effective techniques to image the body and treat disease. It involves application of radioactive substances in very tiny amount to human body by injection, ingestion, or inhalation. In nuclear medicine procedures, a chemical compound labeled with (mixed in a specific manner) radioactive material, called radiopharmaceuticals or tracer, is administered into the human bodies that can target and localize in specific organs or cellular receptors. Because of its inherent chemical properties, similar to the body, they mimic certain physiological mechanism of the body. Once localized, the radiopharmaceutical is detected by special types of cameras that work with computers to provide precise pictures about the area of interest of the body. For example, some images are depicted in Figs. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5.
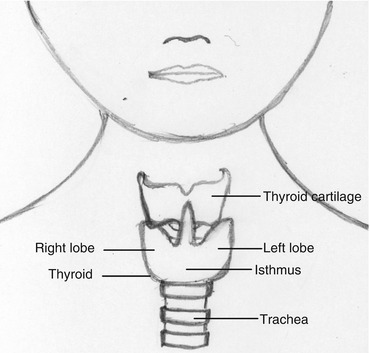
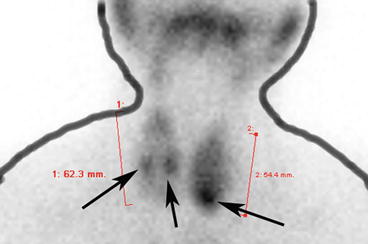
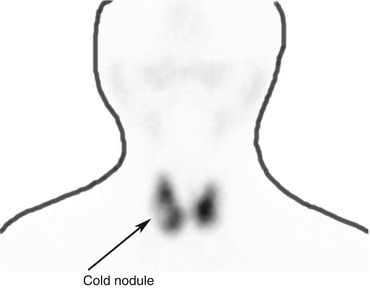

Fig. 1.1
Thyroid gland

Fig. 1.2
Hot nodule thyroid where part of the thyroid hyperfunctions and accumulates more iodine

Fig. 1.3




Cold nodule thyroid where part of the thyroid is not or less functioning and does not accumulate iodine
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




