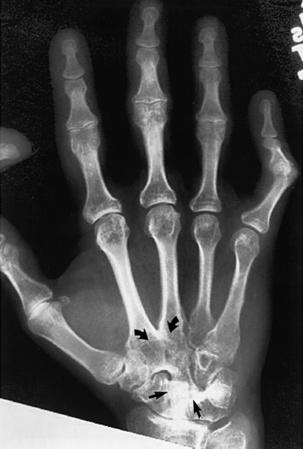
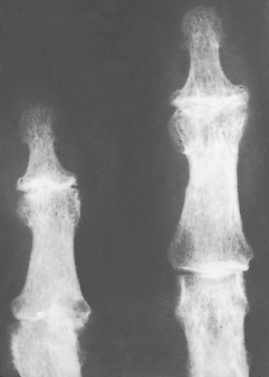
• This is the most common joint disorder – it is a balance between degenerative joint destruction (stressed bone) and repair (non-stressed bone) • Primary OA: there is no underlying cause • Secondary OA: joints are damaged by previous disease Central erosions and marginal osteophytes (a ‘gull wing’ pattern) affecting the DIP joints • Differential: psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis – however these will have no 1st CMC joint involvement and will have marginal (as opposed to central) erosions with no true osteophyte formation • There is recurrent bleeding into a joint due to a deficiency of blood clotting factors • Acute: joint effusion and oedema • Chronic: juxta-articular osteoporosis resulting from haemorrhage and periarticular hyperaemia Conditions associated with neuropathic arthropathy* • This is otherwise known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile chronic arthritis • It is an inflammatory disorder of the connective tissues characterized by joint swelling, pain and tenderness affecting ≥ 1 joints for at least 6 weeks in patients who are < 16 years of age • Acute systemic onset type (Still’s disease): constitutional symptoms • Oligoarthritis: ≤ 4 joints involved during the 1st 6 months, usually progressing to: • Polyarthritis: ≥ 5 joints involved (both presentations are equally common) • Systemic arthritis: arthritis + a systemic illness • A multifocal entity characterized by ‘flowing’ ligamentous spinal ossification involving • There is no apophyseal or sacroiliac joint fusion (cf. ankylosing spondylitis)
Joint disease
INTRODUCTION
CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN JOINT DISEASE
Condition
Site of involvement
Discriminatory findings
Primary osteoarthritis (F>M  > 45 years)
> 45 years)
Hands
Large joints (e.g. hip, knee)
Spine
PIP and DIP joint involvement (Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes)  no osteopenia
no osteopenia
Joint space narrowing  subchondral sclerosis
subchondral sclerosis  subchondral cysts
subchondral cysts  marginal osteophytes
marginal osteophytes
Degenerative disc disease  spondylosis deformans
spondylosis deformans  apophyseal joint involvement
apophyseal joint involvement  spinal stenosis
spinal stenosis  foraminal stenosis
foraminal stenosis
Erosive osteoarthritis (affects middle-aged females)
Hands
PIP and DIP joint involvement  joint ankylosis
joint ankylosis  ‘gull-wing’ deformities (central erosions and marginal osteophytes)
‘gull-wing’ deformities (central erosions and marginal osteophytes)
Rheumatoid arthritis (F>M  Rh factor positive)
Rh factor positive)
Hand and wrist
Large joints
Spine
Symmetrical arthritis  MCP and PIP joint involvement
MCP and PIP joint involvement  periarticular (early) and diffuse (late) osteopenia
periarticular (early) and diffuse (late) osteopenia  marginal erosions
marginal erosions  subluxation (swan neck and boutonnière deformities)
subluxation (swan neck and boutonnière deformities)  periostitis is uncommon
periostitis is uncommon
Joint space narrowing  marginal erosions
marginal erosions  synovial cysts
synovial cysts  protrusio acetabulae
protrusio acetabulae
Atlantoaxial subluxation
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (M = F  affects children)
affects children)
Hands
Large joints (e.g. knee)
Cervical spine
Joint ankylosis  florid periosteal reaction
florid periosteal reaction  osteopenia
osteopenia
Abnormalities of growth and maturation  epiphyseal overgrowth and premature closure of the physis
epiphyseal overgrowth and premature closure of the physis  widened intercondylar notch
widened intercondylar notch
Apophyseal joint fusion  atlantoaxial subluxation
atlantoaxial subluxation
Psoriatic arthritis (M>F  nail changes
nail changes  HLA-B27 +ve)
HLA-B27 +ve)
Upper extremities (e.g. hands and feet)
SI joints
Spine
‘Sausage’ digit  DIP joint involvement
DIP joint involvement  terminal tuft erosion
terminal tuft erosion  pencil-in-cup deformity
pencil-in-cup deformity  joint ankylosis
joint ankylosis  arthritis mutilans
arthritis mutilans  periosteal reaction
periosteal reaction  no osteopenia
no osteopenia
Asymmetric or unilateral sacroiliitis
Coarse syndesmophytes
Reiter’s syndrome (affects young male adults)
Lower extremities (e.g. foot)
Spine
SI joints
Hallux involvement  periosteal reaction
periosteal reaction  calcaneal erosions
calcaneal erosions  osteopenia not prominent
osteopenia not prominent
Coarse syndesmophytes
Asymmetric or unilateral sacroiliitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (M>F  affects young adults
affects young adults  HLA-B27 +ve in 95%)
HLA-B27 +ve in 95%)
SI joints
Spine
Pelvis
Bilateral symmetrical sacroiliitis  ankylosis
ankylosis
Anterior vertebral body squaring  syndesmophytes
syndesmophytes  paravertebral ossification
paravertebral ossification  bamboo spine
bamboo spine
‘Whiskering’ of the iliac crests and ischial tuberosities
Enteropathic arthropathies
SI joints
Symmetrical sacroiliitis
Gout (M>F)
Hands and feet (especially the great toe)
MTP joint of the great toe  juxta-articular erosions
juxta-articular erosions  punched-out lesions with an overhanging margin
punched-out lesions with an overhanging margin  no periarticular osteopenia
no periarticular osteopenia  tophi
tophi
CPPD crystal deposition disease (M = F)
Any peripheral joint  predilection for the knee
predilection for the knee
Degenerative changes  chondrocalcinosis
chondrocalcinosis  paucity of subchondral sclerosis
paucity of subchondral sclerosis
HA crystal deposition disease (M = F)
Predilection for the shoulder (supraspinatus tendon)
Periarticular calcification
Haemochromatosis (M>F)
Hands
2nd and 3rd MCP joint involvement (‘squared’ metacarpal heads)  joint space narrowing
joint space narrowing  ‘hook-like’ osteophytes
‘hook-like’ osteophytes  numerous subchondral cysts
numerous subchondral cysts
Alkaptonuria (ochronosis) (M = F)
Intervertebral discs  SI joints
SI joints  large joints
large joints
Degenerative changes: disc calcification  joint space narrowing
joint space narrowing  periarticular sclerosis
periarticular sclerosis
Systemic lupus erythematosus (F>M  affects young adults)
affects young adults)
Hands
Reversible MCP joint subluxation
Scleroderma (F>M  affects adults)
affects adults)
Hands
IP joint arthritis  acro-osteolysis
acro-osteolysis  soft tissue calcifications
soft tissue calcifications
Mixed connective tissue disease (overlap syndrome)
Hands
PIP joint, MCP joint, mid-carpal involvement  soft tissue swelling, calcifications or atrophy
soft tissue swelling, calcifications or atrophy
Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis (F>M)
Hands and feet
DIP joint and carpal involvement  soft tissue swelling
soft tissue swelling  articular erosions
articular erosions  no osteopenia
no osteopenia
Polymyositis / dermatomyositis
Proximal extremities
Hands
Soft tissue calcification
DIP joint erosions
Sarcoidosis
Distal and middle phalanges of the hands and feet
Punched-out cyst-like lesions  ‘lace-like’ appearance
‘lace-like’ appearance
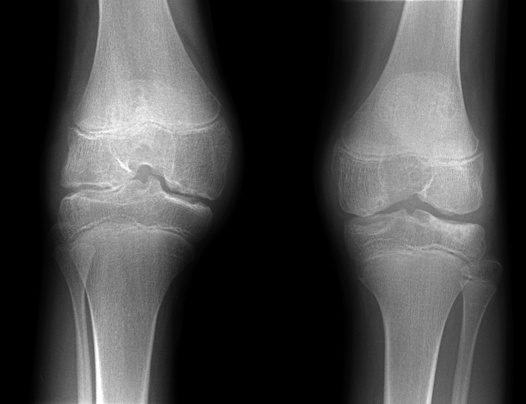
Haemophilic arthropathy (affecting males – but with female carriers)
Predilection for large joints (e.g. knee)
Epiphyseal overgrowth  juxta-articular osteopenia
juxta-articular osteopenia  erosion and cartilage destruction
erosion and cartilage destruction  widened intercondylar and trochlear notches
widened intercondylar and trochlear notches  squared patella
squared patella
Neuropathic arthropathy
Any joint
5 ‘D’s’: normal bone Density  joint Distension
joint Distension  bony Debris
bony Debris  joint Disorganization
joint Disorganization  Dislocation
Dislocation
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
Tubular bones (radius and ulna > tibia and fibula)
Diaphyseal and metaphyseal painful periostitis
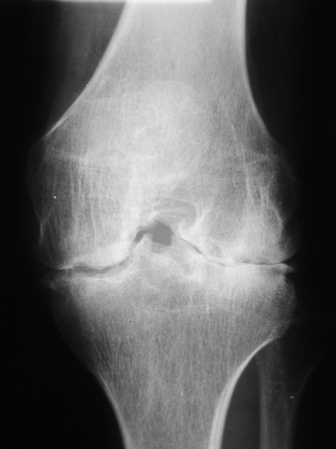
OSTEOARTHRITIS
DEFINITION
 it occurs in the context of normal biomechanical forces
it occurs in the context of normal biomechanical forces
 The joints most at risk: thumb base
The joints most at risk: thumb base  DIP joints
DIP joints  acromioclavicular joints
acromioclavicular joints  knees
knees  hips
hips  1st MTP joints
1st MTP joints  spinal apophyseal joints
spinal apophyseal joints
PEARLS
XR
Radiological finding
Pathological cause
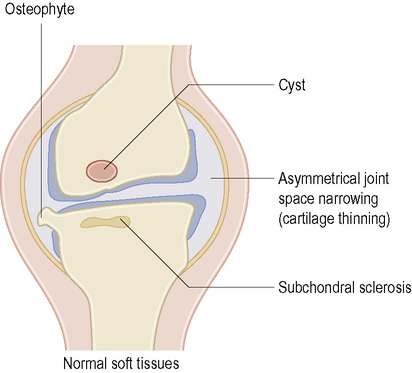
Localized joint space narrowing
Articular cartilage fibrillation, ulceration and erosion lead to changes in collagen and protein polysaccharide structure of cartilage. This results in reduced turgor
Subchondral bony sclerosis
Increased osteoblastic activity resulting in new bone formation and increased cellularity of the subchondral bone
Osteophyte formation (most commonly marginal)
Cartilage and bone proliferation and revascularization of remaining cartilage
Bone cysts and bone collapse
Subchondral micro-fractures and passage of synovial fluid under pressure through the damaged cartilage to excavate a subchondral cyst
Gross deformity with subluxation
Ligamentous laxity resulting from mechanical force applied after the distortion of capsular structures
Loose bodies
Fragments of bone and cartilage become separated and, if not resorbed, become loose in the joint. They may reattach to the membrane, become vascularized and undergo endochondral ossification
Fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage calcification
This is usually due to calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD). The reparative response is usually quite florid
HAEMOPHILIC AND NEUROPATHIC ARTHROPATHIES
HAEMOPHILIC ARTHROPATHY
DEFINITION
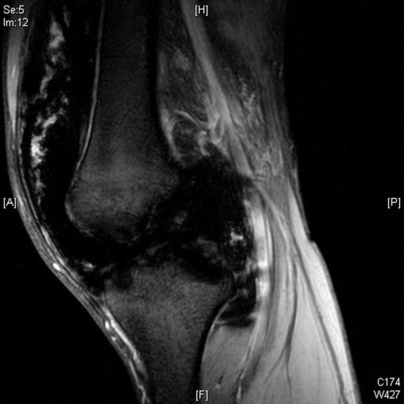
 the repeated intra-articular bleeding leads to villous synovial hypertrophy with the accumulation of haemosiderin within macrophages
the repeated intra-articular bleeding leads to villous synovial hypertrophy with the accumulation of haemosiderin within macrophages
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
Location
XR
 increased radio-opacity of the periarticular soft tissues and synovium (due to haemosiderin deposition)
increased radio-opacity of the periarticular soft tissues and synovium (due to haemosiderin deposition)  articular erosion and cartilage destruction (due to a thickened synovium)
articular erosion and cartilage destruction (due to a thickened synovium)  secondary osteoarthritis (subchondral cysts are common)
secondary osteoarthritis (subchondral cysts are common)
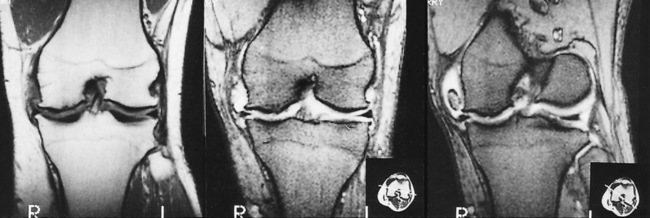
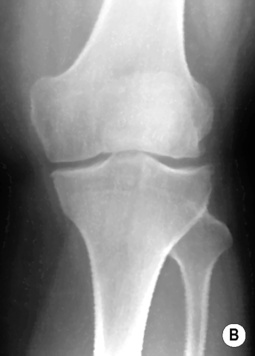
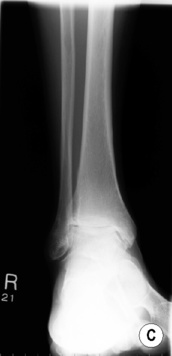
 Knee: a widened intercondylar notch
Knee: a widened intercondylar notch  a squared patella
a squared patella  it demonstrates similar appearances to juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
it demonstrates similar appearances to juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
 Stage I: soft tissue swelling (± joint effusion)
Stage I: soft tissue swelling (± joint effusion)  normal joint surfaces
normal joint surfaces
 Stage II: stage I + periarticular osteoporosis
Stage II: stage I + periarticular osteoporosis  epiphyseal overgrowth
epiphyseal overgrowth
 Stage III: erosions, sclerosis and subchondral cysts
Stage III: erosions, sclerosis and subchondral cysts  the joint space is preserved
the joint space is preserved
 Stage IV: stage III + focal or diffuse joint space narrowing
Stage IV: stage III + focal or diffuse joint space narrowing
 Stage V: a stiff contracted joint with significant degenerative change
Stage V: a stiff contracted joint with significant degenerative change
Condition
Prevalence of arthropathy
Joints most commonly affected
Congenital insensitivity to pain
100%
Ankle, tarsal, knee, hip
Syringomyelia
20–50%
Shoulder, elbow, wrist, cervical spine
Neurosyphilis
5–10%
Knee, hip
Diabetes mellitus
1%
Midfoot, forefoot
Alcohol related
Rare
Foot
JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS AND DISH
JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS (JIA)
DEFINITION
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 hepatosplenomegaly
hepatosplenomegaly  there is little joint involvement
there is little joint involvement
 there is often asymmetrical involvement of the peripheral joints
there is often asymmetrical involvement of the peripheral joints
 there can also be a psoriatic arthritis and an enthesitis-related arthritis
there can also be a psoriatic arthritis and an enthesitis-related arthritis
DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC SKELETAL HYPEROSTOSIS (DISH) (FORESTIER’S DISEASE)
DEFINITION
 4 contiguous vertebrae with preservation of the underlying disc height (cf. degenerative disc disease)
4 contiguous vertebrae with preservation of the underlying disc height (cf. degenerative disc disease)
 there is hyperostosis of certain ligamentous attachments
there is hyperostosis of certain ligamentous attachments
Joint disease


 systemic, metabolic or endocrine disorders (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, ochronosis, haemochromatosis)
systemic, metabolic or endocrine disorders (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, ochronosis, haemochromatosis)  crystal deposition disease
crystal deposition disease  neuropathic disorders
neuropathic disorders  congenital hip dislocation
congenital hip dislocation  bone dysplasias
bone dysplasias reduced movement
reduced movement  joint crepitus (± effusion)
joint crepitus (± effusion)  early morning stiffness
early morning stiffness primary and secondary OA have similar radiological appearances
primary and secondary OA have similar radiological appearances subchondral cysts and sclerosis
subchondral cysts and sclerosis  marginal osteophytes
marginal osteophytes  loose bodies
loose bodies  chondocalcinosis
chondocalcinosis osteoporosis and ankylosis are not features
osteoporosis and ankylosis are not features distal and proximal IP joint prominences are commonly seen (Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes, respectively)
distal and proximal IP joint prominences are commonly seen (Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes, respectively) the medial joint compartment shows the greatest narrowing (as it is subject to greater stressors)
the medial joint compartment shows the greatest narrowing (as it is subject to greater stressors)  it usually affects the lateral facet of patellofemoral joint
it usually affects the lateral facet of patellofemoral joint  there is articular and meniscal cartilage chondrocalcinosis
there is articular and meniscal cartilage chondrocalcinosis there is a tendency for superolateral femoral head subluxation (but there may be lateral restraining osteophytes)
there is a tendency for superolateral femoral head subluxation (but there may be lateral restraining osteophytes)  rarely medial migration can lead to protrusio acetabuli
rarely medial migration can lead to protrusio acetabuli destructive changes outstrip productive changes and can mimic an erosive arthritis (such as psoriatic arthropathy)
destructive changes outstrip productive changes and can mimic an erosive arthritis (such as psoriatic arthropathy)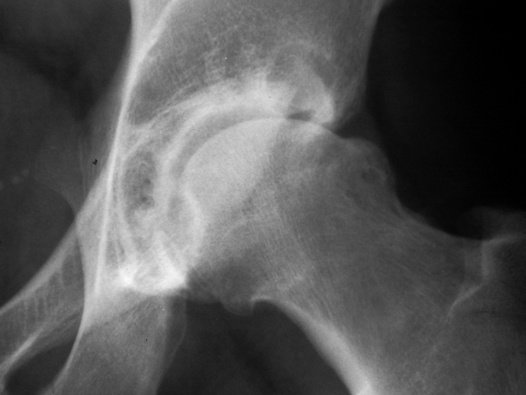
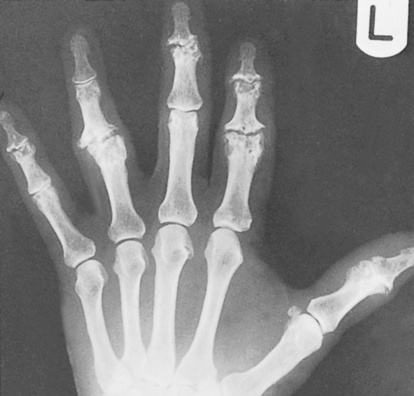

 factor VIII deficiency
factor VIII deficiency
 factor IX deficiency
factor IX deficiency joint deformities
joint deformities small peripheral joints are rarely involved
small peripheral joints are rarely involved there is neither uniform nor symmetrical joint involvement
there is neither uniform nor symmetrical joint involvement
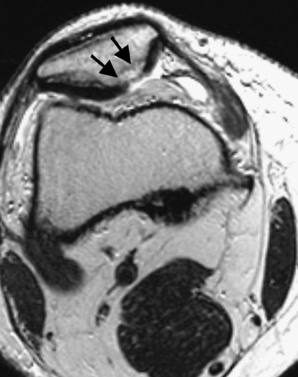
 it can differentiate between acute and chronic soft tissue bleeding
it can differentiate between acute and chronic soft tissue bleeding
 it occurs particularly within the femur and around the pelvis
it occurs particularly within the femur and around the pelvis  it presents as a painless expanding mass, with soft tissue and bone destruction
it presents as a painless expanding mass, with soft tissue and bone destruction T2WI: central high SI (due to blood breakdown products)
T2WI: central high SI (due to blood breakdown products) resorption of the ends of affected bones results in sharp pointed ends
resorption of the ends of affected bones results in sharp pointed ends  there is an absence of osteoporosis, sclerosis, fragmentation or soft tissue debris
there is an absence of osteoporosis, sclerosis, fragmentation or soft tissue debris  it may lead to joint dislocation
it may lead to joint dislocation it begins with a joint effusion
it begins with a joint effusion  the joint spaces are initially widened but then narrowed
the joint spaces are initially widened but then narrowed  there is marked bony sclerosis (and no osteoporosis)
there is marked bony sclerosis (and no osteoporosis)  fragmentation of the articular surfaces results in bony debris, which may later fuse into a large dense and well-organized corticated bony mass (± fusion with the underlying bone or dissection into the muscle planes)
fragmentation of the articular surfaces results in bony debris, which may later fuse into a large dense and well-organized corticated bony mass (± fusion with the underlying bone or dissection into the muscle planes)  there is periosteal new bone formation
there is periosteal new bone formation  subluxation and dislocation preceeds total joint disorganization
subluxation and dislocation preceeds total joint disorganization  pathological fractures can occur
pathological fractures can occur joint Distension
joint Distension  bony Debris
bony Debris  joint Disorganization
joint Disorganization  Dislocation
Dislocation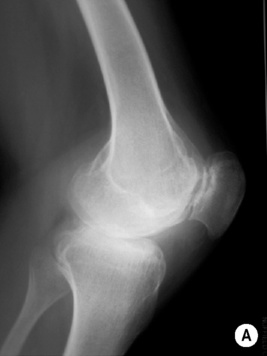
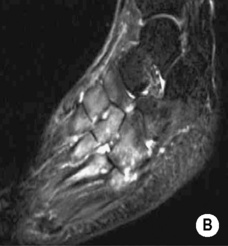
 also involved: feet, shoulders, elbows and hips
also involved: feet, shoulders, elbows and hips synovitis
synovitis  synovial hyperplasia and pannus formation
synovial hyperplasia and pannus formation  a widened joint space (secondary to an effusion)
a widened joint space (secondary to an effusion)  periarticular osteopenia
periarticular osteopenia cartilage loss
cartilage loss  there is often extensive ankylosis (affecting the CMC and mid-carpal joints)
there is often extensive ankylosis (affecting the CMC and mid-carpal joints)  joint space narrowing
joint space narrowing a widened intercondylar notch of the knee
a widened intercondylar notch of the knee  overtubulated diaphyses
overtubulated diaphyses  enlarged and osteoporotic epiphyses with compression fractures
enlarged and osteoporotic epiphyses with compression fractures  florid periosteal new bone formation within the phalanges, metacarpals and metatarsals (cf. RA)
florid periosteal new bone formation within the phalanges, metacarpals and metatarsals (cf. RA)  enlarged, irregular and squared carpal bones (due to erosion and repair)
enlarged, irregular and squared carpal bones (due to erosion and repair) atlantoaxial subluxation is common
atlantoaxial subluxation is common  compression fractures
compression fractures  scoliosis (with advanced disease)
scoliosis (with advanced disease) contractures
contractures  AVN (due to JIA or the resultant steroid therapy)
AVN (due to JIA or the resultant steroid therapy) back pain and stiffness
back pain and stiffness  tendinosis (commonly affecting the elbow and heel)
tendinosis (commonly affecting the elbow and heel) ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament is seen at the affected level (up to 2cm)
ossification of the anterior longitudinal ligament is seen at the affected level (up to 2cm) superior ⅓ of the sacroiliac joints
superior ⅓ of the sacroiliac joints  symphysis pubis
symphysis pubis  calcaneus
calcaneus  tarsal bones
tarsal bones  patella
patella  olecranon
olecranon  humerus
humerus  hands
hands