Chapter 124
Lingual Thyroid
Epidemiology
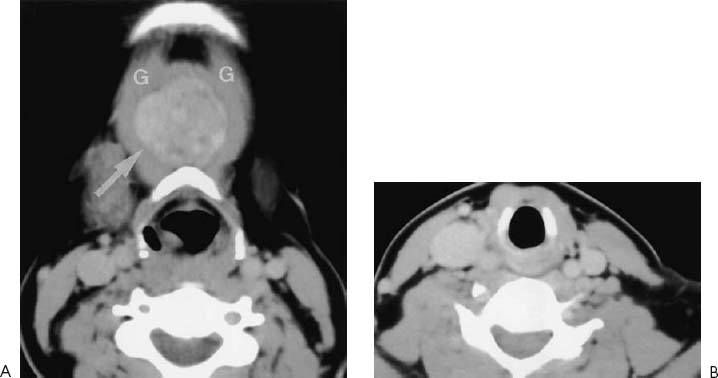
The thyroid anlage is located in the foramen cecum. This region corresponds to the junction of the anterior two thirds and the posterior one third of the tongue. During embryogenesis, the primordial thyroid gland descends anterior to the hyoid bone, larynx, and trachea. The hollow thyroglossal duct connects the foramen cecum to the descending thyroid during embryogenesis. Arrest in the migration of the thyroid gland may be partial or complete. A complete arrest results in a lingual thyroid gland. This phenomenon is more commonly seen in women and occurs in 1 in 3000 patients with thyroid disease. Incomplete arrest may be seen and small amounts of thyroid tissues can also be found along the thyroglossal duct or within thyroglossal cysts.
Clinical Findings
The lingual thyroid is easily detected as a midline mass at the junction between the anterior two thirds and posterior one third of the tongue. Although this is a congenital anomaly patients often present at puberty when the thyroid gland rapidly increases in size. Ectopic thyroid tissues usually present as nodular lesions close to the midline in the upper neck.
Pathology
The cause of thyroid maldescent is unknown. These ectopic thyroid tissues have normal histological appearances and they may represent the only normal-functioning thyroid tissues in the body. They may undergo malignant changes similar to the thyroid gland in the normal site. Malignant changes in the lingual thyroid have been reported to be more frequent than carcinomas in thyroglossal cysts.