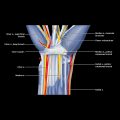
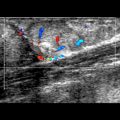
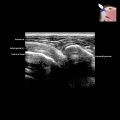
Lymph Node Abnormality
KEY FACTS
Imaging
 Accurate at differentiating between benign and malignant nodes
Accurate at differentiating between benign and malignant nodes
 More accurate than CT and MR provided that nodes are accessible to US assessment
More accurate than CT and MR provided that nodes are accessible to US assessment
 Can guide fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology or biopsy
Can guide fine-needle aspiration (FNA) cytology or biopsy
 Appearances vary depending on whether node is normal, reactive, metastatic, lymphomatous, or infected (tuberculosis or nontuberculosis infection)
Appearances vary depending on whether node is normal, reactive, metastatic, lymphomatous, or infected (tuberculosis or nontuberculosis infection)
 Important discriminatory criteria: Size, nodal configuration, border, internal architecture, and pattern of vascularity
Important discriminatory criteria: Size, nodal configuration, border, internal architecture, and pattern of vascularity
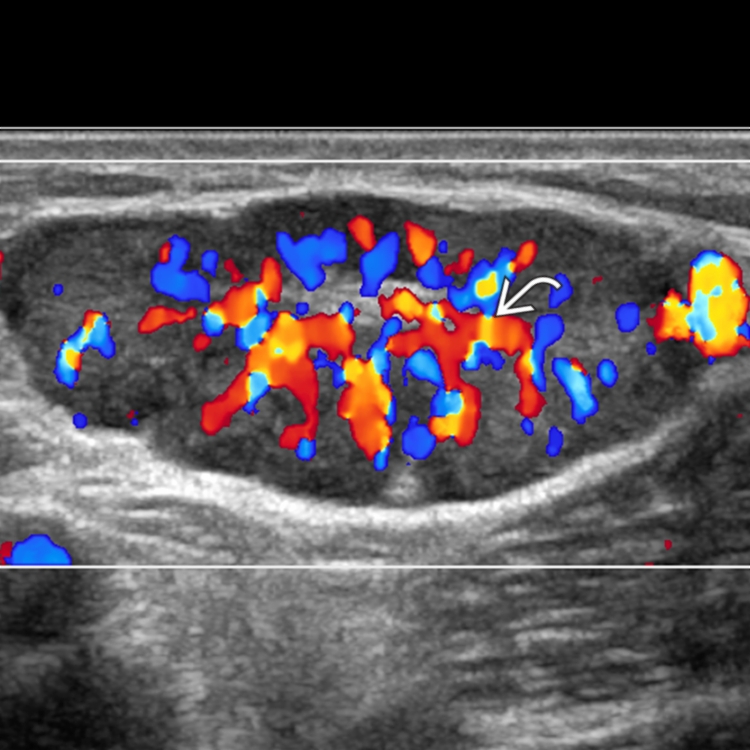
 Color Doppler to assess pattern of vascularity
Color Doppler to assess pattern of vascularity
 Spectral analysis is not routinely helpful
Spectral analysis is not routinely helpful
 US-guided FNA or biopsy for microbiologic, cytologic, or histologic analysis
US-guided FNA or biopsy for microbiologic, cytologic, or histologic analysis
IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
Ultrasonographic Findings


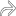 and a distinctive central echogenic fatty hilum
and a distinctive central echogenic fatty hilum 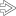 .
.
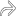 extending from the hilum into the hypoechoic cortical parenchyma.
extending from the hilum into the hypoechoic cortical parenchyma.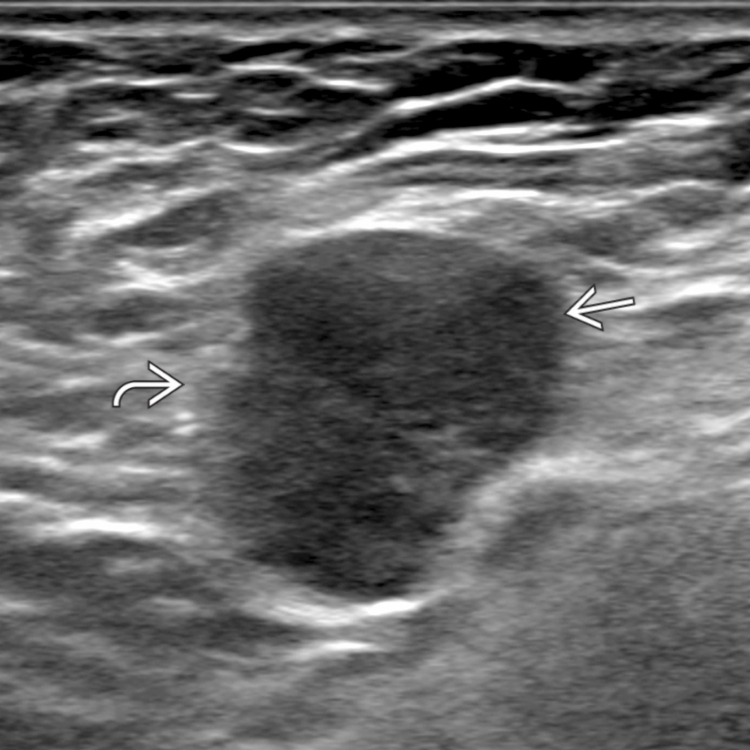
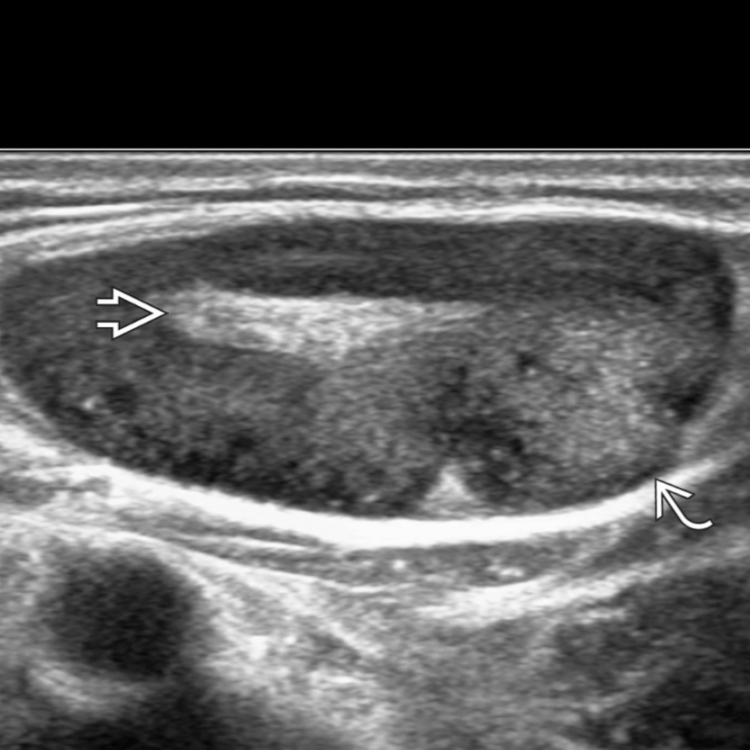
 in a patient with primary lung cancer. The lymph node is roundish in shape, irregular in contour
in a patient with primary lung cancer. The lymph node is roundish in shape, irregular in contour 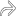 , and diffusely hypoechoic due to metastatic infiltration with early extracapsular spread.
, and diffusely hypoechoic due to metastatic infiltration with early extracapsular spread.
 is highly suggestive of metastasis, which was confirmed on fine-needle aspiration cytology.
is highly suggestive of metastasis, which was confirmed on fine-needle aspiration cytology.