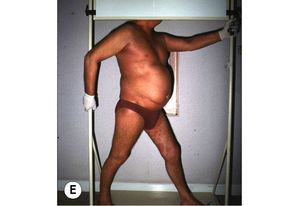
Figure 20.25).
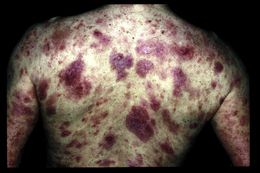
The development of lymphadenopathy or visceral organ involvement worsens prognosis markedly and the development of large abnormal circulating T cells, the so-called Sézary cells, in the peripheral blood in association with lymphadenopathy and erythroderma is diagnostic of Sézary syndrome. Patients with this condition are also at greater risk of developing other squamous cell carcinomas of the skin and internal malignancies, especially lung cancer.
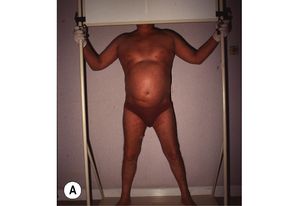
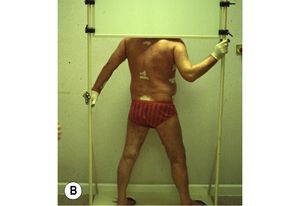
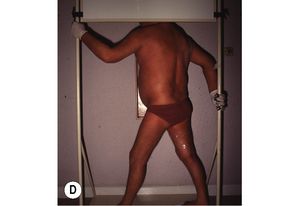
There is a wide range of treatments for cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Topical chemotherapy with nitrogen mustard, carmustine or PUVA, all have high response rates for early disease. For thicker plaques, total skin electron therapy is effective (
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree