• A systemic skeletal disease characterized by a low bone mass and micro-architectural deterioration of the bone tissue with a consequent increase in bone fragility and an associated susceptibility to fracture • It is the most common metabolic disorder affecting 50% of woman and 20% of men (> 50 years old) • WHO definition: this is based on the bone mineral density (BMD) measured at the hip and spine by dual-energy XR absorptiometry (DXA) • It can be asymptomatic • Bone loss typically begins during the 4th decade (females) or 5th and 6th decades (males) • Spine: a vertical ‘striated’ appearance to the vertebral bodies due to preferential loss of the horizontal trabeculae (this is seen within most vertebrae, in comparison with a haemangioma that affects a single vertebra) • Sacrum: insufficiency fracture lines are parallel to the SI joint on CT These are low trauma fractures due to increased bone fragility • Common sites: pubic rami • The axial skeleton is affected more frequently than the appendicular skeleton (and most commonly within the thoracic and thoracolumbar regions) • Vitamin D deficiency resulting in defective mineralization of osteoid in the mature skeleton • Causes: nutritional deficiency • Vitamin D deficiency resulting in defective mineralization of osteoid in the immature skeleton • Causes: as for osteomalacia but also including inborn errors of vitamin D metabolism Initially loss of the normal ‘zone of provisional calcification’ adjacent to the metaphysis • Later features: a widened growth plate • There may be features of secondary hyperparathyroidism (in response to the hypocalcaemia) • Harrison’s sulcus: rib in-drawing near the diaphragm • Craniotabes: softening of the cranial vault • Rachitic rosary: expanded long bone metaphyses can cause anterior rib enlargement • Bone deformities: skull bossing • Post treatment: XR features of healing lag behind biochemical and clinical improvements (2 weeks) • 95% have no radiological abnormalities (as a result of effective early therapy) • Subperiosteal erosions of cortical bone: pathognomonic • Other sites (indicating more severe and long-standing disease): distal phalanges (acro-osteolysis)
Metabolic and endocrine skeletal disease
OSTEOPOROSIS
OSTEOPOROSIS
DEFINITION
 it results from:
it results from:
 Reduced bone accumulation during development
Reduced bone accumulation during development
 Bone resorption outstrips new bone formation during later life (the ratio of osteoid matrix to hydroxyapatite mineral is normal)
Bone resorption outstrips new bone formation during later life (the ratio of osteoid matrix to hydroxyapatite mineral is normal)
 it is not appropriate for use in children (where you use > 2SD below the mean BMD matched for age, gender and ethnicity)
it is not appropriate for use in children (where you use > 2SD below the mean BMD matched for age, gender and ethnicity)
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 there can be insufficiency fractures presenting with pain (e.g. vertebral crush fractures)
there can be insufficiency fractures presenting with pain (e.g. vertebral crush fractures)  the pain resolves spontaneously after 6–8 weeks unlike a more sinister pathology
the pain resolves spontaneously after 6–8 weeks unlike a more sinister pathology  vertebral fractures may result in an increasing thoracic kyphosis
vertebral fractures may result in an increasing thoracic kyphosis
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
XR
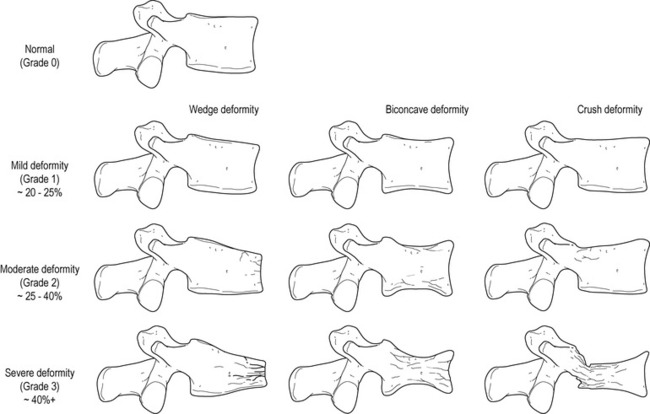
 Wedge, biconcave (‘cod-fish’) or crush deformities: the vertebral anterior and central mid-portions withstand any compressive forces relatively poorly
Wedge, biconcave (‘cod-fish’) or crush deformities: the vertebral anterior and central mid-portions withstand any compressive forces relatively poorly
PEARLS
Insufficiency fractures
 sacrum
sacrum  vertebrae
vertebrae  calcaneus
calcaneus  distal forearm
distal forearm  proximal femur
proximal femur  vertebral bodies
vertebral bodies
 fractures are uncommon above the level of T7 (consider metastases here)
fractures are uncommon above the level of T7 (consider metastases here)
Primary
Juvenile
Idiopathic of young adults
Postmenopausal
Senile
Secondary
Endocrine
Glucocorticoid excess
Oestrogen/testosterone deficiency
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Growth hormone deficiency (childhood onset)
Nutritional
Intestinal malabsorption
Chronic alcoholism
Chronic liver disease
Partial gastrectomy
Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy)
Hereditary
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Homocystinuria
Marfan’s syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Haematological
Thalassaemia
Sickle-cell disease
Gaucher’s disease
Tertiary
Other
Rheumatoid arthritis
Haemochromatosis
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
OSTEOMALACIA
DEFINITION
 malabsorption states and biliary disease (vitamin D is fat soluble and absorbed in the small bowel)
malabsorption states and biliary disease (vitamin D is fat soluble and absorbed in the small bowel)  chronic liver disease (affecting the initial prohormone hydroxylation step)
chronic liver disease (affecting the initial prohormone hydroxylation step)  chronic renal disease (the active metabolite is not produced)
chronic renal disease (the active metabolite is not produced)  drug therapy (e.g. long-term anticonvulsants)
drug therapy (e.g. long-term anticonvulsants)
RICKETS
DEFINITION
 abnormalities predominate at the growing ends of bones where endochondral ossification is occurring
abnormalities predominate at the growing ends of bones where endochondral ossification is occurring
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
XR
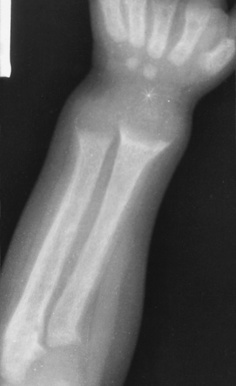
 indistinct metaphyseal margins (‘frayed’ metaphyses)
indistinct metaphyseal margins (‘frayed’ metaphyses)  metaphyseal splaying and cupping (following weight bearing on uncalcified bone)
metaphyseal splaying and cupping (following weight bearing on uncalcified bone)  indistinct and relatively osteopenic epiphyses (± Looser’s zones)
indistinct and relatively osteopenic epiphyses (± Looser’s zones)
 delayed fontanelle closure
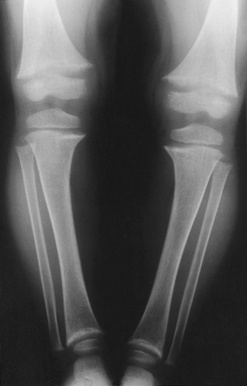
delayed fontanelle closure  bowing of the long bones (particularly the lower limbs)
bowing of the long bones (particularly the lower limbs)  thoracic kyphosis with a ‘pigeon chest’
thoracic kyphosis with a ‘pigeon chest’  genu valgus and varum
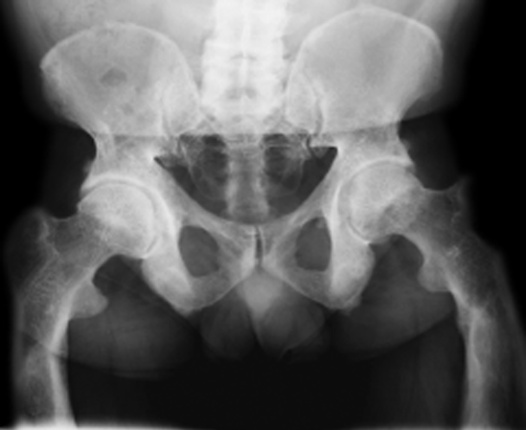
genu valgus and varum  coxa vara and valga
coxa vara and valga  protrusio acetabuli
protrusio acetabuli  a triradiate pelvis
a triradiate pelvis
Serum
Urine
Calcium
Phosphorus
Alkaline phosphatase
Calcium
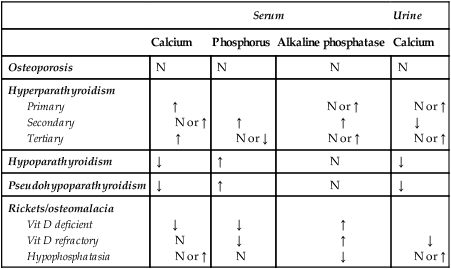
Osteoporosis
N
N
N
N
Hyperparathyroidism
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
↑
N or ↑
↑
↑
N or ↓
N or ↑
↑
N or ↑
N or ↑
↓
N or ↑
Hypoparathyroidism
↓
↑
N
↓
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
↓
↑
N
↓
Rickets/osteomalacia
Vit D deficient
Vit D refractory
Hypophosphatasia
↓
N
N or ↑
↓
↓
N
↑
↑
↓
↓
N or ↑
ENDOCRINE BONE DISORDERS
HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
DEFINITION
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
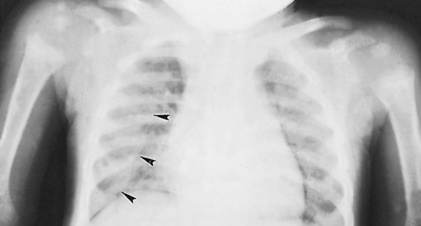
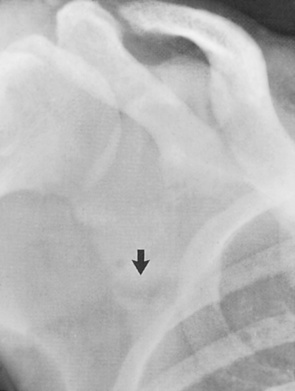
 initially affects the radial aspects of the middle phalanges of the index and middle fingers – if it is not seen here then it is unlikely to be identified elsewhere
initially affects the radial aspects of the middle phalanges of the index and middle fingers – if it is not seen here then it is unlikely to be identified elsewhere
 proximal medial tibial cortex
proximal medial tibial cortex  outer ends of the clavicles
outer ends of the clavicles  symphysis pubis
symphysis pubis  ribs
ribs  vertebral bodies (Schmorl’s nodes)
vertebral bodies (Schmorl’s nodes)  sacroiliac joints
sacroiliac joints  proximal humeral shaft
proximal humeral shaft![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Metabolic and endocrine skeletal disease




 thin or absent trabeculae (with thickened remaining trabeculae due to increased stresses)
thin or absent trabeculae (with thickened remaining trabeculae due to increased stresses)  thinned, irregular or a scalloped cortex (due to endosteal resorption)
thinned, irregular or a scalloped cortex (due to endosteal resorption)  intracortical tunnelling and porosity (representing enlarged Haversian systems and Volkmann’s canals)
intracortical tunnelling and porosity (representing enlarged Haversian systems and Volkmann’s canals)
 it occurs 15–20 years after the menopause
it occurs 15–20 years after the menopause  there is a disproportionate loss of trabecular bone
there is a disproportionate loss of trabecular bone it is due to age-related impaired bone formation associated with secondary hyperparathyroidism (there is a reduced vitamin D production in the elderly)
it is due to age-related impaired bone formation associated with secondary hyperparathyroidism (there is a reduced vitamin D production in the elderly)  there is a proportionate loss of trabecular and cortical bone
there is a proportionate loss of trabecular and cortical bone it is precipitated by a variety of causes (e.g. following a fracture or related to tumour)
it is precipitated by a variety of causes (e.g. following a fracture or related to tumour) there is a sudden onset of pain with no associated trauma
there is a sudden onset of pain with no associated trauma it affects the vertebral bodies and the long bones (particularly the distal tibial metaphysis)
it affects the vertebral bodies and the long bones (particularly the distal tibial metaphysis)  it may be life threatening if thoracic involvement leads to a kyphoscoliosis (± respiratory failure)
it may be life threatening if thoracic involvement leads to a kyphoscoliosis (± respiratory failure) it is possibly due to inadequate bone mass formation during development
it is possibly due to inadequate bone mass formation during development a minimum of 4 weeks has to have elapsed after the initial injury
a minimum of 4 weeks has to have elapsed after the initial injury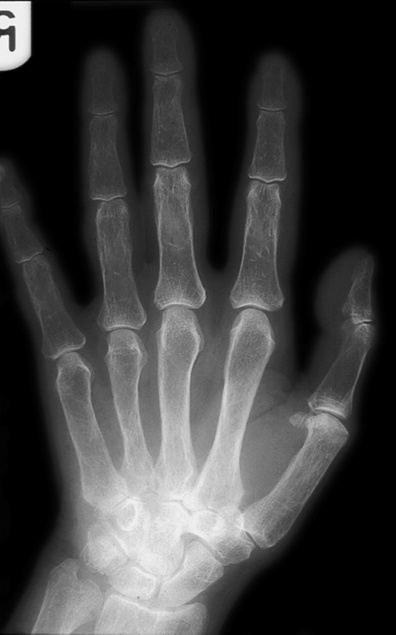
 typically bilateral and symmetrical
typically bilateral and symmetrical pubic rami
pubic rami  lateral border of the scapula and ribs
lateral border of the scapula and ribs fractures occur medially on the concave side of a bone (incremental fractures in Paget’s disease tend to occur on the convexity of a bone)
fractures occur medially on the concave side of a bone (incremental fractures in Paget’s disease tend to occur on the convexity of a bone) commonly seen around the knee and wrist, the anterior ends of the middle ribs, the proximal femur and the distal tibia
commonly seen around the knee and wrist, the anterior ends of the middle ribs, the proximal femur and the distal tibia
 normal or elevated vitamin D levels
normal or elevated vitamin D levels  radiographically similar to rickets but refractory to vitamin D therapy
radiographically similar to rickets but refractory to vitamin D therapy  it may be seen with X-linked hypophosphataemia or Fanconi’s syndrome
it may be seen with X-linked hypophosphataemia or Fanconi’s syndrome there is a normal serum calcium
there is a normal serum calcium this can mimic rickets but is differentiated by a normal serum biochemistry
this can mimic rickets but is differentiated by a normal serum biochemistry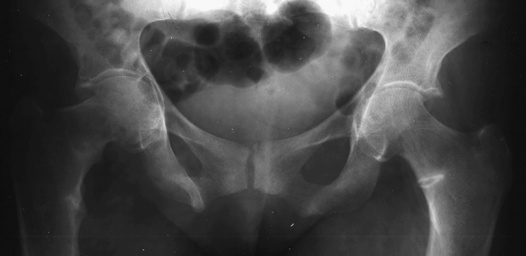
 hyperplasia (15–20%)
hyperplasia (15–20%)  carcinoma (0.5%)
carcinoma (0.5%)
 intestinal malabsorption of calcium
intestinal malabsorption of calcium  chronic renal failure (causing a lack of the active vitamin D metabolite)
chronic renal failure (causing a lack of the active vitamin D metabolite) hypertension
hypertension  pseudogout (chondrocalcinosis)
pseudogout (chondrocalcinosis)  osteoporosis
osteoporosis  peptic ulcers
peptic ulcers  acute pancreatitis
acute pancreatitis  depression
depression  proximal muscle weakness
proximal muscle weakness  lethargy
lethargy