Abstract
Both retrognathia and micrognathia are facial deformations related to the development or position of the fetal mandible. The former is characterized by an abnormal position in relation to the maxilla and the latter refers to a mandibular hypoplasia and is frequently associated to different genetic syndromes. Due to this association, it is advisable to offer a study of the fetal karyotype and an echocardiogram when fetal micrognathia is detected.
Both abnormalities can be detected by ultrasound. The evaluation of the inferior facial angle (IFA), measured in a sagittal view, is useful to identify micrognathia and make the differential diagnosis with retrognathia. The jaw index, the mandibular/maxillar width, and the mandibular ratio measured in the axial view are particularly useful to assess the severity of the micrognathia. Fetal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be helpful to assess the severity of fetal micrognathia evaluating a potential obstruction of the airway.
In those cases in which there is a suspicion of an obstruction in the upper airway, polyhydramnios can be associated and an ex utero intrapartum treatment (EXIT) delivery is indicated.
Keywords
micrognathia, retrognathia, fetal mandible
Introduction
The fetal mandible is a common site for defects caused by numerous genetic conditions and adverse environmental factors. When an anomaly in the fetal mandible is detected on ultrasound (US), the clinician should look for other anomalies in the fetal anatomy because such associations are frequent.
Disease
Definition
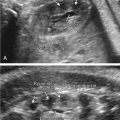
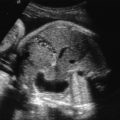
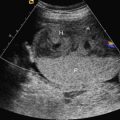
Retrognathia refers to a facial malformation characterized by abnormal development of the mandible with an abnormal position in relation to the maxilla ( Fig. 68.1 ). Micrognathia refers to a facial malformation characterized by mandibular hypoplasia causing a small receding chin ( Fig. 68.2 ).


Prevalence and Epidemiology
Fetal micrognathia has an incidence of 1 : 1000 births. It is always accompanied by retrognathia, although fetal retrognathia can be present without micrognathia.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
The etiology of mandibular hypoplasia is unclear. It may be the result of a positional malformation, intrinsic growth abnormalities, or a connective tissue disorder. Attempts have been made to explain why fetal micrognathia is associated with different syndromes. The harmonious development of different anatomic structures in the mandible and the overall growth of the mandible are regulated by several factors, such as the prenatal activity of the masticatory muscles, the growth of the tongue, the inferior alveolar nerve and its branches, and the development and migration of the teeth. Because normal development of the fetal mandible is a multifactorial process, the maldevelopment of the masticatory muscles or nerves may lead to a hypoplastic mandible. Also, the failure of mandibular formation displaces the tongue upward, which prevents the lateral palatine shelves from medial migration and midline fusion, and explains the high association of micrognathia with cleft palate.
The normal development of the mandible can be disrupted by genetic or environmental factors (chromosomal and nonchromosomal syndromes) or environmental ones ( Table 68.1 ). Some neuromuscular conditions in which a fixed contracture of the temporomandibular joint prevents the opening of the mouth are associated with micrognathia secondary to impaired development of the mandible.
| Syndrome | Predominant Features | Inheritance | Prenatal Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acrofacial dysostosis | Preaxial limb deficiencies, CHD, CNS anomalies | AD | Yes |
| Treacher-Collins | Hypoplasia of facial bones, ear anomalies, cleft palate | AD | Yes |
| Rodriguez type | Preaxial limb deficiencies, CHD | AR | Yes |
| Nager type | Microcephaly, preauricular tags, CHD, preaxial limb defects | Sporadic | Yes |
| Miller (Genee-Widemann) type or POADS (postaxial) | Syndactyly, thumb hypoplasia, absence of fifth digit | AR | — |
| Branchiooculofacial syndrome | Microcephaly, ear anomalies, hypertelorism, microphthalmia, renal anomalies, polydactyly, vermian agenesis | AD | Yes |
| Cerebrocostomandibular syndrome | Microthorax, CHD, small thorax, abnormal ribs, renal ectopia, polyhydramnios | AD-AR | Yes |
| Mandibuloacral dysplasia | Joint contractures, wide cranial sutures | AD | — |
| Oral-facial-digital I syndrome | Facial asymmetry, bifid tongue, polycystic kidney, syndactyly, CNS anomalies | X-linked dominant | Yes |
| Oral-facial-digital II syndrome or Mohr syndrome | Hypertelorism, polydactyly, porencephaly | AR | Yes |
| Oral-mandibular-limb hypogenesis spectrum | Acral hypoplasia, syndactyly | Sporadic | — |
| Otopalatodigital syndrome type II | Hypertelorism, omphalocele | X-linked dominant | — |
| Robin sequence | Glossoptosis, cleft palate | Yes | |
| SKELETAL AND NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES FREQUENTLY ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA | |||
| Achondrogenesis types IA and IB | Severe micromelia, short ribs | AR | Yes |
| Amyoplasia congenita disruptive sequence | Diffuse joint contractures, gastroschisis, polyhydramnios | Sporadic | Yes |
| Atelosteogenesis type I | Frontal bossing, midface hypoplasia, small thorax, 11 ribs, rhizomelia, talipes, encephalocele, polyhydramnios | Sporadic | Yes |
| Camptomelic dysplasia | Large anterior fontanelle, hypertelorism, CHD, small thorax, sex reversal in males, hydronephrosis, bowing of tibiae and less so of femora | AD | Yes |
| Cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome | Microcephaly, microphthalmia, CHD anomalies, contractures | AR | Yes |
| Chondrodysplasia punctata, X-linked dominant type | Microcephaly, rhizomelia | X-linked dominant | Yes |
| Diastrophic dysplasia | Hitchhiker thumbs, scoliosis, short limbs | AR | Yes |
| Langer mesomelic dysplasia | Mesomelia | AR | Yes |
| Multiple pterygium syndrome | Pterygia of neck, axillae, antecubital region, popliteal region | AR | Yes |
| Neu-Laxova syndrome | Microcephaly, exophthalmos, CNS anomalies, joint contractures, syndactyly, subcutaneous edema | AR | Yes |
| Pena-Shokeir phenotype (fetal akinesia deformation sequence) | Diffuse joint contractures, cystic hygroma, microstomia | AR | Yes |
| CHROMOSOMAL SYNDROMES FREQUENTLY ASSOCIATED WITH MICROGNATHIA | |||
| Cat-eye syndrome | Preauricular tags, TAPVR, renal agenesis | AD inv dup (22)q11 | Yes |
| Deletion 3p syndrome | Microcephaly, malformed ears, polydactyly in hands | Del 3p | — |
| Deletion 4p syndrome (Wolf-Hirschhorn) | Hypertelorism, preauricular tags, CHD, polydactyly, talipes, CNS anomalies | Isolated 4p16.3 | Yes |
| Deletion 5p syndrome (cri du chat) | Microcephaly, hypertelorism, CHD | 5p15.2 | Yes |
| Deletion 9p syndrome | Trigonocephaly, abnormal ears, hypertelorism, CHD | AD, isolated | — |
| Deletion 11q syndrome | Trigonocephaly, microcephaly, joint contractures | — | |
| Deletion 13q syndrome | Microcephaly, CHD, small or absent thumbs | Isolated | — |
| Deletion 22q 11.2 syndrome | Conotruncal CHD, thymus aplasia | AD | Yes |
| Monosomy X (Turner) syndrome | Left-sided CHD, cystic hygroma | Sporadic | Yes |
| Pallister-Killian syndrome | Thin upper lip, CDH, CHD, CNS anomalies, rhizomelia | Sporadic | Yes |
| Triploidy syndrome | IUGR, hypotonia, hypertelorism, syndactyly, CHD, CNS anomalies | Sporadic, 69,XYY | Yes |
| Trisomy 8 mosaic syndrome | Hypertelorism, joint contractures | Sporadic | Yes |
| Trisomy 9 mosaic syndrome | Joint contractures, CHD | Sporadic | Yes |
| Trisomy 13 syndrome | IUGR, microcephaly, microphthalmia, cleft palate, CNS anomalies, CHD, renal anomalies, polydactyly | Sporadic | Yes |
| Trisomy 18 syndrome | Clenched hands, CHD, omphalocele, renal anomalies, CHD anomalies | Sporadic | Yes |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree