B SCAN (OPHTHALMIC SONOGRAPHY)
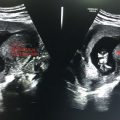
Usually done by high-frequency probes up to 10 MHz. Recently, high-resolution B-scan probes of 20–50 MHz have been manufactured for detailed anatomic resolution of the anterior segment (Figure 43.1).
Done for imaging various ocular and orbital pathologies.
Main method is mainly contact method in which the probe is placed directly on the closed eyelid after applying gel. Patient’s eye is deviated to right, left, and all directions of gaze to observe the motion of intraocular structures.
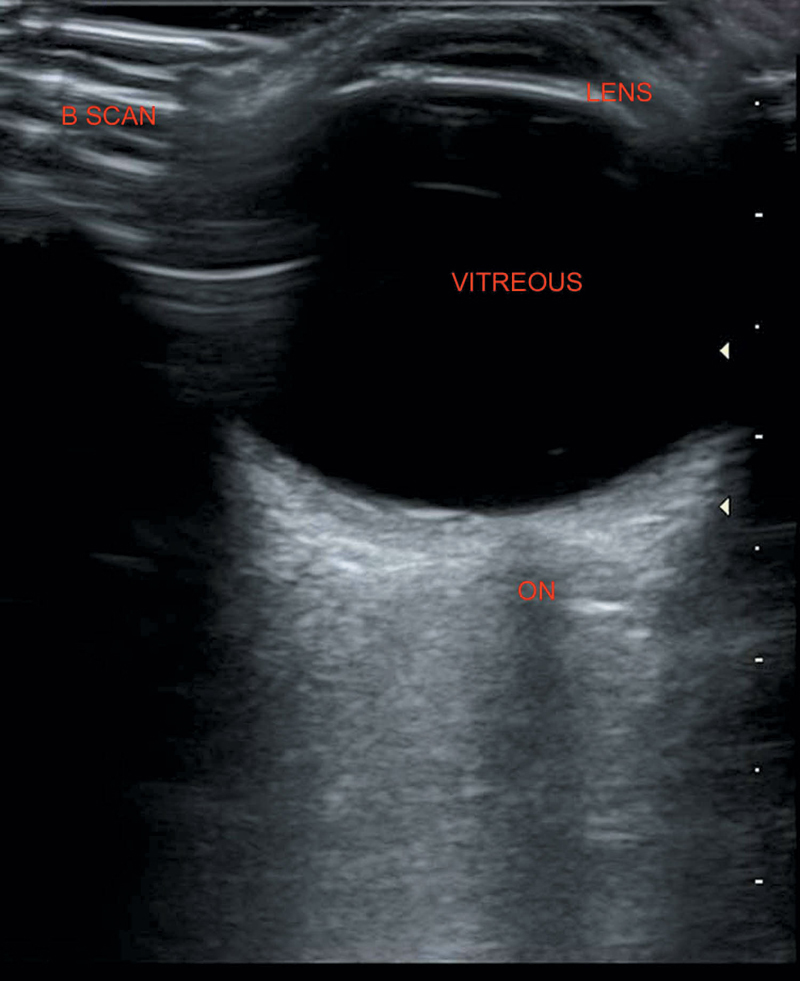
Figure 43.1 Normal B scan illustrating normal anatomy.
Transverse position of the probe delineates the lateral extent of the pathology and longitudinal position determines its radial extent.
Doppler should be used for added information.
Lens—Bright, highly reflective
Membranes (sclera, choroid, and retina)—Highly reflective
Vitreous—Anechoic
Optic nerve—Wedge-shaped hypoechoic in retrobulbar region
Extra ocular muscles—Hypoechoic
Inferior rectus is the thinnest and superior rectus—Levator palpebrae superior is the thickest. Inferior oblique is usually not visualized except in pathological conditions.
Both the eyes should be examined for comparison.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree