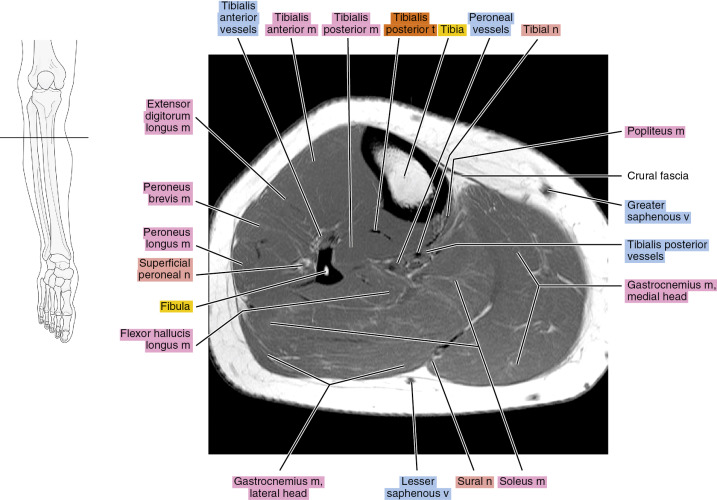
Table 13-1.
Muscles of the Leg
| MUSCLE | ORIGIN | INSERTION | NERVE SUPPLY |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tibialis anterior | Distal part of the lateral condyle of the tibia, lateral surface of the proximal half of the shaft of the tibia, adjacent interosseous membrane, overlying fascia near the condyle of the tibia, and intermuscular septum between it and the extensor digitorum longus | Medial surface of the first cuneiform and the base of the first metatarsal | Branch from the common peroneal and another from the deep peroneal |
| Extensor digitorum longus | Lateral condyle of the tibia, anterior crest of the fibula intermuscular membrane between it and the tibialis anterior, lateral margin of the interosseous membrane, the septum between it and the peroneus longus, and fascia of the leg near the tibial origin | Each tendon, located on the dorsal surface of the toe to which it goes, divides into three fasciculi: the intermediate, attached to the dorsum of the base of the middle phalanx; and two lateral, which converge to the dorsum of the base on the distal phalanx. The margins of each tendon are bound to the sides of the back of the proximal phalanx | By two branches of the deep peroneal |
| Peroneus tertius | Distal one third of the anterior surface of the fibula, neighboring interosseous membrane, and anterior intermuscular septum | Onto the base of the fifth metatarsal and often onto the base of the fourth | The more distal nerve to the extensor digitorum supplies this muscle (deep peroneal) |
| Extensor hallucis longus | Middle half of the anterior surface of the fibula near the interosseous crest and distal half of the interosseous membrane | At the base of the dorsal aspect of the great toe | Deep peroneal |
| Peroneus longus | Proximal two thirds of the lateral surface of the fibula | Inferior surface of the first cuneiform and on the adjacent part of the inferolateral border and the base of the first metatarsal | Usually, the common peroneal, sometimes partially by superficial peroneal |
| Peroneus brevis | Middle one third of the lateral surface of the fibula, from the septum that separate it from the anterior and posterior groups of muscles | Dorsal aspect of the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal | Superficial peroneal or a branch to peroneus longus |
| Popliteus | Facet at the anterior end of the groove on the lateral aspect of the femoral condyle | Proximal lip of the popliteal line of the tibia and the shaft of the tibia proximal to this line | Tibial: a branch that arises independently, or with the nerve to the posterior tibial muscle |
| Flexor digitorum longus | Popliteal line, medial side of the second quarter of the dorsal surface of the tibia, fibrous septum between the muscle and the tibialis fascia posterior, and the covering its proximal extremity | Onto the bases of the terminal phalanges of the second to fourth toes | Tibial: in company with nerves to other muscles of this group |
| Flexor hallucis longus | Distal two thirds of the posterior surface of the fibula, the septa between it and the tibialis posterior, and peroneal muscles | Onto the base of the terminal phalanx of the great toe | Tibial: often in company with the nerve to the flexor digitorum longus or other muscles of this group |
| Tibialis posterior | Lateral half of the popliteal line and lateral half of the middle one third of the posterior surface of the tibia, medial side of the head and part of the body of the fibula next to the interosseous membrane in the proximal two thirds, the entire proximal and lateral portion of the lateral part of the posterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and the septum between its proximal portion and the long flexor muscles | The tendon divides into two parts: the deep part becomes attached primarily to the tubercle of the navicular bone, and usually to the first cuneiform; the superficial part attaches to the third cuneiform and the base of the fourth metatarsal, and also, in part, to the second cuneiform, to the capsule of the naviculocuneiform joint, to the sulcus of the cuboid, and usually also to the origin of the short flexor of the big toe and base of the second metatarsal; slip may extend to other structures | Tibial: in company with nerves to other muscles of this group |
| Gastrocnemius | Medial head: posterior surface of the medial condyle of the femur above the articular surface; lateral head: a facet on the proximal part of the posterolateral surface of the lateral condyle of the femur | Via the Achilles tendon onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus | Sciatic, tibial part |
| Soleus | By a fibular head from the back of the head and the proximal one third of the posterior surface of the shaft of the fibula; intermuscular septum between it and the peroneus longus, by a tibial head from the popliteal line and the middle one third of the medial border of the tibia | Via the calcaneal tendon onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus | Sciatic, tibial part |
| Plantaris | Distal part of the lateral line of the bifurcation of the linea aspera, in close association with the lateral head of the gastrocnemius | Via a flat narrow tendon running along the medial edge of the Achilles tendon to the posterior surface of the calcaneus | Sciatic, tibial part |
Axial
Figure 13.1.1
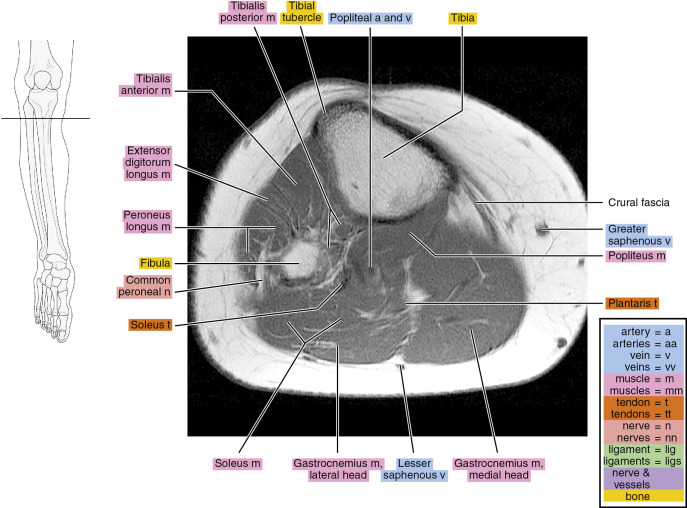
Figure 13.1.2
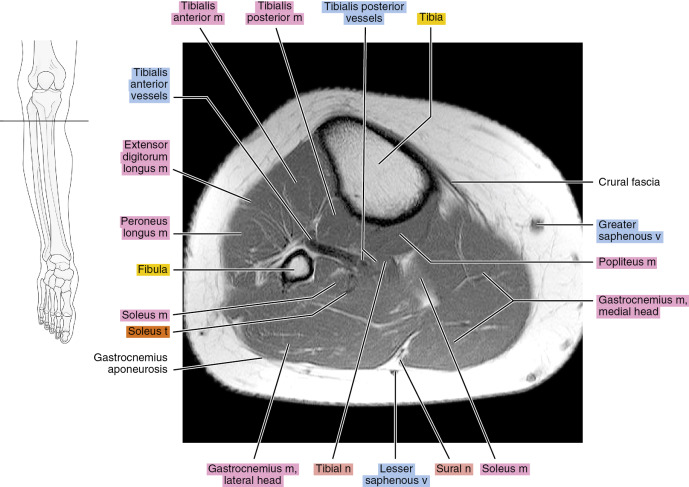
Figure 13.1.3
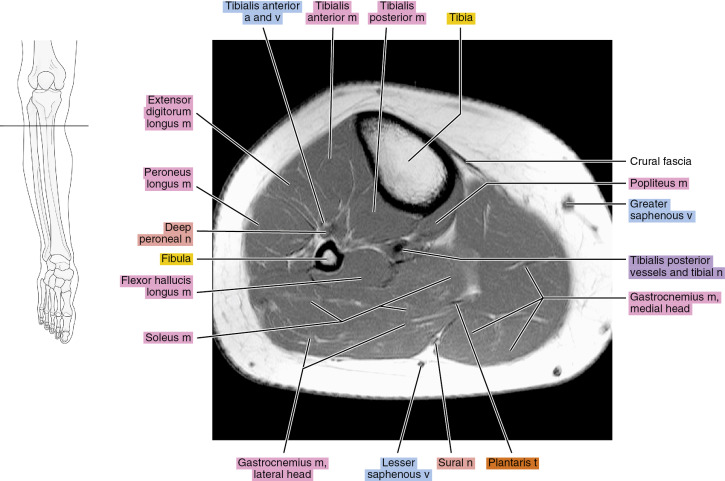
Figure 13.1.4
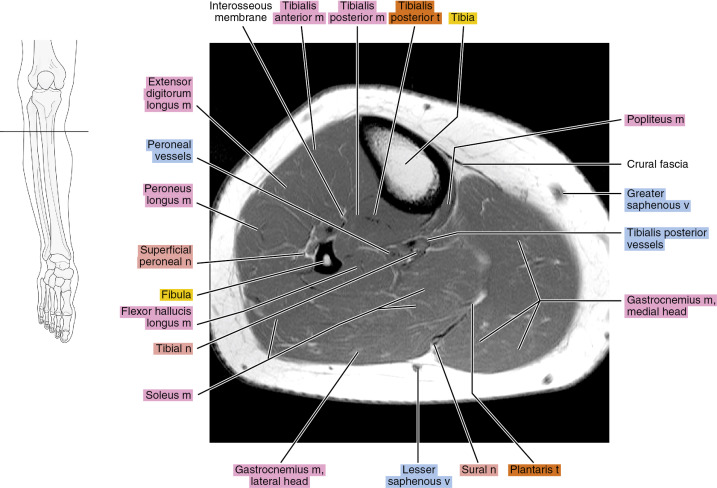
Figure 13.1.5