KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Synonyms: Mucinous cystic neoplasm, macrocystic cystadenoma/carcinoma, mucinous cystadenoma/carcinoma
- •
Septated cystic neoplasm composed of mucin-producing epithelium and distinctive ovarian-type stroma, ranging in grade from potentially malignant to invasive carcinoma
Imaging
- •
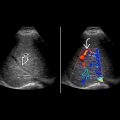
Solitary, uni- or multilocular, well-circumscribed cystic lesion in body or tail of pancreas
- •
Echogenic septations
- •
Typically < 6 cystic components, which are each > 2 cm in size
- •
Cyst contents may be anechoic or echogenic with debris representing mucin
- •
May contain peripheral calcification
- •
2 cm to > 10 cm in diameter; mean: 8.7 cm
- •
No communication with pancreatic duct
- •
Mural nodularity and solid component suggest malignancy
- •
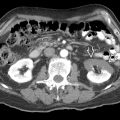
Contrast-enhanced CT or MR used to accurately characterize morphology and guide treatment
- •
Endoscopic US: Invasive technique reserved for when fine-needle aspiration is being considered
- •
Hypovascular on color Doppler (nodules and septations may show flow)
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
- •
Macrocystic variant of serous cystadenoma
- •
Solid pseudopapillary tumor
- •
Pseudocyst
- •
Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor
Clinical Issues
- •
Seen almost exclusively in middle-aged women; termed “mother lesion”; mean age: 50 years
- •
M:F = 1:20
- •
10% of cystic pancreatic tumors
- •
Often asymptomatic
- •
May present with epigastric pain, palpable mass, or fullness
- •
Excellent prognosis without invasive carcinoma
- •
All tumors in this class are considered surgical lesions
- •
Worse prognosis when invasive carcinoma is present; however, better than with typical ductal-type adenocarcinoma (75% vs. 5%)
Scanning Tips
- •
Findings on US are nonspecific and further evaluation with CT or MR is necessary
 in the tail of the pancreas. Note that the pancreatic duct
in the tail of the pancreas. Note that the pancreatic duct  is displaced but not obstructed.
is displaced but not obstructed.
 in the body of the pancreas with a few hyperechoic peripheral foci
in the body of the pancreas with a few hyperechoic peripheral foci  . Note the normal pancreas
. Note the normal pancreas  .
.