Fig. 1
Acinar Cell Carcinoma (a–c) Surgical specimen (pancreaticoduodenectomy): voluminous tumor (a) with multinodular aspect involving extensively the head of the pancreas and dislocating the common bile duct (C in a); foci of necrosis are present (asterisk in a). Histopathology: the tumor is mostly characterized by polarized cells resembling acinar cells (b). Immunohistochemical staining for trypsin (c)
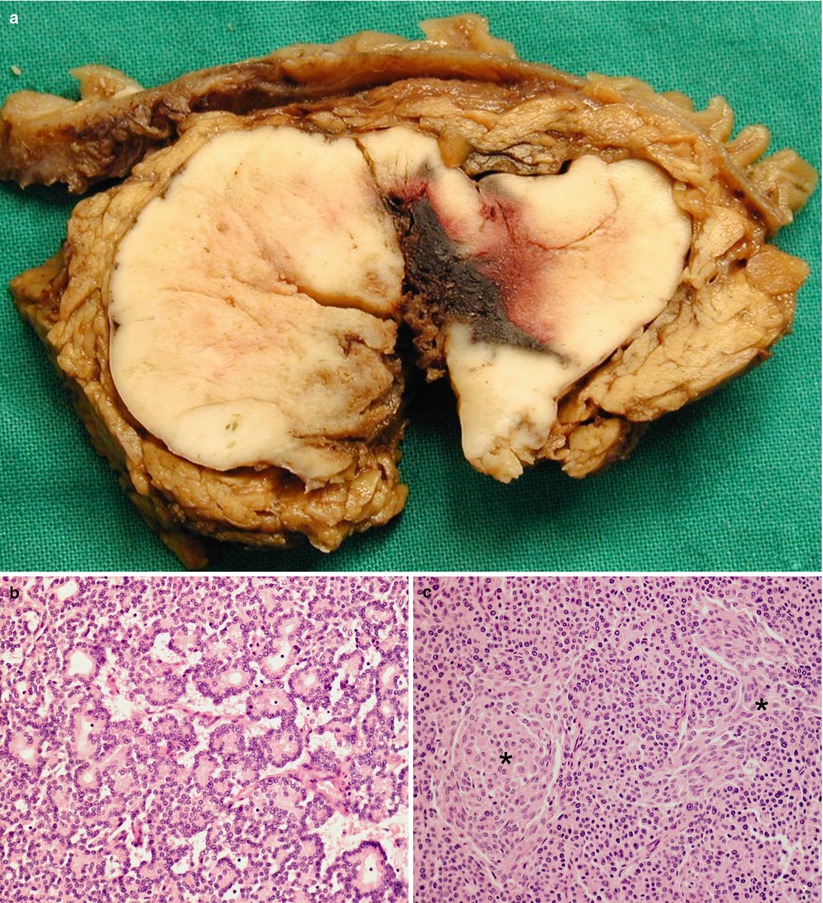
Fig. 2
Pancreatoblastoma (a–c) Surgical specimen (pancreaticoduodenectomy): voluminous solid mass (a) with clear-cut margins involving extensively the head of the pancreas with central hemorrhagic area. At histopathology (b), prominent acinar differentiation and characteristic squamoid corpuscles (asterisks in c) are seen
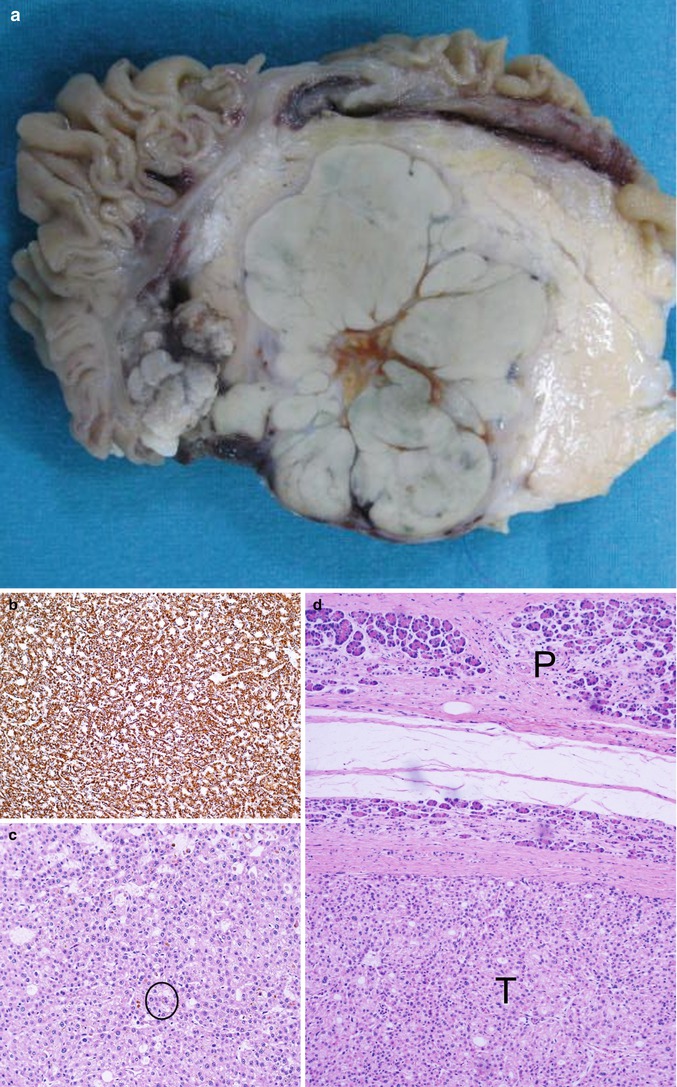
Fig. 3
Hepatoid carcinoma (a–d) Surgical specimen (pancreaticoduodenectomy): voluminous solid-lobulated mass (a). Immunohistochemical staining (b) for hepatocyte paraffin-1 antibody. Neoplasm with solid-nested trabecular architecture (c); in this case bile pigment is present (circle in c). The tumor (T in d) is well demarcated from normal pancreas (P in d)
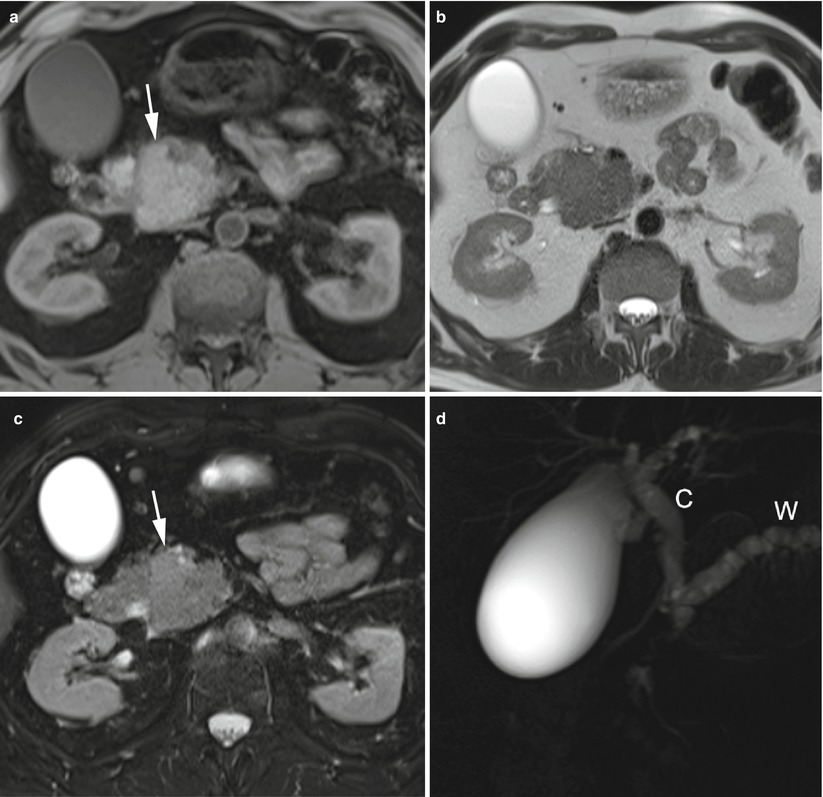
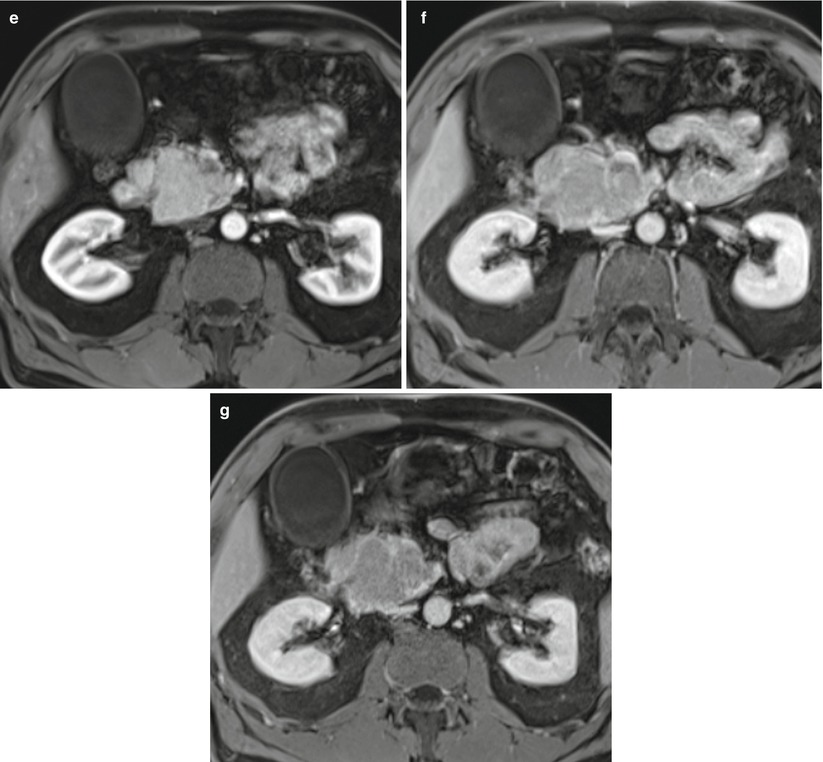
Fig. 4
Acinar Cell Carcinoma (a–g) MR study: pancreatic head mass slightly hyperintense on T1-weighted images (arrow in a) and slightly hyperintense on T2-weighted and fat-saturated T2-weighted images (arrow in c). The mass presents clear-cut margins but involves the superior mesenteric vessels. On MRCP (d) double duct sign is present with dilation of both common bile duct (C in d) and Wirsung duct (W in d). On dynamic phases (e–g) the mass is well vascularized
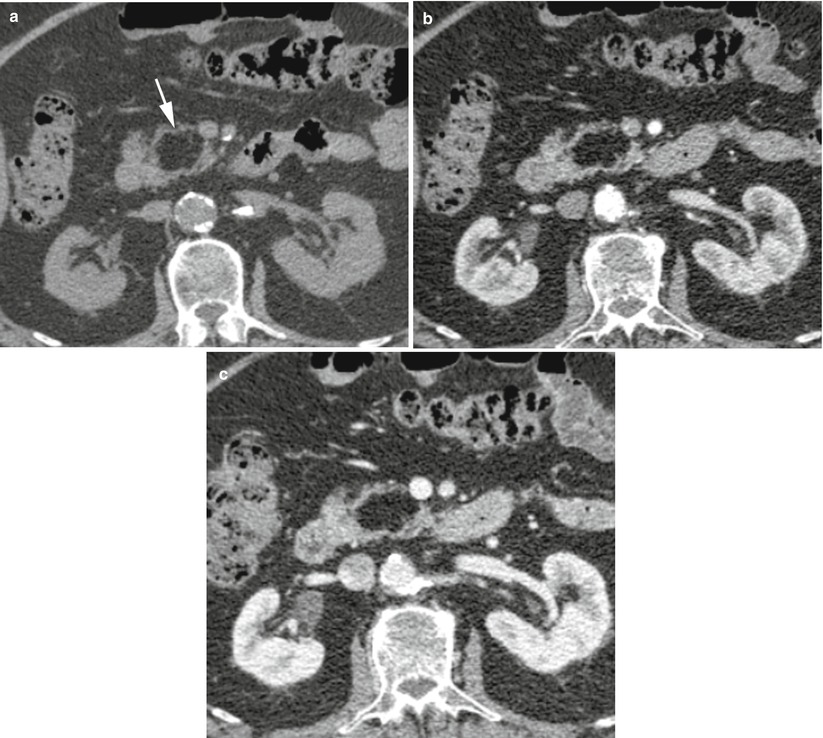
Fig. 5
Pancreatic lipoma (a–c) CT study: in the basal scan a hypodense, with fat density, well-demarcated lesion (arrow in a) with lobulated contours is visible in the pancreatic head. On dynamic phases (b, c), no enhancement of the lesion is appreciable
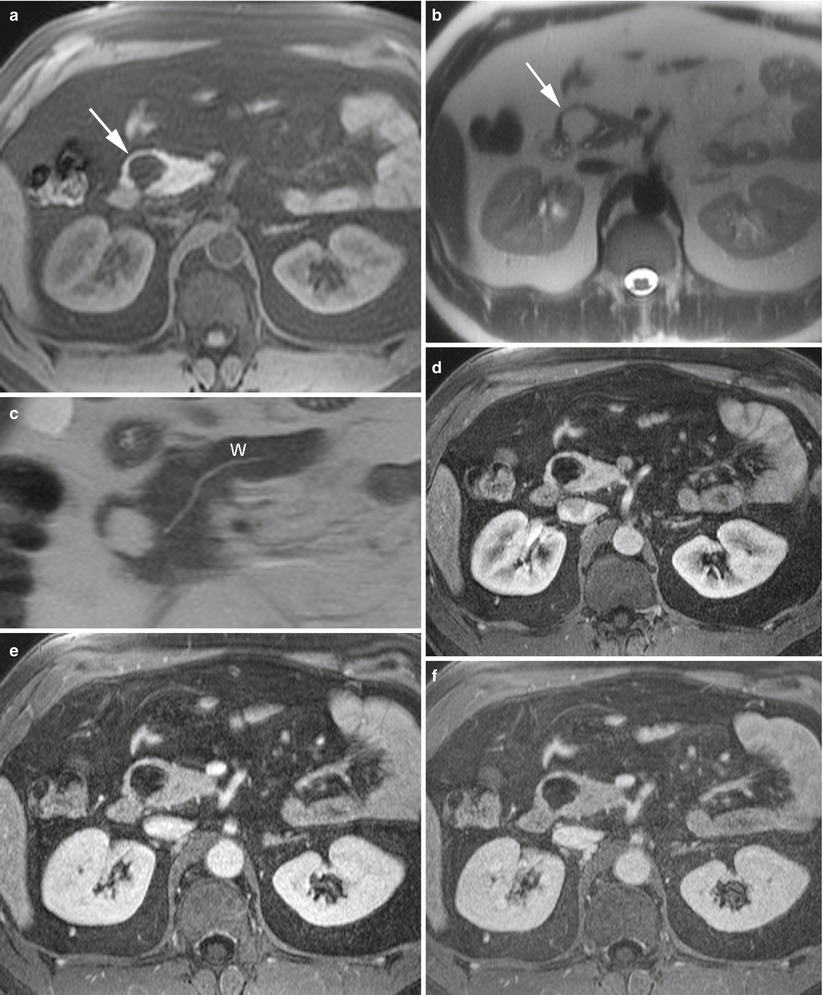
Fig. 6
Pancreatic lipoma (a–f) MR study: pancreatic head mass hypointense on fat saturated T1-weighted images (arrow in a) and hyperintense, with fat intensity, on T2-weighted images (arrow in b). The Wirsung duct is normal (W in c). In the dynamic phases (d–f), no enhancement of the lesion, except for very thin septa, is appreciable
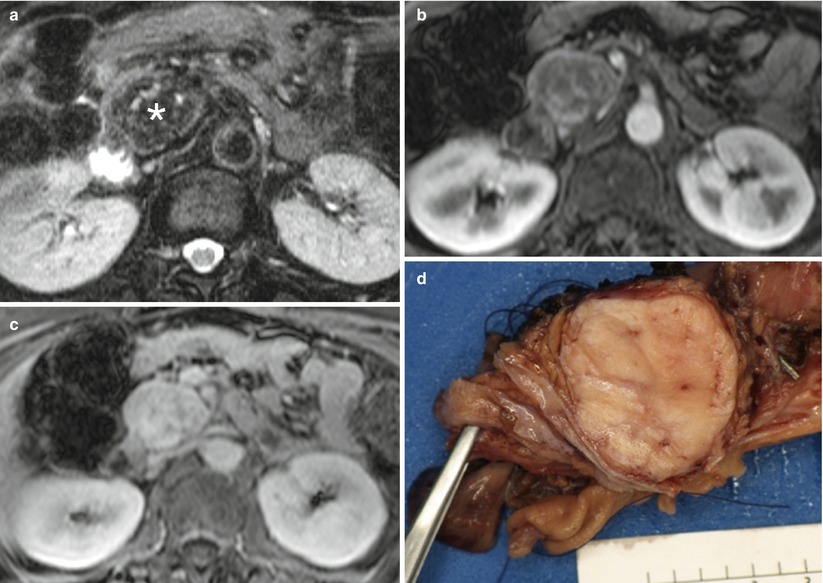
Fig. 7
Solitary fibrous tumor (a–c) MR study: T2-weighted images (a) reveal predominantly low signal mass (asterisk in a) in pancreatic head. Pancreatic phase image (b) from gadolinium-enhanced Gradient recalled echo sequence reveals enhancing septa, but the mass remains predominantly low signal. Late venous phase image (c) from the same sequence reveals the lesion has progressively enhanced. Slow enhancement with retention of contrast is typical of fibrous tissue. (d) Pathology specimen (pancreaticoduodenectomy): specimen reveals a tan 3.5 cm sharply circumscribed neoplasm in the pancreatic head. The tumor was predominantly spindle cell morphology. Immunohistochemical stains were positive for CD34, BCL-2, focally for B-catenin and weak staining for CD-99. This supports a fibroblastic origin
References
1.
Hammond NA, Miller FH, Day K, Nikolaidis P (2013) Imaging features of the less common pancreatic masses. Abdom Imaging 38(3):561–572PubMed
2.
Bosman FT, World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer (2010) WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
3.
Hruban RH, Pitman MB, Klimstra DS, American Registry of Pathology, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (US) (2007) Tumors of the pancreas. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington DC
4.
Chen J, Baithum SI (1985) Morphological study of 391 cases of exocrine pancreatic tumours with special reference to the classification of exocrine pancreatic carcinoma. J Pathol 146:17–29PubMed
5.
Cubilla AL, Fitzgerald PJ (1975) Morphological patterns of primary nonendocrine human pancreas. Cancer Res 35:2234–2238PubMed
6.
Cubilla AL, Fitzgerald PJ (1979) Cancer of the pancreas (nonendocrine): a suggested morphological classification. Semin Oncol 6:285–297PubMed
7.
Morohoshi T, Held G, Kloppel G (1983) Exocrine pancreatic tumours and their histological classification: a study based on 167 autopsy and 97 surgical cases. Histopathology 7(5):645–661PubMed
8.
Ordonez NG (2001) Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma. Adv Anat Pathol 8(3):44–159
9.
Becker WF (1957) Pancreatoduodenectomy for carcinoma of the pancreas in an infant: report of a case. Ann Surg 145:864–870PubMedCentralPubMed
10.
Kissane JM (1994) Pancreatoblastoma and solid and cystic papillary tumor: two tumors related to pancreatic ontogeny. Semin Diagn Pathol 11:152–164PubMed
11.
Horie A, Yano Y, Kotoo Y, Miwa A (1977) Morphogenesis of pancreatoblastoma, infantile carcinoma of the pancreas: report of two cases. Cancer 39(1):247–254PubMed
12.
Kerr NJ, Fukuzawa R, Reeve AE, Sullivan MJ (2002) Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, pancreatoblastoma, and the wnt signaling pathway. Am J Pathol 160(4):1541–1542PubMed
13.
Dhebri AR, Connor S, Campbell F, Ghaneh P, Sutton R, Neoptolemos JP (2004) Diagnosis, treatment and outcome of pancreatoblastoma. Pancreatology 4(5):441–451PubMed
14.
Ohtomo K, Furui S, Onoue M, Okada Y, Kusano S, Shiga J, Suga K (1992) Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas: MR imaging and pathologic correlation. Radiology 184(2):567–570PubMed
15.
Dong PR, Lu DS, Degregario F, Fell SC, Au A, Kadell BM (1996) Solid and papillary neoplasm of the pancreas: radiological-pathological study of five cases and review of the literature. Clin Radiol 51(10):702–705PubMed
16.
Cavallini A, Falconi M, Bortesi L, Crippa S, Barugola G, Butturini G (2009) Pancreatoblastoma in adults: a review of the literature. Pancreatology 9(1–2):73–80PubMed
17.
Levey JM, Banner BF (1996) Adult pancreatoblastoma: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol 91(9):1841–1844PubMed
18.
Rajpal S, Warren RS, Alexander M, Yeh BM, Grenert JP, Hintzen S, Ljung BM, Bergsland EK (2006) Pancreatoblastoma in an adult: case report and review of the literature. J Gastrointest Surg 10(6):829–836PubMed
19.
Dunn JL, Longnecker DS (1995) Pancreatoblastoma in an older adult. Arch Pathol Lab Med 119(6):547–551PubMed
20.
Palosaari D, Clayton F, Seaman J (1986) Pancreatoblastoma in an adult. Arch Pathol Lab Med 110(7):650–652PubMed
21.
Klimstra DS, Wenig BM, Adair CF, Heffess CS (1995) Pancreatoblastoma. A clinicopathologic study and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol 19(12):1371–1389PubMed
23.
Ishikura H, Fukasawa Y, Ogasawara K et al (1985) An AFP-producing gastric carcinoma with features of hepatic differentiation. A case report. Cancer 56:840–848PubMed
24.
Chetty R et al (2009) Solitary fibrous tumor of the pancreas. Ann Diagn Pathol 13(5):339–343PubMed
25.
Bismar TA, Basturk O, Gerald WL, Schwarz K, Adsay NV (2004) Desmoplastic small cell tumor in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol 28(6):808–812PubMed
26.
Chappell JS (1973) Case reports. Benign hemangioendothelioma of the head of the pancreas treated by pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Pediatr Surg 8(3):431–432PubMed
27.
Tunell WP (1976) Hemangioendothelioma of the pancreas obstructing the common bile duct and duodenum. J Pediatr Surg 11(5):827–830PubMed
28.
Mundinger GS, Gust S, Micchelli ST, Fishman EK, Hruban RH, Wolfgang CL (2009) Adult pancreatic hemangioma: case report and literature review. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2009(839730):1–5
29.
Lee J, Raman K, Sachithanandan S (2011) Pancreatic hemangioma mimicking a malignant pancreatic cyst. Gastrointest Endosc 73(1):174–176PubMed
30.
Künzli BM, Shrikhande SV, Büchler MW, Friess H (2004) Pancreatic lesions in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome: report of a case. Surg Today 34(7):626–629PubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree