Fig. 7.1
In the DMSA renal scan, posterior view, are displayed three patients with normal left kidney and ultrasonographic finding of small right kidney: (a) right kidney is smaller than the other one, but shows good and homogeneous uptake of radiotracer without evidence of cortical defect; right kidney DRF is 39 %, as seen in hypoplastic kidneys; (b) right kidney is smaller than the other one, with moderate-severe reduction of radiotracer uptake (right kidney DRF: 21 %, “moderate-severe hypodysplasia”); (c) right kidney is markedly smaller than the other one, with severe reduction of the radiotracer uptake (right kidney DRF: 5 %, “severe hypodysplasia”)

Fig. 7.2
In the DMSA renal scan, posterior view, are displayed three patients with normal left kidney and ultrasonographic finding of multiple hypoechoic round areas in right kidney: (a) DMSA renal scan in a 8-month-old boy with prenatal diagnosis of multicystic kidney: there is no visualization of right kidney (multicystic dysplastic kidney is not able to uptake radiotracer, because there is no functioning parenchyma); (b) DMSA renal scan in a 3-year-old boy with prenatal diagnosis of renal cystic dysplasia: right kidney is larger than the other one and shows irregular shape, with nonhomogenous intraparenchymal radiotracer distribution and multiple focal areas of reduced uptake, especially in the upper pole, associated with cortical defects, related to the presence of cystic lesions (polycystic dysplasia); (c) DMSA renal scan, in a 5-year-old boy with severe hydronephrosis: right kidney is larger than the other one, with irregular shape; moderate reduction of radiotracer uptake is evident associated with multiple areas devoid of tracer corresponding to dilated collecting system, surrounded by thin parenchyma without cortical defects (right DRF: 35 %). DMSA renal scan is considered the gold standard for split renal function assessment, even if MAG3 renal scan allows an analog split function evaluation and adds definition of urinary drainage, useful in follow-up after surgery

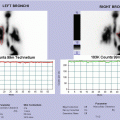
Fig. 7.3




MAG3 dynamic renal scan: dynamic images (a) show good radiotracer uptake in left kidney with nonhomogeneous intraparenchymal distribution due to an area devoid of tracer corresponding to dilated renal pelvis and collecting system; shape is irregular and drainage is poor; right kidney is smaller than the other one, with very irregular shape, severe reduction of uptake, and poor drainage; radiotracer uptake is evident only in lower third of the kidney. (b) Left renogram shows normal function but poor drainage of left kidney (“rising curve”); right renogram has low width and shows severe hypofunction of right kidney with impaired drainage; flow T/A curves show synchronous but asymmetrical (reduced in right kidney) perfusion. Gravity-assisted drainage-1 test shows significant improvement in left kidney drainage, but still poor drainage of right kidney (c). Diuretic dynamic images (d) and diuretic renogram (e) show very slow response to furosemide and no significant improvement in drainage in the right kidney. Right kidney drainage remains still poor even after gravity-assisted drainage-2 test (f)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree