, Lawrence A. Zumo2 and Valerie Sim3
(1)
Parkinson’s Clinic of Eastern Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
(2)
Silver Spring, Cheverly, MD, USA
(3)
Centre for Prions and Protein Folding Diseases, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Abstract
Rapid neuroimaging with CT scan is often used in trauma cases associated with altered level of consciousness as it can quickly reveal surgical emergencies such as fractures and bleeds. In this chapter we present cases of epidural and subdural hematomas, intracerebral contusions, cerebral edema with herniation and vertebral body fractures. Many of these are neurosurgical emergencies and require accurate and rapid assessment.
Case 8.1 Epidural Hematoma
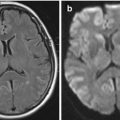
A 53 year old male presented with a history of falls and decreased level of consciousness. A CT scan was performed (Fig. 8.1).
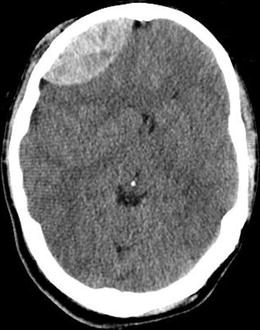

Figure 8.1
Axial CT showing right frontal epidural hematoma
Explanation and Diagnosis
Figure 8.1 shows a bi-convex hyperdensity in right frontal area with mild mass effect and midline shift. The correct diagnosis is acute right frontal epidural hematoma. This is a surgical emergency.
Case 8.2 Subdural Hematoma
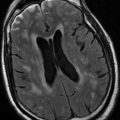
A 74 year old right-handed male presented after a fall on his driveway. He had consumed alcohol prior to the fall. He was noticed to have twitching of his right side which lasted for several seconds. A few hours later he had another episode of shaking of his right side lasting 30–60 s. A CT scan was performed (Fig. 8.2).
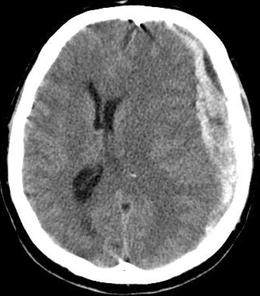





Figure 8.2
Axial CT showing left frontoparietal subdural hematoma with midline shift with loss of occipital horn
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree