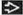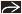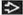Nodal Hodgkin Lymphoma in Neck
Christine M. Glastonbury, MBBS
Key Facts
Terminology
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)
Characterized by presence of Reed-Sternberg cells
Imaging
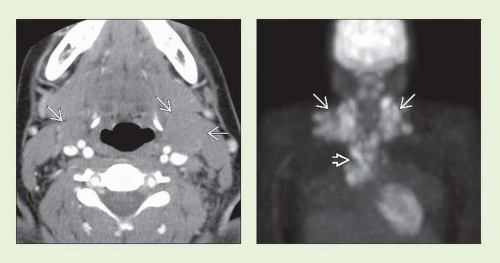
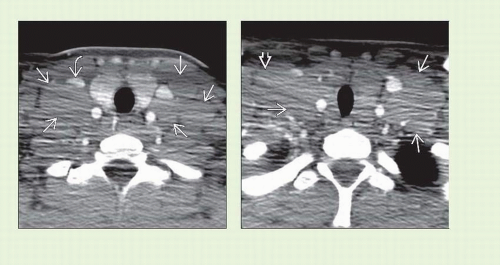
Most HL patients present due to neck adenopathy
Single nodal group or contiguous groups
Mediastinal nodes frequently involved at presentation
Head and neck HL is rarely extranodal
CECT: Homogeneous solid nodal masses
Necrosis or calcification uncommon
CECT and FDG PET are basic staging modalities
FDG PET shows marked activity
Persistently positive PET during treatment has high sensitivity for prediction of relapse
FDG PET differentiates post-treatment inactive scar from residual tumor
Top Differential Diagnoses
Reactive lymph nodes
Nodal differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Nodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Nodal squamous cell carcinoma
Pathology
Neoplastic cells are Reed-Sternberg cells
Most of tumor bulk is reactive inflammatory cells
95% classic HL; aggressive tumor
5% nodular lymphocyte-predominant HL
Clinical Issues
Young adult with enlarging, painless neck mass
40% have B symptoms: Fever, sweats, weight loss
HL is potentially curable
5-year survival: Stages I-III (≥ 85%), stage IV (80%)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL)
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL)
Synonyms
Hodgkin disease
Definitions
HL: Classical or nodular lymphocyte-predominant
Characterized by presence of Reed-Sternberg cells
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Young patient with neck & mediastinal adenopathy
Location
HL most commonly cervical & mediastinal nodes
Internal jugular, spinal accessory, & transverse cervical nodal chains
Involves contiguous nodal groups
Rarely involves Waldeyer ring or other extranodal neck sites (< 1%)
Size
Variable nodal size: 2-10 cm
Morphology
Single nodal chain ± spread to contiguous chain
60-80% present with neck/supraclavicular nodes
30% with axillary adenopathy
50-60% have mediastinal nodes at presentation
CT Findings
NECT
Homogeneous lobulated round masses
Nodes isodense to muscle
Calcification uncommon except after treatment
CECT
Variable enhancement
Necrosis may be seen as low-density center
MR Findings
T1WI
Enlarged iso- to hypointense round nodes
T2WI
Nodes hyperintense compared to muscle
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree