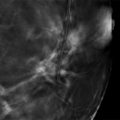
Presentation and Presenting Images
( ▶ Fig. 14.1, ▶ Fig. 14.2, ▶ Fig. 14.3, ▶ Fig. 14.4)
A 44-year-old female presents for asymptomatic screening mammography.
14.2 Key Images
( ▶ Fig. 14.5, ▶ Fig. 14.6, ▶ Fig. 14.7, ▶ Fig. 14.8)
14.2.1 Breast Tissue Density
The breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses.
14.2.2 Imaging Findings
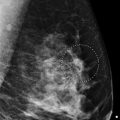
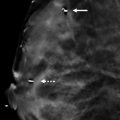
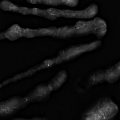
Within the subareolar region of the right breast, there is a partially circumscribed and partially obscured mass with heterogeneous composition. There are elements of fat and fibroglandular tissue within the mass. The anterior, medial/lateral, and superior/inferior margins are well seen on the conventional digital mammograms ( ▶ Fig. 14.5 and ▶ Fig. 14.6). The posterior margin is obscured. The synthetic mammograms highlight this mass within the breast tissue and make it stand out more than on the conventional mammogram ( ▶ Fig. 14.3 and ▶ Fig. 14.4). The digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) images better define all margins of this mass ( ▶ Fig. 14.7 and ▶ Fig. 14.8). The craniocaudal (CC) DBT is best for demonstrating the posterior margin ( ▶ Fig. 14.7). The left breast is normal.
14.3 BI-RADS Classification and Action
Category 2: Benign
14.4 Differential Diagnosis
Hamartoma: This mass is encapsulated which is clearly seen on the DBT images. It also contains adipose and fibroglandular components.
Fibroadenoma: These masses do not contain adipose components, They are isodense masses that typically present as circumscribed or partially circumscribed masses.
Lipoma: Lipomas are encapsulated fatty masses; however, they do not contain fibroglandular components.
14.5 Essential Facts
Hamartomas account for 4.8% of benign breast tumors.
Most hamartomas are asymptomatic, but, if symptomatic, they present as a palpable lump.
Histologically hamartomas have all the constituents of normal breast tissue and thus are often reported as normal breast tissue on a biopsy report.
Hamartomas consist of varying degrees of normal breast tissue elements (benign parenchyma, epithelium, fibrous tissue, and adipose tissue).
Mammographically hamartomas appear as encapsulated or pseudoencapsulated tumors, but microscopically they are not encapsulated. Rather, the margin is composed of condensed fibrous tissue or collagen around the mass.
At DBT, a hamartoma has a round or oval shape with a thin, water-density capsule delineating its border.
14.6 Management and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Principles
Most encapsulated masses that contain fat, such as hamartomas, lipomas, galactoceles, and lipid cysts, can be classified as benign.
Hamartomas (also called fibroadenolipomas) contain normal components of breast tissue. They are benign masses; however, due to their breast tissue components, they have the risk of developing breast cancer within them. Suspicious findings within a hamartoma should be evaluated.
14.7 Further Reading
[1] Freer PE, Wang JL, Rafferty EA. Digital breast tomosynthesis in the analysis of fat-containing lesions. Radiographics. 2014; 34(2): 343‐358 PubMed
[2] Wahner-Roedler DL, Sebo TJ, Gisvold JJ. Hamartomas of the breast: clinical, radiologic, and pathologic manifestations. Breast J. 2001; 7(2): 101‐105 PubMed

Fig. 14.1 Right craniocaudal (RCC) mammogram.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree