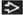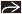Opportunistic Intestinal Infections
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Gastrointestinal infection of immunocompromised host by virus (CMV), protozoa (Cryptosporidium), or Mycobacterium (MAI)
Imaging
Best imaging tool
Small bowel follow through, CECT
Protocol advice
CECT: 150 mL IV contrast at 2.5 mL/sec with 5 mm collimation
Top Differential Diagnoses
Giardiasis
Tuberculosis
Gastrointestinal lymphoma
Whipple disease
Clinical Issues
Most common signs/symptoms
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, GI bleeding
CMV and cryptosporidiosis respond to nitazoxanide in early stage
MAI in AIDS patients often difficult to treat
CMV: Antiviral therapy with acyclovir or ganciclovir
MAI: Antituberculous chemotherapy
Cryptosporidiosis: Chemotherapy with nitazoxanide
Diagnostic Checklist
Image interpretation pearls
CMV: Deep ulcerations and focal enteritis or colitis
MAI: Enteritis and low-attenuation nodes
Cryptosporidiosis: Thickened bowel wall and edematous folds
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare (MAI), atypical mycobacterial infection, cryptosporidiosis, Cryptosporidium parvum
Definitions
Gastrointestinal (GI) infection of immunocompromised host by virus (CMV), protozoa (Cryptosporidium), or Mycobacterium (MAI)
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
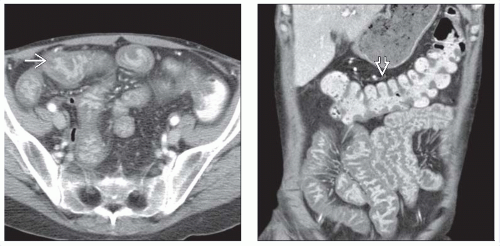
CMV: Thickened folds with deep ulcerations of small bowel (SB) or colon on barium studies
MAI: Thickened SB folds, mesenteric, or periportal adenopathy with low-attenuation nodes
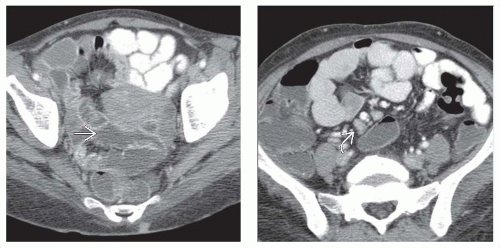
Cryptosporidiosis: Secretory enteritis with thickened small bowel folds and increased fluid in bowel
Location
CMV: Small bowel, colon, stomach
MAI: Small bowel, nodes
Cryptosporidiosis: Small bowel
Fluoroscopic Findings
CMV: Barium enema
Diffuse colitis
Early stage resembles ulcerative colitis
Aphthous ulcers
Terminal ileum characteristically involved, with thickened folds &/or ulceration
Later stages show deep ulceration
CMV: Small bowel follow through (SBFT)
Thickened edematous folds
Discrete ulcerations
Deep ulcers in sinus tracts
MAI: Small bowel follow through
Diffuse enteritis with thickened folds
Micronodular mucosal pattern
Cryptosporidiosis: Small bowel follow-through
Secretory enteritis
Thickened folds
Increased fluid in bowel
CT Findings
CECT
CMV
Mural thickening of colon, stomach, small bowel (especially terminal ileum)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree