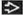Osteosarcoma of H&N
H. Ric Harnsberger, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Definition: Malignant tumor arising from bone with ability of neoplastic cells to produce osteoid
Imaging
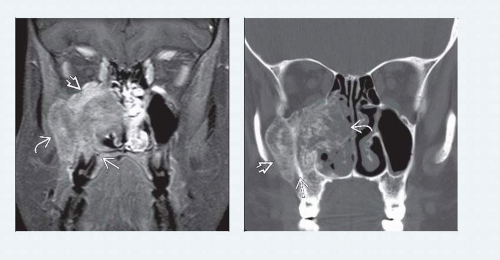
Bone CT: Shows bone tumor with both osteolytic & osteoblastic components
MR imaging: Best evaluates extent of osteosarcoma
Intramedullary and extraosseous soft tissues
PET/CT: Used for local recurrence and distant metastasis identification
Top Differential Diagnoses
Mandible-maxilla osteomyelitis
Mandible-maxilla metastasis
Ewing sarcoma
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Mandible-maxilla osteoradionecrosis
Pathology
Heterogeneous mass with ossified and nonossified components
Chondroblastic > osteoblastic > fibroblastic
Clinical Issues
Mean age: 35 years
Prognosis depends on pathologic type, size, location, and presence of metastases
5-year survival = 60%
Complete resection affords best chance of survival
Diagnostic Checklist
Osteoid matrix in tumor of mandible or maxilla suggests osteosarcoma
If not present, consider metastasis or osteomyelitis
Consider radiation-induced osteosarcoma if patient had radiation years prior
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Osteosarcoma of head & neck (OSa H&N)
Synonyms
Osteogenic sarcoma
Definitions
Malignant tumor arising from bone with ability of neoplastic cells to produce osteoid
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
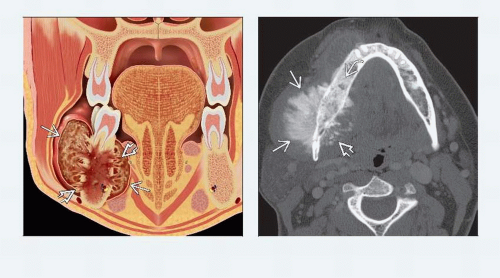
H&N bone tumor demonstrating tumor matrix mineralization with aggressive bone destruction and soft tissue extension leads directly to radiologic diagnosis of osteosarcoma
Location
Mandible ≈ maxilla > > calvarium/skull base
All other sites are extremely rare
Hard palate, mastoid, zygoma, paranasal sinuses
Mandible OSa in mandibular body
Maxillary bone OSa in alveolar ridge
Postradiation OSa: Typically at border of radiation field
Most commonly involves multiple bones at this site
Size
Ranges in size from 1-15 cm
Majority present in 3-6 cm size range
Median size is 5.5 cm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree