• Incomplete formation of the embryonic ventral abdominal wall leads to a congenital midline anterior abdominal wall defect around the umbilicus (the umbilical cord inserts at the tip of the defect) • Associated chromosomal abnormalities are common (50%): trisomy 13 and 18 • A small defect in the ventral abdominal wall, classically to the right side of a normally positioned umbilicus • An obstruction distal to the ampulla of Vater – malrotation and a midgut volvulus constitute the greatest emergency • ‘Apple peel’ syndrome: this is thought to follow an intrauterine occlusion of the distal SMA • Malrotation is a generic term used to describe any variation in the intestinal position • The abnormal positions of the duodenojejunal junction and caecum means that the base of the small bowel mesentery is short • This commonly presents within the 1st month of life with bilious vomiting • Symptoms of shock intervene if bowel ischaemia and necrosis have developed • A tight volvulus results in complete duodenal obstruction with a distended stomach and proximal duodenum (mimicking the ‘double bubble’ of duodenal atresia) • Closed loop obstruction: this is a more ominous sign and is associated with distal small bowel obstruction • A gasless abdomen can be seen with prolonged vomiting, a closed loop obstruction with viable small bowel, or with a massive midgut necrosis • Normal: on a supine AXR the normal duodenojejunal junction lies to the left of the left-sided pedicles at the height of the duodenal bulb • Malrotation: the duodenojejunal junction is displaced inferiorly and to the right on a supine AXR • ‘Corkscrew’ pattern: this describes the duodenum and jejunum spiralling around the mesenteric vessels and is pathognomonic for a midgut volvulus
Paediatric gastrointestinal disorders
ABDOMINAL WALL DEFECTS
OMPHALOCELE (EXOMPHALOS)
DEFINITION
 Larger omphaloceles (containing liver tissue): due to failure of lateral body fold fusion
Larger omphaloceles (containing liver tissue): due to failure of lateral body fold fusion
 Smaller omphaloceles (containing bowel only): due to persistence of physiological gut herniation
Smaller omphaloceles (containing bowel only): due to persistence of physiological gut herniation
 Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome: omphalocele (exomphalos) + macroglossia + gigantism (the ‘EMG’ syndrome)
Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome: omphalocele (exomphalos) + macroglossia + gigantism (the ‘EMG’ syndrome)  visceral abnormalities are seen in up to 70% of cases
visceral abnormalities are seen in up to 70% of cases
GASTROSCHISIS
DEFINITION
 due to a localized intrauterine vascular accident leading to focal full-thickness necrosis of the anterior abdominal wall
due to a localized intrauterine vascular accident leading to focal full-thickness necrosis of the anterior abdominal wall
GASTROINTESTINAL CAUSES OF NEONATAL VOMITING
NON-BILIOUS VOMITING
BILIOUS VOMITING
Definition
 Other causes: duodenal atresia and stenosis
Other causes: duodenal atresia and stenosis  duodenal webs and diaphragms
duodenal webs and diaphragms  extrinsic duodenal compression (e.g. an annular pancreas or a preduodenal portal vein)
extrinsic duodenal compression (e.g. an annular pancreas or a preduodenal portal vein)  small bowel atresia
small bowel atresia  small bowel stenosis
small bowel stenosis
 If the AXR demonstrates a complete high intestinal obstruction then no further imaging is required
If the AXR demonstrates a complete high intestinal obstruction then no further imaging is required  if the AXR shows a low intestinal obstruction (i.e. distal to the mid ileum) then a contrast enema is preferred
if the AXR shows a low intestinal obstruction (i.e. distal to the mid ileum) then a contrast enema is preferred
DUODENAL ATRESIA AND STENOSIS
SMALL BOWEL ATRESIA AND STENOSIS
Radiological findings
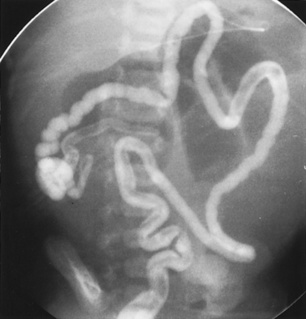
 there is a proximal jejunal atresia, with agenesis of the mesentery and absence of the mid small bowel
there is a proximal jejunal atresia, with agenesis of the mesentery and absence of the mid small bowel  the distal ileum spirals around its narrow vascular pedicle (giving the syndrome its name)
the distal ileum spirals around its narrow vascular pedicle (giving the syndrome its name)  a malrotated microcolon is also usually present
a malrotated microcolon is also usually present
MALROTATION
MALROTATION
DEFINITION
 intestinal malfixation invariably accompanies malrotation in an attempt to fix the gut in place
intestinal malfixation invariably accompanies malrotation in an attempt to fix the gut in place
 Peritoneal (Ladd) bands: these stretch from the abnormally high-lying caecum, across the duodenum, and to the region of the porta hepatis and the anterior and posterior abdominal walls
Peritoneal (Ladd) bands: these stretch from the abnormally high-lying caecum, across the duodenum, and to the region of the porta hepatis and the anterior and posterior abdominal walls  Ladd bands can cause duodenal obstruction
Ladd bands can cause duodenal obstruction
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
 older children may present with non-specific symptoms of chronic or intermittent abdominal pain, non-bilious emesis, diarrhoea, or a failure to thrive
older children may present with non-specific symptoms of chronic or intermittent abdominal pain, non-bilious emesis, diarrhoea, or a failure to thrive
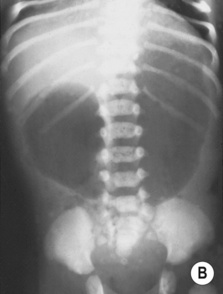
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
AXR
 the volvulus causes venous obstruction and small bowel necrosis – the small bowel loops will be thickened and oedematous (± pneumatosis) and any gas cannot be reabsorbed from the bowel lumen
the volvulus causes venous obstruction and small bowel necrosis – the small bowel loops will be thickened and oedematous (± pneumatosis) and any gas cannot be reabsorbed from the bowel lumen
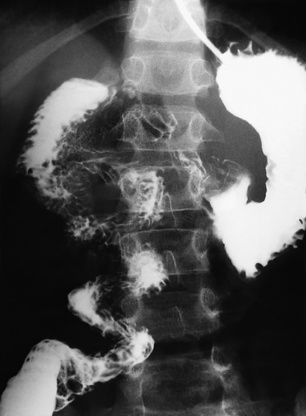
Upper GI study
 on a lateral view, the junction of the 2nd and 3rd parts of the duodenum is retroperitoneal
on a lateral view, the junction of the 2nd and 3rd parts of the duodenum is retroperitoneal
 the junction of the 2nd and 3rd parts of the duodenum turns sharply anterior
the junction of the 2nd and 3rd parts of the duodenum turns sharply anterior  the distal jejunal loops lie to the right of the midline
the distal jejunal loops lie to the right of the midline  the caecal pole may lie high and more to the left side
the caecal pole may lie high and more to the left side


 respiratory embarrassment following repair of the defect
respiratory embarrassment following repair of the defect  short bowel syndrome and intestinal dysmotility
short bowel syndrome and intestinal dysmotility  intestinal atresias and stenoses (secondary to the prenatal ischaemic insult)
intestinal atresias and stenoses (secondary to the prenatal ischaemic insult)
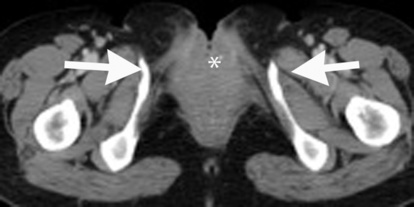
 the caecum opens onto the anterior abdominal wall between the two exstrophied hemi-bladders
the caecum opens onto the anterior abdominal wall between the two exstrophied hemi-bladders




 the bladder is thin walled, of a large capacity (without trabeculation), and has a wide neck
the bladder is thin walled, of a large capacity (without trabeculation), and has a wide neck  there may be a patent urachus or a urachal diverticulum
there may be a patent urachus or a urachal diverticulum  the posterior urethra is dilated proximally with typical conical narrowing (± dilatation of the anterior urethra)
the posterior urethra is dilated proximally with typical conical narrowing (± dilatation of the anterior urethra) vesico-ureteral reflux is seen in ⅔ of patients
vesico-ureteral reflux is seen in ⅔ of patients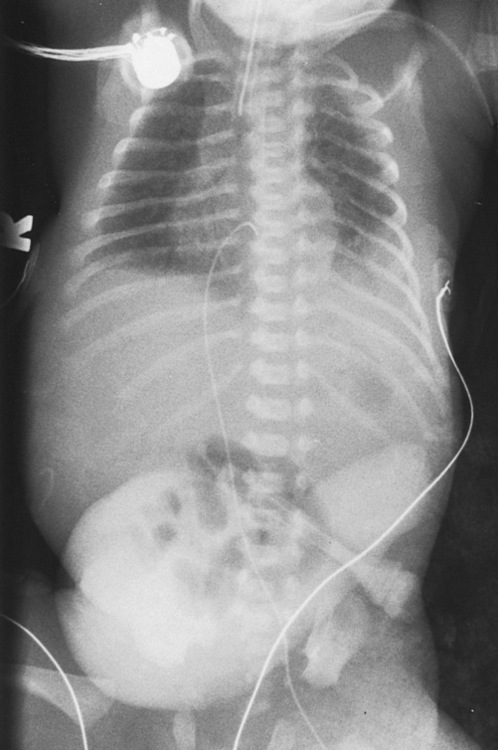


 occasionally a true atresia is present with a fibrous cord uniting the two blind ends
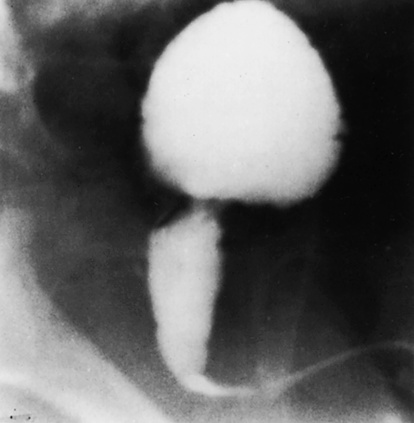
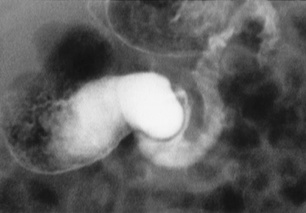
occasionally a true atresia is present with a fibrous cord uniting the two blind ends a large fetal gastric bubble
a large fetal gastric bubble in 80% of cases the level of obstruction is just distal to the ampulla of Vater
in 80% of cases the level of obstruction is just distal to the ampulla of Vater
 malrotation (20–30%)
malrotation (20–30%)  congenital heart disease (20%)
congenital heart disease (20%)  components of the VACTERL association may also be present
components of the VACTERL association may also be present maternal polyhydramnios
maternal polyhydramnios distal gas will be present if the obstruction is partial (or rarely if there is a bifid pancreatic duct straddling the atretic segment)
distal gas will be present if the obstruction is partial (or rarely if there is a bifid pancreatic duct straddling the atretic segment) a duodenal web may be seen as a thin, filling defect extending across the duodenal lumen
a duodenal web may be seen as a thin, filling defect extending across the duodenal lumen an atresia is more common than a stenosis
an atresia is more common than a stenosis  the proximal jejunum and distal ileum are the most frequently affected segments
the proximal jejunum and distal ileum are the most frequently affected segments abdominal distension is seen with more distal atresias
abdominal distension is seen with more distal atresias bubbles of distal gas are seen with a stenosis (cf. an atresia)
bubbles of distal gas are seen with a stenosis (cf. an atresia)  fine intraluminal calcifications may be seen with a more distal atresia
fine intraluminal calcifications may be seen with a more distal atresia  a meconium peritonitis (with calcification of the peritoneum) may be seen if an intrauterine perforation has occurred
a meconium peritonitis (with calcification of the peritoneum) may be seen if an intrauterine perforation has occurred
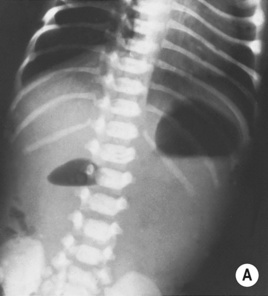


 the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) lies ventral or to left of the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) in about ⅔ of patients
the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) lies ventral or to left of the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) in about ⅔ of patients