• The pancreas develops in two parts from the endoderm of the primitive duodenum • Dorsal part: this is the first part to appear, initially appearing as a diverticulum from the dorsal wall of the duodenum • Ventral part: this develops more caudally and initially appears as a diverticulum from the developing bile duct – Before this occurs the dorsal duct (the duct of Santorini) opens into the duodenum proximal to the major papilla (the ampulla of Vater) – The ventral duct (the duct of Wirsung) opens into the major papilla with the CBD • British Society of Gastroenterology Guidelines: immediate CT is not indicated as the full extent of necrosis is only evident after 4 days (therefore the initial extent of necrosis may be underestimated) • Mild acute pancreatitis (70–80%) • Necrotizing acute pancreatitis (a hallmark of severe acute pancreatitis) • Interstitial edematous pancreatitis (IEP) • Acute necrotizing pancreatitis (sterile or infected) • Pancreatic and peripancreatic collections (sterile or infected) – Acute peripancreatic fluid collections (APFC):presents within 4 weeks and usually resorbed spontaneously without infection – Pseudocyst: after 4 weeks, an APFC may transition to a pseudocyst with a well-defined enhancing fibrous wall (containing no non-liquefied components)
Pancreas
CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES
EMBRYOLOGY
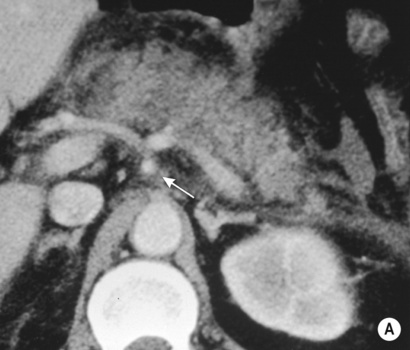
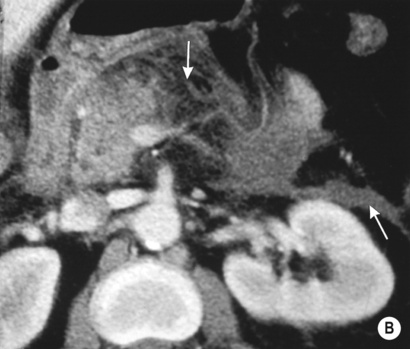
 it forms the neck, body and tail of the gland and part of the head
it forms the neck, body and tail of the gland and part of the head
 it forms the remaining part of the head and uncinate process
it forms the remaining part of the head and uncinate process
 The duodenum undergoes partial rotation and the 2 parts approximate each other and fuse
The duodenum undergoes partial rotation and the 2 parts approximate each other and fuse
 Usually fusion of the two ducts occurs at the junction of the head and body of the gland, with the ventral duct becoming the main excretory pancreatic duct (in >90% of cases)
Usually fusion of the two ducts occurs at the junction of the head and body of the gland, with the ventral duct becoming the main excretory pancreatic duct (in >90% of cases)
PANCREATITIS
ACUTE PANCREATITIS
Radiological features
 the contrast medium may also exacerbate any renal impairment
the contrast medium may also exacerbate any renal impairment
 An immediate CT should only be performed if the extent of necrosis dictates the management or if the diagnosis is unclear
An immediate CT should only be performed if the extent of necrosis dictates the management or if the diagnosis is unclear
 A follow-up CT is only required if there is a failure to improve or a clinical deterioration
A follow-up CT is only required if there is a failure to improve or a clinical deterioration
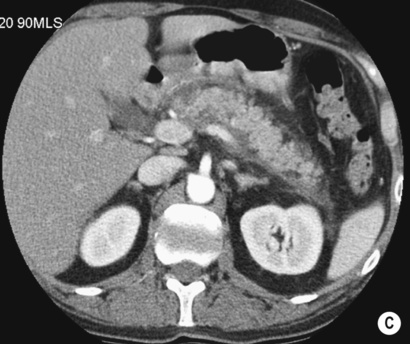
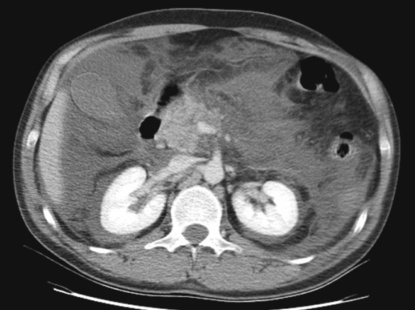
 A normal or enlarged gland of uniform enhancement (± peripancreatic fat stranding and thickening of the fascial planes)
A normal or enlarged gland of uniform enhancement (± peripancreatic fat stranding and thickening of the fascial planes)  cuffs of fluid may be seen around the adjacent vessels
cuffs of fluid may be seen around the adjacent vessels
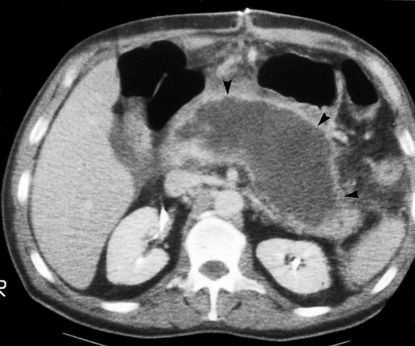
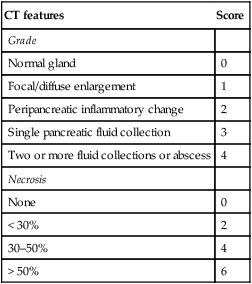
 There are non-enhancing pancreatic regions
There are non-enhancing pancreatic regions  if this involves > 30% of the gland the mortality rate approaches 30%
if this involves > 30% of the gland the mortality rate approaches 30%
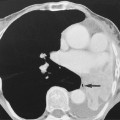
 Infected necrosis (20–70%): this is suggested if there are gas bubbles within any necrotic tissue (this can also be caused by a fistula to the GI tract)
Infected necrosis (20–70%): this is suggested if there are gas bubbles within any necrotic tissue (this can also be caused by a fistula to the GI tract)  it is a major determinant of morbidity and mortality
it is a major determinant of morbidity and mortality
Pearls
 Parenchymal necrosis alone – non-enhancing pancreatic areas
Parenchymal necrosis alone – non-enhancing pancreatic areas
 Peripancreatic necrosis alone – commonly within retroperitoneum/lesser sac
Peripancreatic necrosis alone – commonly within retroperitoneum/lesser sac
 no non-liquefied components
no non-liquefied components  usually adjacent to the pancreas
usually adjacent to the pancreas  no discernable wall
no discernable wall
 these rarely become infected
these rarely become infected
 IEP/AFPC/pseudocyst: usually self-limiting and spontaneously resolves
IEP/AFPC/pseudocyst: usually self-limiting and spontaneously resolves
 Necrotizing pancreatitis: if clinical status allows, supportive treatment for 2 weeks followed by surgical/radiological drainage as required
Necrotizing pancreatitis: if clinical status allows, supportive treatment for 2 weeks followed by surgical/radiological drainage as required
 Sterile pancreatic necrosis: CT monitoring every 7–10 days to exclude complication or infection
Sterile pancreatic necrosis: CT monitoring every 7–10 days to exclude complication or infection  percutaneous drainage and supportive measures as required
percutaneous drainage and supportive measures as required
 Infected pancreatic necrosis: percutaneous drainage/surgical debridement
Infected pancreatic necrosis: percutaneous drainage/surgical debridement

 it is the commonest congenital pancreatic anomaly
it is the commonest congenital pancreatic anomaly  it may result in functional stenosis and pancreatitis and there is an increased incidence of pancreatic malignancies
it may result in functional stenosis and pancreatitis and there is an increased incidence of pancreatic malignancies this is the 2nd most common congenital anomaly
this is the 2nd most common congenital anomaly oesophageal atresia
oesophageal atresia  tracheo-oesophageal fistula
tracheo-oesophageal fistula  Down’s syndrome
Down’s syndrome 85% of patients have severe exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and steatorrhoea
85% of patients have severe exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and steatorrhoea dystrophic calcification
dystrophic calcification  pancreatic cysts
pancreatic cysts serous cystic pancreatic neoplasms and pancreatic islet cell tumours may also occur
serous cystic pancreatic neoplasms and pancreatic islet cell tumours may also occur hepatic cysts may also occur and pancreatic cysts are seen in 10% of patients
hepatic cysts may also occur and pancreatic cysts are seen in 10% of patients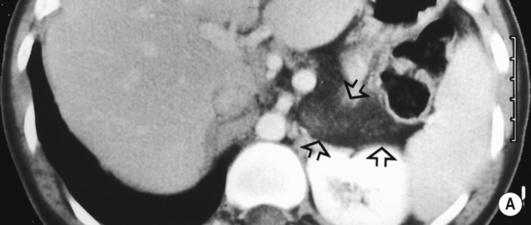
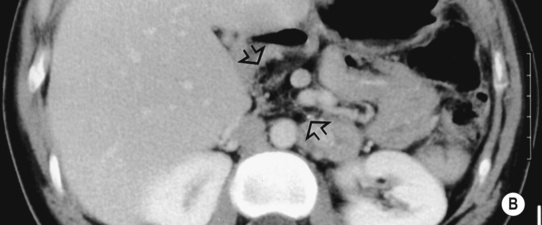
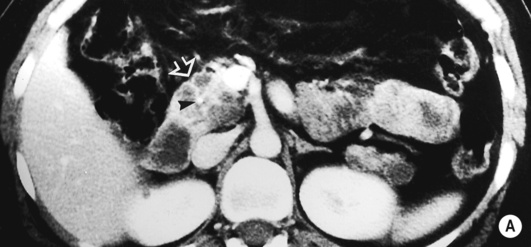
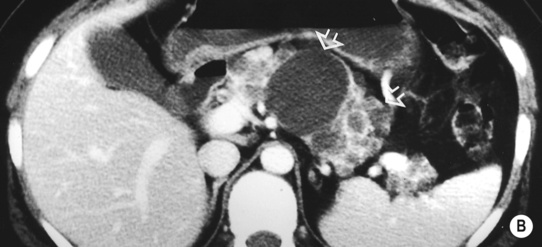
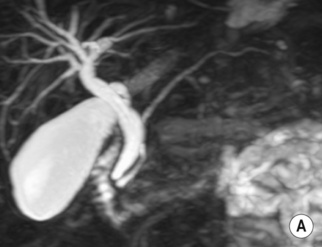
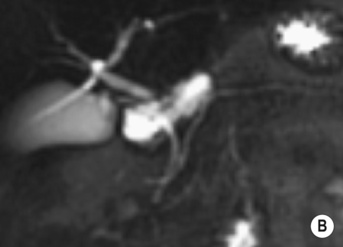
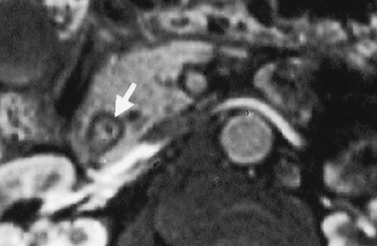
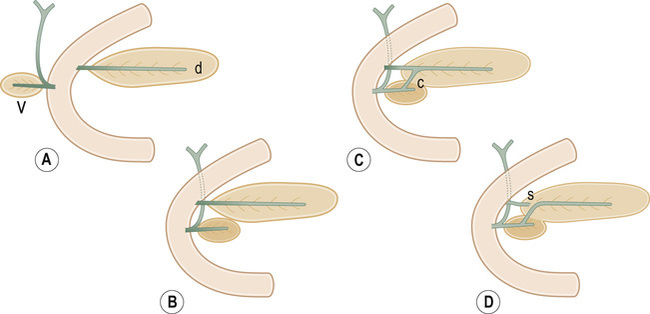
 it may be caused by the reflux of bile and pancreatic enzymes into the pancreatic parenchyma
it may be caused by the reflux of bile and pancreatic enzymes into the pancreatic parenchyma idiopathic (10–30% – possibly related to congenital duct anomalies such as pancreas divisum)
idiopathic (10–30% – possibly related to congenital duct anomalies such as pancreas divisum)  alcohol (20–25%)
alcohol (20–25%)  trauma
trauma  surgery
surgery  metabolic (hyperlipidaemia and hypercalcaemia)
metabolic (hyperlipidaemia and hypercalcaemia)  viral infection (mumps, cytomegalovirus and AIDS)
viral infection (mumps, cytomegalovirus and AIDS)  drugs (steroids and thiazide diuretics)
drugs (steroids and thiazide diuretics) nausea and vomiting
nausea and vomiting  raised serum amylase
raised serum amylase  signs of haemorrhagic pancreatitis:
signs of haemorrhagic pancreatitis: a gasless abdomen
a gasless abdomen  ascites
ascites  intrapancreatic gas bubbles
intrapancreatic gas bubbles ill-defined pancreatic margins
ill-defined pancreatic margins  peripancreatic fluid
peripancreatic fluid  hepatic steatosis (if there is an associated high alcohol intake)
hepatic steatosis (if there is an associated high alcohol intake)



 liquefaction within 2–6 weeks
liquefaction within 2–6 weeks  any collection replacing pancreatic tissue within 4 weeks is an ANC and not an APFC/pseudocyst
any collection replacing pancreatic tissue within 4 weeks is an ANC and not an APFC/pseudocyst