Radiological features of acromegaly Radiological features of Cushing’s syndrome Radiological features of hypopituitarism Radiological features of hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) Radiological features of hypothyroidism (cretinism and juvenile myxoedema) Radiological features of myxoedema Histological typing of primary bone tumours
Pearls in musculoskeletal imaging and pathology
PEARLS IN PATHOLOGY
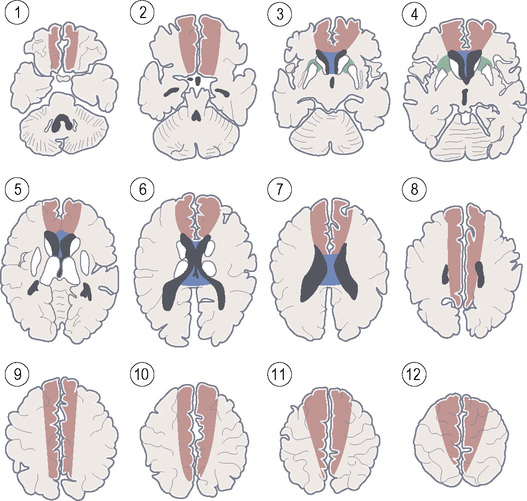
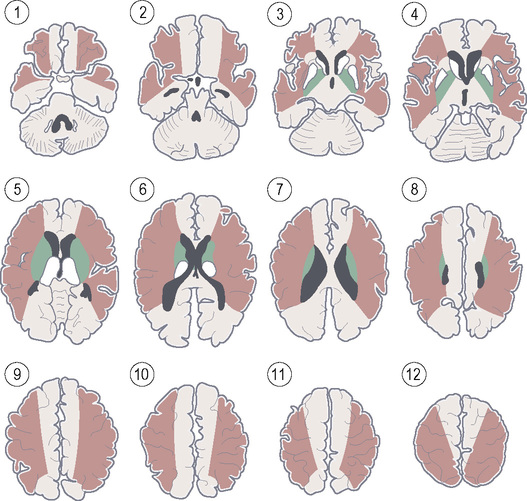
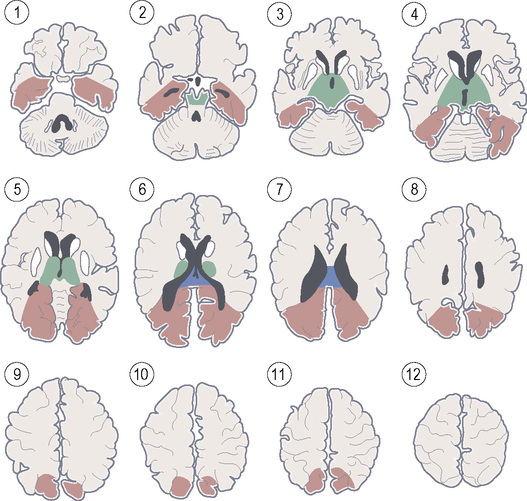
STROKE VASCULAR TERRITORIES
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES OF COMMON ENDOCRINOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
Skull
Vault thickened
Paranasal and mastoid air cells enlarged
Pituitary fossa enlarged
Floor of the fossa asymmetrical or ballooned
Mandible
Prognathism with increased angle
Spine
Kyphosis
Enlarged vertebral bodies
Posterior scalloping of vertebral bodies
Chest
Increased anteroposterior diameter
Ribs increased in calibre and length
Hands
General enlargement
Enlarged bases of phalanges and terminal tufts, spade-like
Enlarged muscle attachments
Feet
Thickening of ‘heel pad’: M > 23mm, F > 21.5mm
Long bones
Thickened by periosteal new bone formation
Joints
Widening of joint spaces due to thickened cartilage
Premature degeneration (OA) changes (shoulders, hips, knees)
Chondrocalcinosis
Soft tissues
Enlarged heart, kidneys, liver
Calcification of pinna of ears
Skull
Pituitary fossa usually normal
Skeleton
Osteoporosis
Vertebral collapse
Kyphosis
Concave vertebral margins
Wedged vertebral bodies
Rib fractures – multiple, painless with excess callus
Necrosis of femoral heads
Secondary osteoarthritis
Skull
Unfused sutures
Skeleton
Small but normal proportions (Lorain dwarf)
Slender bones
Small pituitary fossa
Unfused epiphyses
Skull
Exophthalmos
Skeleton
Osteopenia
Cortical striation – acropachy
In childhood, early appearance and accelerated growth of ossification centres
Heart
Cardiac enlargement
Cardiac failure
Thymus
Enlargement
Skull
Delayed closure of fontanelles
Relatively large sella
Poorly developed paranasal sinus
Usually brachycephalic
Dentition delayed: dental caries
Wormian bones
Skeleton
Dwarfism
Increased density
Ossification centres
Retarded growth
Multicentric and irregular
Bilateral and symmetrical
Epiphyses
Delayed fusion and appearance
Inhomogeneous epiphyses
Fine or coarse stippling
Fragmentation
Spine
Kyphosis
Flattening of bodies
Increase in width of intervertebral space
Bullet-shaped vertebral bodies, usually L1 and L2
Long bones
Short
Dense transverse bands at metaphyseal ends
Pelvis
Narrow with coxa vara
Heart
Enlargement
Body cavities
Pleural effusion
Ascites
Gastrointestinal tract
Abnormalities of oesophageal peristalsis
Decreased incidence of peristalsis
Constipation
‘Pseudo-obstruction’
PEARLS IN MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING
HISTOLOGICAL TYPING: BONE TUMOURS
Benign
Malignant
I. Bone-forming tumours
Osteoma
Osteoid osteoma
Osteoblastoma![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access