Achondroplasia |
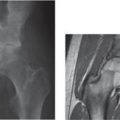
Champagne-glass appearance of the inner margins of the pelvis, squared iliac wings (elephant ears), short and narrow sciatic notch, flat acetabular roof, short and narrow sciatic notch, and flat acetabular roof. Large skull, canal stenosis at the foramen magnum, narrowing (rather than widening) of the interpediculate distance from upper to lower lumbar spine, short vertebral pedicles with spinal canal stenosis, scalloped vertebral bodies. |
Pseudoachondroplasia |
Poorly formed, irregular acetabulum and round ilium. Spinal, metaphyseal, and epiphyseal changes. |
Thanatophoric dysplasia |
Short and small iliac bones, horizontal acetabular roofs, small sacroiliac notches, bowed femurs (French telephone receiver), “H”-shaped appearance of vertebral bodies, very short ribs, small scapula. |
Campomelic dysplasia |
Narrow and tall iliac wings, incomplete ossification of pubis and ala of sacrum, narrow vertical ischia. Hip dislocation. |
Chromosome disorders (particularly 13 and 18) |
|
Achondrogenesis types I and II |
Poor osseous mineralization. Deformed and short iliac wings, absent ossification of pubis and sacrum. Often lethal. |
Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune syndrome) |
(see Table 5.3 ) |
Chondroectodermal dysplasia (Ellis-van Creveld syndrome) |
Flared hypoplastic iliac wing, horizontal acetabulum with medial and lateral spurs (trident pelvis), small sacroiliac notch. Short limbs, short ribs, postaxial polydactyly, and dysplastic nails and teeth. Sixty percent have congenital heart disease. Ninth carpal bone (after the age of 5 y). |
Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen dysplasia and Smith-McCort syndrome |
Lacy appearance of iliac crest, wide sacroiliac joints, small sacrosciatic notches, wide pubic symphysis, and ischiopubic synchondrosis. Smith-McCort syndrome similar to Dyggve-Melchior-Clausen dysplasia but without mental retardation. |
Metatropic dysplasia |
Flat irregular acetabular roof, short squared iliac wings, narrow sacrosciatic notches, and accessory ossification centers of the ischia. Tail (small appendage or cutaneous fold in coccygeal region). |
Short rib-polydactyly syndrome (types I and III) |
Small iliac bones and flattened acetabular roofs. Types range from lethal to more mild forms. Types II and IV have near normal pelvis. |
Barnes syndrome |
Small bell-shaped thorax, small iliac wings and pelvis, small sacroiliac notch. Laryngeal stenosis. |
Schneckenbecken dysplasia |
Snail-shaped ilia, flat acetabular roofs, handlebar clavicles, hypoplastic scapula, dumbbell-shaped very short long bones, wide fibula, and round vertebral bodies. |
Schwartz-Jampel syndrome |
Triangular deformity of the pelvis, flared iliac wings, femoral head dysplasia. |
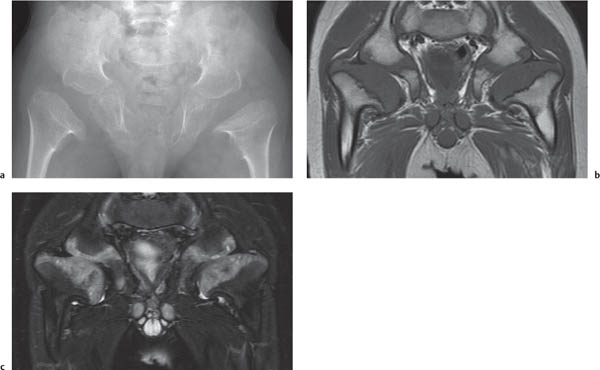
Kniest dysplasia
Fig. 5.23a–c |
Trefoil-shaped pelvis and coxa vara. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia associated with deafness or myopia. Large epiphyses at the knees, large flattened proximal femoral epiphyses with broad metaphyses. |