• Selective catheterization of the coeliac axis, superior mesenteric and inferior mesenteric arteries is required • Direct sign of haemorrhage: contrast medium extravasation into the bowel lumen (this may not be visible if the bleeding is intermittent or too slow) • Indirect signs of haemorrhage: the presence of a pseudoaneurysm • Angiodysplasia: a focal area of increased vasularity with dilated arterioles and an early prominent draining vein • Diverticulitis: bleeding is often venous and difficult to demonstrate • Meckel’s diverticulum: a feeding vitelline artery extending beyond the mesenteric border and with no side branches (ending in a corkscrew appearance) • A reduction in the luminal diameter of the internal or common carotid artery – this is determined by the ratio of the luminal diameter at the point of the maximal stenosis to the luminal diameter in an adjacent normal internal carotid arterial segment • The carotid bifurcation is the commonest extracranial vessel location for atheroma deposition: >90% of carotid artery stenoses are found at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery or within the proximal internal carotid artery • An internal carotid arterial stenosis > 50% is an important cause of an ischaemic stroke or a transient ischaemic attack (TIA) • Patients with a symptomatic carotid stenosis are at higher risk of developing further ischaemic cerebral events than with an asymptomatic stenosis – the risk of developing a cerebral infarction after an ischaemic neurological event is highest within the first 6 months • The external carotid artery can be distinguished from the internal carotid artery by the following: • A 50% diameter reduction is equivalent to a 75% cross-sectional area reduction • Flow through a stenosis is first accelerated, and only decreases when the lumen is severely narrowed • Distal to a stenosis, the waveform broadens with a loss in amplitude and eventually pulsatility • CT: calcified plaque will exaggerate any stenosis on a MIP • TOF MRA: this is a flow-sensitive technique prone to artefactual signal loss due to changes in vessel orientation and high-grade stenoses • CEMRA: this can use 2D time-of-flight sequences or 3D sequences with gadolinium • An arch aortogram is performed first – there is less chance of producing distal embolic complications than with a selective carotid angiography (a selective carotid angiography is associated with a 1% risk of a stroke) • Vessel narrowing can be underestimated if a plaque is partially obscured on frames acquired when there is maximal contrast density • Irregularity due to atheroma must be distinguished from catheter-induced spasm, fibromuscular dysplasia and spontaneous or iatrogenic dissection • The standard non-medical treatment is a surgical carotid endarterectomy • All methods show a benefit if there is a 70–99% stenosis US evaluation of an internal carotid arterial stenosis
Peripheral vascular disease
GASTROINTESTINAL VASCULAR DISORDERS
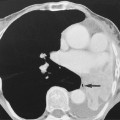
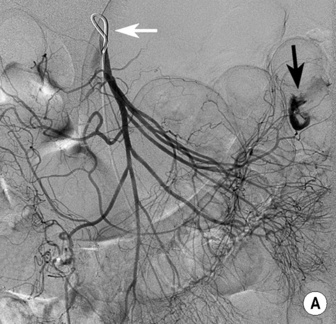
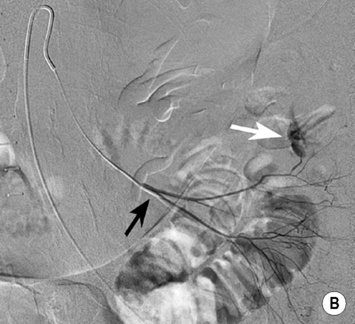
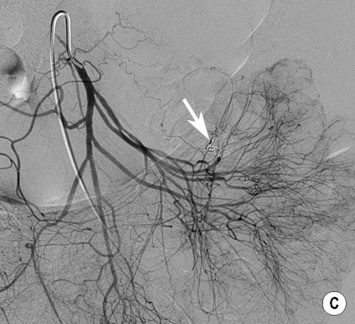
MESENTERIC HAEMORRHAGE
DSA
 early venous return
early venous return  vascular lakes or tumour circulation
vascular lakes or tumour circulation  vessel wall irregularity
vessel wall irregularity
CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS
CAROTID ARTERY STENOSIS
DEFINITION
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
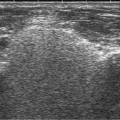
Doppler US
 It is usually more anterior than the internal carotid artery
It is usually more anterior than the internal carotid artery
 It has visible branches (the internal carotid artery does not have any branches within the cervical region)
It has visible branches (the internal carotid artery does not have any branches within the cervical region)
 It has less diastolic flow than the internal carotid artery
It has less diastolic flow than the internal carotid artery
 Tapping the superficial temporal artery as it passes over the zygoma induces fluctuations in the waveform of the external carotid artery (but not the internal carotid artery)
Tapping the superficial temporal artery as it passes over the zygoma induces fluctuations in the waveform of the external carotid artery (but not the internal carotid artery)
 it may be difficult to distinguish a critical stenosis (with very slow distal flow) from a total occlusion
it may be difficult to distinguish a critical stenosis (with very slow distal flow) from a total occlusion
CTA/MRA
 it has been superseded by contrast-enhanced MRA (CEMRA)
it has been superseded by contrast-enhanced MRA (CEMRA)
 it may have a tendency to exaggerate the degree of carotid stenosis
it may have a tendency to exaggerate the degree of carotid stenosis
DSA
PEARLS
Endovascular treatment of a carotid arterial stenosis
 carotid angioplasty and stenting is increasingly used
carotid angioplasty and stenting is increasingly used
 Unlike angioplasty at other sites, this requires predilatation to avoid any arterial wall trauma and subsequent embolization of material on stent advancement (cerebral protection devices are also usually used to catch any released embolic debris)
Unlike angioplasty at other sites, this requires predilatation to avoid any arterial wall trauma and subsequent embolization of material on stent advancement (cerebral protection devices are also usually used to catch any released embolic debris)
Lesion severity
PSV (cm/s)
EDV (cm/s)
Ratio of the internal carotid PSV to the middle/distal common carotid PSV
≥ 50%
150
60
2.5
≥ 60%
175
70
2.75
≥ 70%
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 pancreatitis
pancreatitis  gastro-oesophageal varices
gastro-oesophageal varices  as a complication of endoscopic, surgical, or percutaneous biliary procedures
as a complication of endoscopic, surgical, or percutaneous biliary procedures diverticular disease
diverticular disease  neoplasms
neoplasms  haemorrhoids
haemorrhoids it is performed if an endoscopy is negative or if it is not possible to control the site of haemorrhage
it is performed if an endoscopy is negative or if it is not possible to control the site of haemorrhage precise identification of a bleeding site is required to avoid ischaemia or infarction
precise identification of a bleeding site is required to avoid ischaemia or infarction however it cannot precisely localize a bleeding site
however it cannot precisely localize a bleeding site it can detect bleeding rates as low as 0.3ml/min
it can detect bleeding rates as low as 0.3ml/min  an unenhanced CT scan is first performed followed by CT imaging in the arterial and portal venous phase
an unenhanced CT scan is first performed followed by CT imaging in the arterial and portal venous phase  high attenuation material within the bowel lumen at CTA not present on the unenhanced CT is diagnostic for acute GI haemorrhage
high attenuation material within the bowel lumen at CTA not present on the unenhanced CT is diagnostic for acute GI haemorrhage
 embolization
embolization  dissection
dissection  vasculitis
vasculitis thrombolysis is an option if the bowel remains viable
thrombolysis is an option if the bowel remains viable clinical symptoms are rare due to an excellent mesenteric collateral vessel supply (at least two of the three mesenteric arteries must be significantly stenosed for symptoms to occur)
clinical symptoms are rare due to an excellent mesenteric collateral vessel supply (at least two of the three mesenteric arteries must be significantly stenosed for symptoms to occur)  it can present with postprandial abdominal pain and weight loss
it can present with postprandial abdominal pain and weight loss
 stenting of more than one vessel improves the long-term outcome and may reduce the restenosis rate
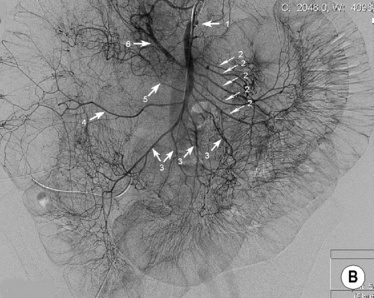
stenting of more than one vessel improves the long-term outcome and may reduce the restenosis rate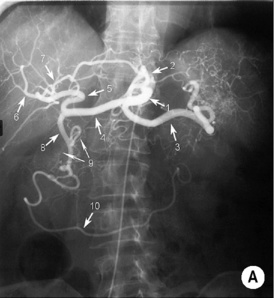
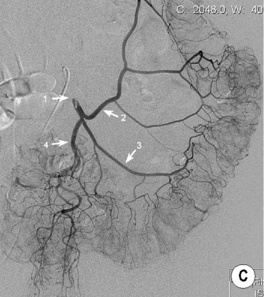
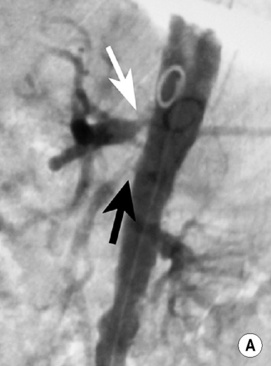
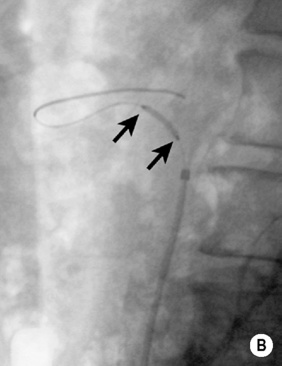
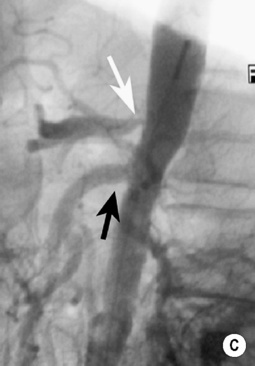
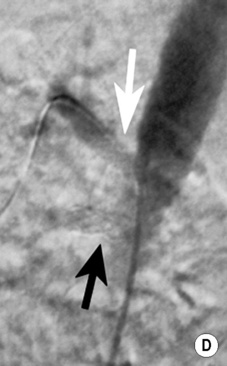
 it is occasionally used as a problem-solving tool if the non-invasive methods are discordant
it is occasionally used as a problem-solving tool if the non-invasive methods are discordant