• >100ml of free fluid within the peritoneal cavity due to benign or malignant causes • Sequence of peritoneal fluid movement: it initially collects around the liver • This occurs either as a result of torsion or from a spontaneous venous thrombosis The majority of peritoneal neoplasms are malignant, and usually secondary to: • Intraperitoneal seeding (peritoneal carcinomatosis) CT Sensitivity is reduced for tumour implants < 1cm in diameter – Smooth nodular (or plaque-like) thickening and contrast enhancement of the parietal peritoneal surfaces of the diaphragm, liver and spleen (this can also be seen with tuberculosis, peritoneal mesothelioma and peritoneal lymphomatosis) – Nodular tumour implants on the undersurface of the right diaphragm can indent the liver surface (mimicking capsular or subcapsular liver metastases) – Ascites is not always present – if it is present it is often loculated and septated (and therefore absent from any dependent areas) • Lymphatic or embolic haematogenous spread *Early peritoneal invasion is manifested as linear strands in the fat adjacent to the primary tumour – Tumors metastasizing to the omentum are similar to those responsible for peritoneal carcinomatosis (and usually an ovarian primary) – Metastatic disease may involve the greater omentum by direct spread along the transverse mesocolon, gastrosplenic or gastrocolic ligaments (as well as by peritoneal or haematogenous spread)
Peritoneum, mesentery and omentum
BENIGN DISEASES
ASCITES
DEFINITION
 it then flows to the pouch of Douglas
it then flows to the pouch of Douglas  it then flows symmetrically to both lateral paravesical spaces
it then flows symmetrically to both lateral paravesical spaces  it finally ascends both paracolic gutters (due to negative intra-abdominal pressures during respiration)
it finally ascends both paracolic gutters (due to negative intra-abdominal pressures during respiration)
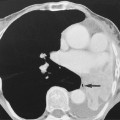
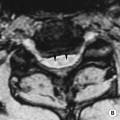
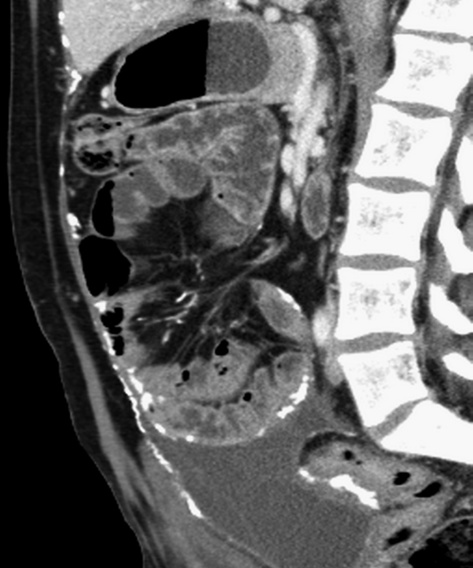
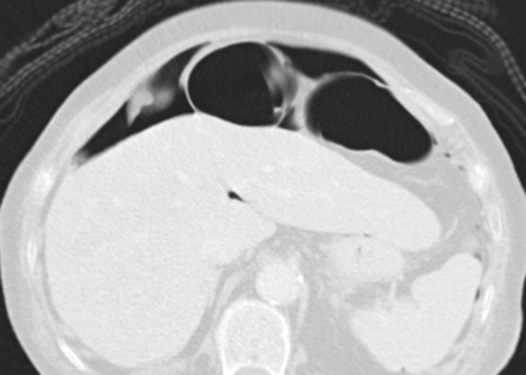
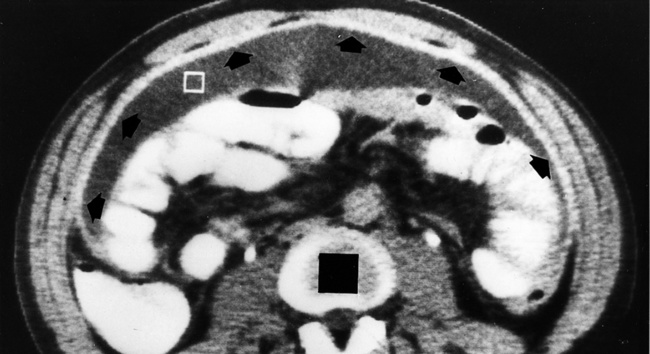
INFARCTION OF OMENTUM OR EPIPLOIC APPENDAGE (EPIPLOIC APPENDAGITIS)
DEFINITION
 it is a benign, self-limiting condition presenting with acute abdominal pain
it is a benign, self-limiting condition presenting with acute abdominal pain
NEOPLASTIC PERITONEAL/OMENTAL DISORDERS
NEOPLASTIC PERITONEAL DISORDERS
 Definition: malignant tumour seeding of the peritoneum
Definition: malignant tumour seeding of the peritoneum
 Anywhere where ascites pools will favour malignant growth, therefore the most common seeding sites are: the pouch of Douglas
Anywhere where ascites pools will favour malignant growth, therefore the most common seeding sites are: the pouch of Douglas  the distal small bowel mesentery (near the ileocaecal junction)
the distal small bowel mesentery (near the ileocaecal junction)  the sigmoid mesocolon
the sigmoid mesocolon  the greater omentum
the greater omentum  the right paracolic gutter
the right paracolic gutter
 Calcified peritoneal implants seen pre-chemotherapy suggests that the primary site is usually a serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary (or rarely a gastric carcinoma)
Calcified peritoneal implants seen pre-chemotherapy suggests that the primary site is usually a serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary (or rarely a gastric carcinoma)
 Pseudomyxoma peritonei: this follows rupture of a mucinous cystadenocarcinoma or cystadenoma of the ovary or appendix
Pseudomyxoma peritonei: this follows rupture of a mucinous cystadenocarcinoma or cystadenoma of the ovary or appendix  ascites (with septations representing mucinous nodules) and scalloping of the liver edge can be seen
ascites (with septations representing mucinous nodules) and scalloping of the liver edge can be seen
Primary malignancy
Organ directly invaded
Route of invasion*
Stomach
Spleen
Gastrosplenic ligament
Superior margin of the transverse colon
Gastrocolic ligament
Pancreas
Liver
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Inferior margin of the transverse colon
Transverse mesocolon
Spleen
Splenorenal ligament
Ovary
Diffuse spread through all adjacent peritoneal surfaces

NEOPLASTIC OMENTAL DISORDERS
Definition
 These are more common than a primary neoplasm
These are more common than a primary neoplasm


 it appears as a cystic lesion with mass effect
it appears as a cystic lesion with mass effect free air is most commonly seen anterior to the liver (if the patient is supine)
free air is most commonly seen anterior to the liver (if the patient is supine) gas within a loculated fluid collection is not pathognomonic for an abscess (a necrotic non-infected tumour or mass communicating with the bowel may contain air)
gas within a loculated fluid collection is not pathognomonic for an abscess (a necrotic non-infected tumour or mass communicating with the bowel may contain air) peritoneal (± mesenteric) thickening
peritoneal (± mesenteric) thickening thickening and nodularity of the peritoneal surfaces
thickening and nodularity of the peritoneal surfaces  enlarged low attenuation lymph nodes
enlarged low attenuation lymph nodes sclerosing peritonitis may develop in a minority
sclerosing peritonitis may develop in a minority peritoneal calcification
peritoneal calcification  loculated fluid collections
loculated fluid collections  small bowel tethering
small bowel tethering
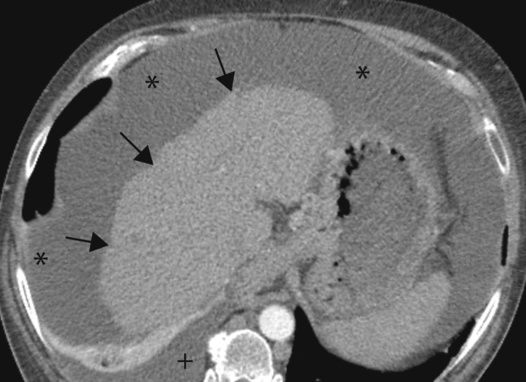
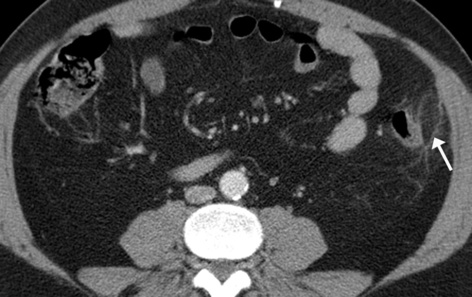
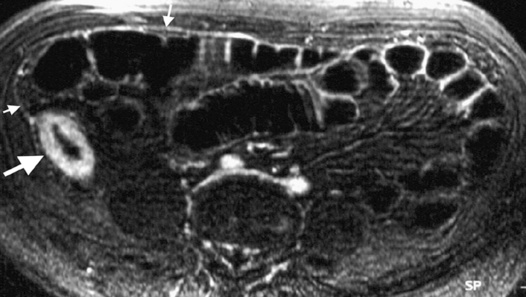

 they may demonstrate enhancement
they may demonstrate enhancement