Plantar Fasciitis and Fibromatosis
KEY FACTS
Terminology
Imaging
 Thickened plantar fascial insertion, especially at medial aspect of calcaneum
Thickened plantar fascial insertion, especially at medial aspect of calcaneum
 Plantar fascia thickness > 4.5 mm (most useful sign)
Plantar fascia thickness > 4.5 mm (most useful sign)
 ± hypoechogenicity of plantar fascia
± hypoechogenicity of plantar fascia
 ± decreased fascial definition
± decreased fascial definition
 ± perifascial edema
± perifascial edema
 ± edema, disruption, and atrophy of heel fat pad
± edema, disruption, and atrophy of heel fat pad
 Spur is located deep to (and not within) fascia
Spur is located deep to (and not within) fascia
 Bilateral in 1/3
Bilateral in 1/3
 Subclinical disease on opposite side is not uncommon so do not use opposite side as internal normal reference
Subclinical disease on opposite side is not uncommon so do not use opposite side as internal normal reference
 Discrete fusiform-shaped nodule of plantar fascia separated from calcaneal insertion
Discrete fusiform-shaped nodule of plantar fascia separated from calcaneal insertion
 Hypoechoic (75%) or isoechoic (25%) to plantar fascia
Hypoechoic (75%) or isoechoic (25%) to plantar fascia
 Posterior acoustic enhancement (40%) or shadowing (20%)
Posterior acoustic enhancement (40%) or shadowing (20%)
 Intrinsic vascularity (10%)
Intrinsic vascularity (10%)
 Majority are located within central or medial bands of plantar fascia
Majority are located within central or medial bands of plantar fascia
 Bilateral in 1/3 and multiple on symptomatic side in 1/4
Bilateral in 1/3 and multiple on symptomatic side in 1/4
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Definitions
IMAGING
General Features
Ultrasonographic Findings
 Discrete fusiform-shaped nodule of plantar fascia separated from calcaneal insertion
Discrete fusiform-shaped nodule of plantar fascia separated from calcaneal insertion
 Hypoechoic (75%) or isoechoic (25%) to plantar fascia
Hypoechoic (75%) or isoechoic (25%) to plantar fascia
 Posterior acoustic enhancement (40%) or shadowing (20%)
Posterior acoustic enhancement (40%) or shadowing (20%)
 Intrinsic vascularity (5%)
Intrinsic vascularity (5%)
 Majority are located within midsubstance or superficial aspect of plantar fascia
Majority are located within midsubstance or superficial aspect of plantar fascia
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






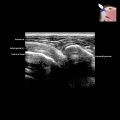
 . The thickness (3.7 mm) of the plantar fascia is measured at the leading edge of the calcaneum
. The thickness (3.7 mm) of the plantar fascia is measured at the leading edge of the calcaneum  . The normal thickness is < 4.3 mm.
. The normal thickness is < 4.3 mm.
 at the attachment to the medial calcaneal tuberosity
at the attachment to the medial calcaneal tuberosity  . This is consistent with moderate-severity plantar fasciitis.
. This is consistent with moderate-severity plantar fasciitis.
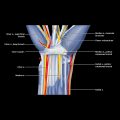
 at the midfoot level. The flexor digitorum brevis muscle
at the midfoot level. The flexor digitorum brevis muscle  is attached to the deep surface of the plantar fascia. The subcutaneous fat of the sole
is attached to the deep surface of the plantar fascia. The subcutaneous fat of the sole  is superficial.
is superficial.
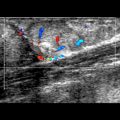
 within the cental band of the plantar fascia
within the cental band of the plantar fascia  at the midfoot region. Moderate posterior enhancement
at the midfoot region. Moderate posterior enhancement  is present. Additional plantar fibroma was present elsewhere in the feet.
is present. Additional plantar fibroma was present elsewhere in the feet.