Presentation and Presenting Images
A 42-year-old female presents for screening mammography.
62.2 Key Images
62.2.1 Breast Tissue Density
The breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses.
62.2.2 Imaging Findings
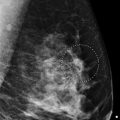
The patient had a conventional digital screening mammogram. In the lower inner quadrant of the left breast, there is a possible focal asymmetry ( ▶ Fig. 62.3 and ▶ Fig. 62.4).
62.3 BI-RADS Classification and Action
Category 0: Mammography: Incomplete. Need additional imaging evaluation and/or prior mammograms for comparison.
62.4 Diagnostic Images
( ▶ Fig. 62.5, ▶ Fig. 62.6, ▶ Fig. 62.7)
62.4.1 Imaging Findings
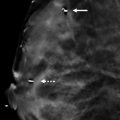
The diagnostic imaging demonstrates a possible persistent asymmetry on the craniocaudal (CC) spot-compression mammogram ( ▶ Fig. 62.5). The mediolateral oblique (MLO) spot-compression ( ▶ Fig. 62.6) and medioateral (ML) mammograms ( ▶ Fig. 62.7) are less suggestive of a true asymmetry. The corresponding CC and MLO digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) movies demonstrate that the focal asymmetry seen on screening mammography is a summation artifact created by overlapping tissues in the same imaging plane.
62.5 BI-RADS Classification and Action
Category 1: Negative
62.6 Differential Diagnosis
Summation artifact (superimposition of breast tissue): The DBT movies obtained at the diagnostic evaluation best demonstrated that this asymmetry is created by overlapping tissue.
Radial scar: Subtle asymmetries can represent a radial scar. The DBT images did not support any underlying architectural distortion or other suspicious findings.
Carcinoma: Carcinomas can initially present as subtle findings, especially lobular carcinoma. It is reassuring that the DBT images revealed overlapping tissue.
62.7 Essential Facts
Many screening mammograms are recalled for summation artifacts.
DBT is designed to reduce the summation effects of overlapping tissues and improve lesion conspicuity.
DBT makes suspicious findings more apparent and helps the reader to recognize normal structures more clearly.
In DBT the reconstruction of the three-dimensional breast image into slices helps to uncover those areas of overlapping tissue.
62.8 Management and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Principles
DBT has demonstrated a reduction in recall rate from 7 to 15% in clinical studies.
Improvements in sensitivity and specificity are seen on DBT irrespective of breast tissue density.
DBT is approved for screening and diagnostic mammography imaging. The role in breast imaging is evolving.
Drawbacks to DBT are the increased radiation for combination exams (FFDM and DBT) and the increased time for reading a study (reported as twice the time).
DBT produces extremely large data files that require extra PACS (picture archiving and communication system) storage capacity.
62.9 Further Reading
[1] Brandt KR, Craig DA, Hoskins TL, et al. Can digital breast tomosynthesis replace conventional diagnostic mammography views for screening recalls without calcifications? A comparison study in a simulated clinical setting. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200(2): 291‐298 PubMed

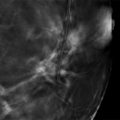
Fig. 62.1 Left craniocaudal (LCC) mammogram.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree