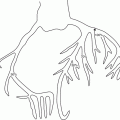
Fig. 2.1
Electrocardiogram
28.
Optimizing selection of patients with heart failure whose symptoms and natural history may improve after revascularization is the goal of performing:
A.
Coronary angiography
B.
Stress echocardiography
C.
Stress MPI study
D.
Viability study
29.
All of the following statements correctly describe findings from a direct comparison of SPECT MPI with PET MPI EXCEPT:
A.
PET has shown significantly improved normalcy rate
B.
PET has shown significantly improved sensitivity
C.
SPECT has shown a superior diagnostic performance when subanalyzed for gender
D.
SPECT ability to identify multivessel ischemia was significantly lower
30.
The exercise stress test should be stopped if:
A.
There are technical difficulties in monitoring systolic blood pressure
B.
1 mm of ST depression is present
C.
Arterial blood pressure is 200/110
D.
Systolic blood pressure drops by 15 mmHg
31.
The counts distribution of all short‐axis slices displayed in concentric rings is called:
A.
A bull’s eye
B.
A counts profile
C.
A planogram
D.
A sinogram
32.
During equilibrium gated radionuclide angiography (ERNA), images are acquired after the administered radioactivity has equilibrated in the:
A.
Endocardium
B.
Lymphatic space
C.
Myocardium
D.
Vascular space
33.
The term incremental value of SPECT MPI implies that perfusion imaging data provide information on the natural history, risk, and outcomes that are:
A.
Additive to information from more available or less expensive tests
B.
More valuable than information from more available or less expensive tests
C.
Contradictive to information from more available or less expensive tests
D.
Less valuable than information from more available or less expensive tests
34.
A strontium Sr-82 generator can be used for up to:
A.
1 week
B.
1 month
C.
6 months
D.
1 year
35.
Peak exercise in normal individuals produces an increase in myocardial oxygen demand and ………………………… increase in myocardial blood flow:
A.
A twofold
B.
A twofold to threefold
C.
A threefold to fourfold
D.
A fourfold to fivefold
36.
Which of the following exercise protocols is most frequently used to assess cardiovascular reserve?
A.
Dynamic exercise
B.
Isometric exercise
C.
Resistive exercise
D.
Static exercise
37.
Patients scheduled for a pharmacological stress test with Lexiscan should be instructed to avoid consumption of any products containing methylxanthines for at least:
A.
3 h
B.
6 h
C.
12 h
D.
24 h
38.
The proportion of tracer removed from the blood as it passes through the myocardium is called:
A.
First-pass extraction fraction
B.
Ejection fraction
C.
Coronary flow reserve
D.
Myocardial blood flow
39.
Gated single photon emission computed tomography (GSPECT) is not suitable for accurate right ventricular function measurement because the RV:
A.
Is not visualized
B.
Is not adequately visualized
C.
Is attenuated by the liver
D.
Is attenuated by the spleen
40.
The room temperature of the treadmill stress testing area should be between:
A.
55° and 63° F
B.
64° and 72° F
C.
73° and 80° F
D.
80° and 85° F
41.
Thallium washes out of the myocardium at a rate dependent on:
A.
Injected dose
B.
Local myocardial perfusion
C.
Local ejection fraction
D.
Blood pressure
42.
During a typical stress Tc-99m tetrofosmin study, imaging begins:
A.
5 min after the exercise stress injection and 10–15 min after the pharmacological stress injection
B.
5 min after the exercise stress injection and 20–30 min after the pharmacological stress injection
C.
10 min after the exercise stress injection and 20–30 min after the pharmacological stress injection
D.
10 min after the exercise stress injection and 30–45 min after the pharmacological stress injection
43.
All of the following approaches have been used in high-speed SPECT technology EXCEPT:
A.
Novel image reconstruction algorithm
B.
Slip ring technology
C.
Solid-state detector columns with cadmium zinc telluride
D.
Wide-angle tungsten collimators
44.
Which of the following protocols stimulating maximal F-18 FDG uptake is based on the simultaneous infusion of insulin and glucose?
A.
Euglycemic hypoinsulinemic clamp protocol
B.
Euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp protocol
C.
Hypoglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp protocol
D.
Hypoglycemic hypoinsulinemic clamp protocol
45.
Viable myocardial tissue is NOT present in:
A.
Infarcted myocardium
B.
Ischemic myocardium
C.
Stunned myocardium
D.
Hibernating myocardium
46.
Visual comparison of MPI stress and rest displays revealing a perfusion defect that is seen on stress but not on rest images describes:
A.
Normal myocardium
B.
Ischemic myocardium
C.
Scarred myocardium
D.
Stunned myocardium
47.
Lexiscan (regadenoson) is contraindicated in patients with:
A.
Asthma
B.
Hypovolemia
C.
Pericarditis
D.
Sinus node dysfunction
48.
The areas of ECG electrode application are rubbed with an alcohol-saturated pad to remove from the skin:
A.
Bacteria
B.
Hair
C.
Oil
D.
Sweat
49.
Tl-201 emits 80 keV of photon energy and has a physical half-life of:
A.
53 h
B.
63 h
C.
73 h
D.
83 h
50.
The Bruce protocol begins with:
A.
A treadmill speed of 1.7 mph and a grade of 0°
B.
A treadmill speed of 1.7 mph and a grade of 10°
C.
A treadmill speed of 3.4 mph and a grade of 0°
D.
A treadmill speed of 3.4 mph and a grade of 10°
51.
Tl-201 compared with the 99mTc-based agents:
A.
Offers improved performance in patients with large breasts
B.
Offers improved performance in obese patients
C.
Delivers a higher radiation dose
D.
Allows the option of higher quality gated images
52.
During a GSPECT acquisition, one cardiac cycle is represented by the:
A.
P–Q interval
B.
P–R interval
C.
R–R interval
D.
R–T interval
53.
All of the following are examples of MPI automated quantitative analysis systems incorporated into SPECT camera-computer equipment EXCEPT:
A.
Cedars QPS
B.
4D-MSPECT
C.
McKesson Practice Choice Software
D.
Emory Toolbox
54.
Which of the following are the physical characteristics of the positron emitted by Rb-82?
A.
Energy of 511 keV and average range of 2.8 mm
B.
Energy of 3.15 MeV and average range of 2.8 mm
C.
Energy of 3.15 MeV and average range of 0.22 mm
D.
Energy of 511 keV and average range of 0.22 mm
55.
The typical ejection fraction (EF) of the left ventricle is approximately:
A.
100 %
B.
87 %
C.
58 %
D.
29 %
56.
During the exercise stress test, the heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG should be recorded (select three):
A.
At the beginning of each stage of exercise
B.
At the onset of an ischemic response
C.
Immediately after stopping exercise
D.
Every minute in the stage 3
E.
In the middle of each stage of exercise
F.
The end of each stage of exercise
57.
An adenosine injection is contraindicated in individuals with:
A.
Atrial fibrillation
B.
Bigeminy
C.
Pacemaker
D.
Third-degree AV block
58.
All of the following diagnostic procedures are available on PET-CT scanners equipped with multislice CT EXCEPT:
A.
Coronary calcium measurement
B.
Coronary angiography
C.
Doppler echocardiography
D.
PET viability study
59.
Gated single photon emission computed tomography (GSPECT) acquisition starts with the R wave on the ECG which corresponds to the:
A.
End-diastole
B.
End-systole
C.
Mid-diastole
D.
Mid-systole
60.
The number of correct findings on a MPI test, regardless of whether the patient has CAD, describes the diagnostic test:
A.
Accuracy
B.
Reproducibility
C.
Sensitivity
D.
Specificity
61.
Which of the following patients are the best candidates for gated SPECT studies?
A.
Patients with atrial fibrillation
B.
Patients with premature atrial contractions
C.
Patients with premature ventricular contractions
D.
Patients with sinus rhythm
62.
Which of the following statements correctly describe properties of Tc-99m versus Tl-201 as radionuclide tracers for myocardial imaging?
A.
Tc-99m has a higher emission energy and a longer half-life than Tl-201
B.
Tc-99m has a higher emission energy and a shorter half-life than Tl-201
C.
Tc-99m has a lower emission energy and a longer half-life than Tl-201
D.
Tc-99m has a lower emission energy and a shorter half-life than Tl-201
63.
Which of the following factors/conditions can be a reason of a false positive MPI study?
A.
Balanced ischemia
B.
Suboptimal level of exercise
C.
Left bundle branch block
D.
Patient on nitrates
64.
The most frequently used clinical myocardial perfusion PET agent is:
A.
F-18 FDG
B.
Rb-82
C.
Tc 99 m-sestamibi
D.
Tl-201
65.
Myocardial oxygen consumption (MVO2) is measured in the units of:
A.
ml O2/min per kg
B.
ml O2/min per 100 g
C.
ml O2/h per 100 g
D.
lO2/min per 100 g
66.
Tl-201, when compared with technetium 99 m-based myocardial imaging:
A.
Creates less soft tissue attenuation
B.
Produces improved image quality
C.
Produces improved image contrast
D.
Creates less liver and gut activity
67.
The most common adverse reaction associated with adenosine administration is/are:
A.
Arrhythmias
B.
Flushing
C.
Hypotension
D.
Paresthesias
68.
Heparin and warfarin are:
A.
Antibiotics
B.
Anticoagulants
C.
Antiemetics
D.
Antipyretics
69.
The major vasodilators used for pharmacologic radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging (rMPI) are (select three):
A.
Adenosine
B.
Aggrenox
C.
Atropine
D.
Dipyridamole
E.
Regadenoson
70.
Which of the following is absolute contraindication for exercise stress testing?
A.
Acute pulmonary embolism
B.
Left main coronary artery stenosis
C.
Physical impairment
D.
Significant tachyarrhythmias
71.
MPI has the greatest diagnostic value for detection of CAD when it is used in patients with:
A.
A very low pretest likelihood of disease
B.
A low pretest likelihood of disease
C.
A moderate pretest likelihood of disease
D.
A high pretest likelihood of disease
72.
Tomographic reconstruction theory can be described as:
A.
A 3-dimensional image volume reconstituted from a series of 2-dimensional images
B.
A 3-dimensional image volume reconstituted from a series of 3-dimensional images
C.
A 2-dimensional image volume reconstituted from a series of 2-dimensional images
D.
A 2-dimensional image volume reconstituted from a series of 3-dimensional images
73.
Upward creep of the heart observed during SPECT acquisition could be prevented by:
A.
Acquiring gated images
B.
Adjusting patient stress dose
C.
Allowing bed rest before SPECT
D.
Adjusting patient rest dose
74.
Beta (+) decay of a nucleus results in emission of a/an:
A.
Electron
B.
Neutron
C.
Positron
D.
Proton
75.
Which of the following belongs to the left cardiovascular system (select three)?
A.
The left side of the heart
B.
The pulmonary arteries
C.
The pulmonary veins
D.
The right side of the heart
E.
The systemic arterial system
F.
The venous system
76.
Medications such as calcium channel blocking drugs and beta-blockers administered on the day of exercise stress MPI may alter:
A.
The heart rate
B.
The respiration rate
C.
The body temperature
D.
The basic metabolic rate
77.
Tomographic reconstruction of projection images produces transaxial images which are:
A.
Perpendicular to the long axis of the patient
B.
Parallel to the long axis of the patient
C.
Horizontal to the long axis of the left ventricle
D.
Vertical to the long axis of the left ventricle
78.
How many separated channels does a Foley catheter have?
A.
One
B.
Two
C.
Three
D.
Four
79.
The LV ejection fraction (LVEF) measured from the GSPECT 8-frame acquisition when compared to the 16-frame acquisition is:
A.
3 units lower
B.
13 units lower
C.
3 units higher
D.
13 units higher
80.
The myocardial blood flow (MBF) in coronary beds without significant stenosis increases ~threefold with:
A.
Exercise
B.
Dipyridamole
C.
Dobutamine
D.
Regadenoson
81.
A vertical change in position of the heart that is usually noticed between the last frame of detector 2 and the first frame of detector 1 is called:
A.
Horizontal shift
B.
Hurricane sign
C.
Upward creep
D.
Star artifact
82.
A 51-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of palpitations and mild lightheadedness. He had experienced briefer episodes over the last 2 months, but this episode persisted for 4 min. The ECG (Fig. 2.2) shows:
A.
Atrial fibrillation
B.
Electronic ventricular pacemaker
C.
Normal sinus rhythm
D.
Ventricular bigeminy
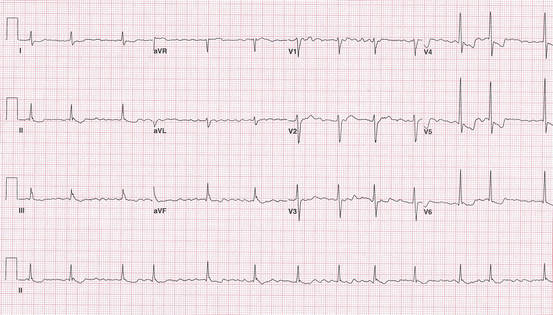

Fig. 2.2
Electrocardiogram
83.
Thallium is predominantly cleared by:
A.
The hepatobiliary system
B.
The kidneys
C.
The skin
D.
The respiratory system
84.
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway converting glucose 6-phosphate to:
A.
Acetate
B.
Fructose
C.
Pyruvate
D.
Sucrose
85.
The percentage of patients without CAD with a negative test result compared with the total number of patients tested without CAD describes the test:
A.
Specificity
B.
Sensitivity
C.
Accuracy
D.
Reproducibility
86.
Activation of adenosine A2A receptors produces:
A.
Atrioventricular conduction delay
B.
Bronchospasm
C.
Coronary vasodilatation
D.
Tachycardia
87.
When performing a pharmacological stress test with Lexiscan, the myocardial perfusion imaging agent should be administered:
A.
1–5 s before Lexiscan administration
B.
Immediately after Lexiscan injection
C.
Immediately after the saline flush
D.
10–20 s after the saline flush
88.
Which of the following medications are commonly referred to as “blood thinners”?
A.
Antibiotics
B.
Anticoagulants
C.
Antiemetics
D.
Antipyretics
89.
The MPI test sensitivity for ischemia is enhanced by getting the patient to perform the exercise portion of the test to a maximal safe level defined as:
A.
The maximal 65 % of age-predicted heart rate is reached
B.
The maximal 75 % of age-predicted heart rate is reached
C.
The maximal 85 % of age-predicted heart rate is reached
D.
The maximal 95 % of age-predicted heart rate is reached
90.
According to the ASNC IMAGING GUIDELINES FOR NUCLEAR CARDIOLOGY PROCEDURES, all exercise tests should be limited by:
A.
Patient age
B.
Achieved double product
C.
Achieved 85 % of maximum heart rate
D.
Symptoms
91.
In hybrid imaging, an attenuation map represents the degree of photon attenuation and is acquired:
A.
For every patient
B.
Daily
C.
Weekly
D.
For group of patients
92.
Chest pain that develops commonly during pharmacologic vasodilator stress testing:
A.
Indicates severe CAD
B.
Indicates poor prognosis
C.
Is a nonspecific finding
D.
Is a marker of vascular reactivity
93.
All of the following appropriateness designation for cardiovascular tests are given in the appropriate use criteria (AUC) document EXCEPT:
A.
Appropriate
B.
Uncertain
C.
Expensive
D.
Inappropriate
94.
The relative differences in count values between myocardial pixels are displayed in the black and white images as a variation in:
A.
Brightness
B.
Dimension
C.
Shape
D.
Sharpness
95.
Uncharacteristic communications between the left and right sides of the heart known as a ventricular septal defect (VSD) initially results in:
A.
Pulmonary hypertension
B.
A R-L shunt
C.
A L-R shunt
D.
A pulmonary embolism
96.
Administered dose of which of the following pharmacologic stress agents is NOT weight-adjusted?
A.
Adenosine
B.
Dipyridamole
C.
Dobutamine
D.
Regadenoson
97.
Figure 2.3 displays images acquired during routine 32 frames multi-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan. The end diastole image is labeled:
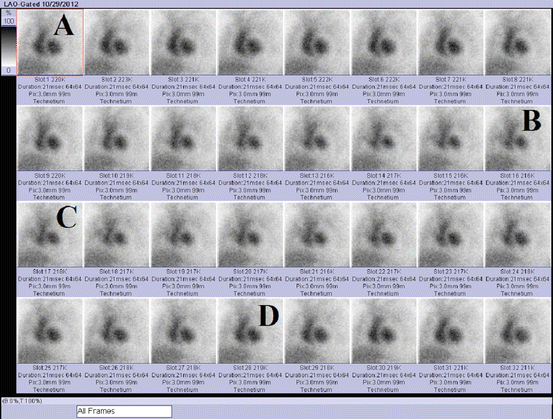

Fig. 2.3
MUGA scan
A.
D
B.
C
C.
B
D.
A
98.
For a trained rescuer performing adult CPR, what do the 2010 American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines for CPR and ECC recommend as the first step in the CPR sequence?
A.
Airway
B.
Breathing
C.
Chest compression
D.
Defibrillation
99.
Infusion of intravenous aminophylline antagonizes the effects of:
A.
Atropine
B.
The vasodilator stress agents
C.
The inotropic stress agents
D.
Propranolol
100.
With increasing workloads, the normal systolic blood pressure of a healthy person:
A.
Decreases progressively by 20 mmHg/stage
B.
Doesn’t change during exercise
C.
Increases progressively to a peak response ranging from 160–200 mmHg
D.
Increases progressively to a peak response ranging from 200–260 mmHg
101.
Which of the following MPI protocols provides optimal defect contrast with minimal background activity?
A.
Same day low dose rest, high stress protocol
B.
Same day low dose stress high dose rest protocol
C.
Two-day protocol
D.
Dual-isotope protocol
102.
The view comprising oblique tomographic cuts generated by slicing along the short axis perpendicular to the long axis of the left ventricle is called:
A.
Long-axis view
B.
Short-axis view
C.
Vertical long-axis view
D.
Horizontal long-axis view
103.
Appropriate use criteria (AUC) assess all of the following aspects of cardiovascular testing EXCEPT:
A.
When to perform a test
B.
How often to perform a test
C.
How much does a test cost
D.
In whom to perform a test
104.
All of the following are cyclotron-produced positron emitters EXCEPT:
A.
F-18
B.
N-13
C.
O-15
D.
Rb-82
105.
Conception is unlikely to have happened:
A.
Within the first 10 day of the menstrual cycle
B.
Within 10–15 days of the menstrual cycle
C.
Within 16–20 days of the menstrual cycle
D.
Within 21–25 days of the menstrual cycle
106.
Soft tissue attenuation artifacts decrease the diagnostic accuracy of SPECT in myocardial perfusion imaging as a result of increase in:
A.
False positive rate
B.
False negative rate
C.
True positive rate
D.
True negative rate
107.
The recommended intravenous dose of Adenoscan for adults is:
A.
100 mcg/kg/min infused for 6 min
B.
140 mcg/kg/min infused for 6 min
C.
100 mcg/kg/min infused for 3 min
D.
140 mcg/kg/min infused for 3 min
108.
The insertion of an intravenous line is suggested for the radiopharmaceutical injection of rest and stress parts of MPI in order to:
A.
Reduce the possibility of an infiltrated dose
B.
Reduce the possibility of motion artifacts
C.
Increase patient comfort
D.
Improve signal-to-noise ratio
109.
All of the following parameters can be assessed by performing an exercise stress in conjunction with MPI EXCEPT the patient’s:
A.
Functional capacity
B.
Stress-induced electrocardiographic changes
C.
Heart rate recovery
D.
Stress-induced echocardiographic changes
110.
A modified Bruce protocol is used for exercise testing in those patients who are:
A.
Assertive
B.
Athletic
C.
Old and frail
D.
Young and strong
111.
Which of the following statements describing properties of technetium-based MPI tracers or thallium is CORRECT?
A.
Technetium first-pass myocardial extraction is 85 %, its energy is lower than optimum for current gamma cameras
B.
Thallium first-pass myocardial extraction is 60 %, its energy is lower than optimum for current gamma cameras
C.
Thallium first-pass myocardial extraction is 85 %, its energy results in less scatter and soft tissue attenuation
D.
Technetium first-pass myocardial extraction is 60 %, its energy results in less scatter and soft tissue attenuation
112.
The heart responds to dobutamine infusion similarly to the way it responds to:
A.
Adenosine
B.
Dipyridamole
C.
Exercise
D.
Regadenoson
113.
An acceptance window of 20 % allows acquiring data from cardiac cycles having a duration within:
A.
± 20 % of the mean R–R interval
B.
± 10 % of the mean R–R interval
C.
± 5 % of the mean R–R interval
D.
± 2 % of the mean R–R interval
114.
Which of the following PET agents is classified as the freely diffusible tracer?
A.
F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose
B.
N-13 ammonia
C.
O-15 water
D.
Rb-82
115.
Present guidelines for the treatment of patients with acute myocardial infarction include all of the following options EXCEPT:
A.
Coronary revascularization
B.
Medical therapy
C.
Radiation therapy
D.
Thrombolytic agents
116.
Which of the following statements, describing extracardiac incidental findings (ECFs) on nuclear SPECT MPI, is FALSE?
A.
ECFs on nuclear SPECT MPI are common and can be easily identified
B.
ECFs can be small or large and they can be single or multiple
C.
Patients with ECFs may have symptoms that can often mimic cardiac symptoms
D.
There is a significant variability in the incidence of reported ECFs, depending on the reader’s skill
117.
What is the correct order of injections when a pharmacological stress test with Lexiscan is performed?
A.
Saline flash, Lexiscan, radiotracer, saline flash
B.
Lexiscan, saline flash, radiotracer, saline flash
C.
Radiotracer, saline flash, Lexiscan, saline flash
D.
Radiotracer, saline flash, Lexiscan, saline flash
118.
The perfusion–metabolism mismatch pattern—reduced perfusion and preserved metabolism—has been considered the hallmark of:
A.
Hibernating myocardium
B.
Normal myocardium
C.
Scarred myocardium
D.
Stunned myocardium
119.
The distribution information obtained by the gated SPECT with Tc-99m-based tracers reflects the perfusion at the time of:
A.
Acquisition
B.
Initial evaluation
C.
Injection
D.
Test termination
120.
A measure of the work load of the heart, equal to systolic blood pressure multiplied by heart rate, is called:
A.
The double product
B.
The heart rate recovery
C.
The metabolic equivalent
D.
The predicted heart rate
121.
LVEF is derived from the end-diastolic volume (EDV) and the end-systolic volume (ESV) using the formula:
A.
(EDV−ESV)/EDV×100
B.
(EDV + ESV)/EDV×100
C.
(EDV−ESV)/ESV×100
D.
(EDV + ESV)/ESV×100
122.
Imaging after Tc-99m sestamibi administration is best done after a brief waiting period to allow for some liver and biliary clearance, but before significant accumulation of the radiotracer in the:
A.
Bladder
B.
Stomach
C.
Spleen
D.
Transverse colon
123.
Sestamibi and tetrofosmin are lipid-soluble cationic compounds with first-pass extraction fractions in the range of:
A.
50 %
B.
60 %
C.
70 %
D.
80 %
124.
F-18fluorodeoxyglucose is trapped in the myocyte as:
A.
F-18 FDG-6-phosphate
B.
F-18 FDG-4-phosphate
C.
F-18 FDG-2-phosphate
D.
F-18 FDG-1-phosphate
125.
The typical stroke volume (SV) of the left ventricle is approximately:
A.
35 ml
B.
70 ml
C.
140 ml
D.
280 ml
126.
Which of the following will increase the sensitivity of Tl-201 for detection of viable myocardium?
A.
Applying attenuation correction
B.
Increasing the tracer dose
C.
Obtaining gated images
D.
Reinjecting the tracer
127.
What is the recommended intravenous dose of Lexiscan?
A.
4 ml (0.5 mg regadenoson)
B.
5 ml (0.2 mg regadenoson)
C.
5 ml (0.4 mg regadenoson)
D.
4 ml (0.4 mg regadenoson)
128.
After oral carbohydrate loading, high myocardial uptake of F-18 FDG reflects increased myocardial glucose utilization due to the release of:
A.
Endogenous insulin
B.
Exogenous insulin
C.
Glucagon
D.
Pyruvate
129.
Arrhythmias, such as multiple PVCs, can adversely affect the gated blood pool study if these beats account for more than:
A.
5 %
B.
10 %
C.
20 %
D.
30 %
130.
In the Bruce protocol, the incline and speed of the treadmill are increased every 3 min through a total of:
A.
Five stages
B.
Six stages
C.
Seven stages
D.
Eight stages
131.
To minimize hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal interference, the optimal time imaging window for Tc-99m-labeled radiopharmaceuticals (Sestamibi or Tetrofosmin) is:
A.
10 min
B.
When radiotracer activity has cleared from the gastrointestinal tract and not concentrated in the liver
C.
When radiotracer activity has cleared from the liver and not concentrated in the gastrointestinal tract
D.
30 min
132.
The standard SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging projection views are acquired over:
A.
90° arc
B.
180° arc
C.
270° arc
D.
360° arc
133.
Which of the following X-ray photons emitted from Tl-201 decay are primarily captured during imaging?
A.
75–80 keV
B.
135 keV
C.
167 keV
D.
135–167 keV
134.
PET tracers: C-11 acetate and O2-15 are markers of:
A.
Cell proliferation
B.
Glucose utilization and metabolism
C.
Membrane synthesis
D.
Oxidative and oxygen metabolism
135.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

Figure 2.4 presents a screenshot of a standard LAO view MUGA scan. The arrow is pointing to the:
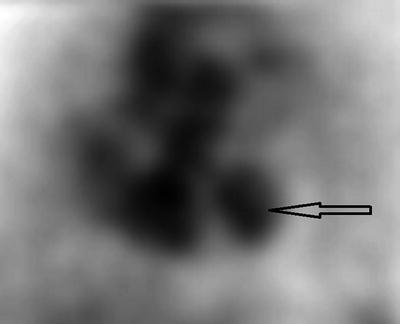

Fig. 2.4
Muga scan
A.
Left atrium