Fig. 4.1
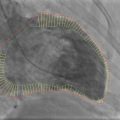
Electrocardiogram
A.
Atrial pacemaker
B.
Biventricular pacemaker
C.
Cardioverter-defibrillator
D.
Ventricular pacemaker
28.
I-131 labeled monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 has been shown to accumulate in lipid-rich, macrophage-rich regions in animal models of:
A.
Angiogenesis
B.
Arrhythmia
C.
Atherosclerosis
D.
Cancer
29.
According to the ASNC recommendations, by 2014, a goal is set to decrease patient radiation exposure associated with myocardial perfusion imaging SPECT to less than:
A.
18 mSv in 100 % of patients
B.
18 mSv in 50 % of patients
C.
9 mSv in 100 % of patients
D.
9 mSv in 50 % of patients
30.
The only significant mechanism available to the heart to increase oxygen consumption is to:
A.
Increase oxygen extraction
B.
Increase fatty acids consumption
C.
Increase perfusion
D.
Increase glucose utilization
31.
The American Society of Nuclear Cardiology and the Society of Nuclear Medicine together recommend:
A.
Against applying attenuation correction in addition to ECG gating with SPECT MPI
B.
In favor of applying attenuation correction in addition to ECG gating with SPECT MPI
C.
Against applying attenuation correction without ECG gating with SPECT MPI
D.
In favor of applying attenuation correction without ECG gating with SPECT MPI
32.
Peripheral sites, other than the antecubital (preferably medial) and external jugular veins, are NOT suitable for first-pass radionuclide angiography (FPRNA) because of the possibility of bolus (select two):
A.
Extravasation
B.
Fractionation
C.
Infiltration
D.
Prolongation
E.
Reduction
33.
Automated method that adjusts the intensity of the myocardial perfusion image to reflect the estimated magnitude of soft tissue tempering on different regions of the heart is called:
A.
Filtering
B.
Attenuation correction
C.
Image fusion
D.
Smoothing
34.
During PET/CT acquisition:
A.
PET emission data and CT scanner “freeze” the heart, lungs, and liver at one point in the respiratory cycle
B.
PET emission data “freeze” the heart, lungs, and liver at one point in the respiratory cycle, whereas the CT scanner averages many respiratory cycles
C.
CT scanner “freezes” the heart, lungs, and liver at one point in the respiratory cycle, whereas the PET emission data are averaged over many respiratory cycles
D.
CT scanner and the PET emission data are averaged over many respiratory cycles
35.
When the existence of a cardiac shunt is assessed using the first pass technique, reappearance of activity in the lungs shortly after the first pass, but before recirculation through body:
A.
Indicates the presence of R–L shunt
B.
Excludes the presence of R–L shunt
C.
Indicates the presence of L–R shunt
D.
Excludes the presence of L–R shunt
36.
An event that can be demonstrated, using sequential exercise testing, when the time to angina and ischemic ST-segment depression can be prolonged on the second of two exercise tests, is known as:
A.
Adaptive response
B.
ST normalization
C.
T wave pseudonormalization
D.
Warm-up phenomenon
37.
The unit of cut-off frequency is:
A.
cm
B.
cm2
C.
cm−1
D.
cm3
38.
The Fick Principle describes the relationship between myocardial oxygen consumption or mixed venous oxygen saturation (MVO2), coronary blood flow (CBF), and the:
A.
Arterial-venous oxygen difference
B.
Glucose level
C.
Heart rate
D.
Level of exercise
39.
The biological half-life of Tl-201 is approximately:
A.
1 day
B.
5 days
C.
10 days
D.
20 days
40.
Perceived exertion ratings between 12 and 14 on the Borg Scale suggest that physical activity is being performed at a:
A.
Very light level
B.
Light level of intensity
C.
Moderate level of intensity
D.
Very hard level of intensity
41.
Which of the following statements describing motion artifacts is FALSE?
A.
The number of frames with motion determines the magnitude of image artifact
B.
The direction and pattern of motion determine the location of artifacts
C.
Motion that occurs when the heart is close to the detector is less likely to create image artifacts
D.
The direction of motion may be lateral, vertical, or rotational
42.
Activation of A1 adenosine receptors produces:
A.
Atrioventricular conduction delay
B.
Bronchospasm
C.
Coronary vasodilatation
D.
Tachycardia
43.
The view comprising long-axis tomograms, generated by slicing along the horizontal plane through the short-axis perspective, is called:
A.
Vertical short-axis view
B.
Horizontal short-axis view
C.
Vertical long-axis view
D.
Horizontal long-axis view
44.
The chemical form of rubidium 82 obtained from a Cardiogen-82 generator is:
A.
Rb-82 carbonate
B.
Rb-82 chloride
C.
Rb-82 oxide
D.
Rb-82 sulfur
45.
The contrast echocardiography viability studies with high-molecular weight inert gases are based on evaluation of:
A.
Cell membrane integrity
B.
Contractile reserve
C.
Myocardial perfusion
D.
Scar tissue
46.
Prone imaging may occasionally create a fixed defect located:
A.
Anteriorly or posteriorly
B.
Anteriorly or laterally
C.
Posteriorly or inferiorly
D.
Laterally or inferiorly
47.
Which of the following statements describing the regadenoson plasma concentration-time profile is CORRECT?
A.
The maximal plasma concentration of regadenoson is within 1 min after injection of Lexiscan
B.
The half-life of initial phase is approximately 4–8 min
C.
The half-life of intermediate phase is on average 1 h
D.
The half-life of terminal phase is approximately 2 h
48.
The auto-regulatory mechanism of the heart seeks to balance the supply and demand of:
A.
Amino acids
B.
Fatty acids
C.
Glucose
D.
Oxygen
49.
Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CZT) crystals absorb the γ-ray energy and generate electron–hole pairs with resulting conversion of the photons into:
A.
A digital image
B.
A digital signal
C.
An electronic signal
D.
A hard copy
50.
Which of the following results of the Duke Treadmill Scores (DTS) identifies patient with high risk CAD?
A.
≤−11
B.
+4 to −10
C.
+ 5 to +10
D.
≥ +10
51.
After the initial uptake and distribution of thallium, the subsequent redistribution of thallium begins within:
A.
5–10 min after injection
B.
10–15 min after injection
C.
15–20 min after injection
D.
20–25 min after injection
52.
According to the ASNC imaging guidelines, the radionuclide of choice for standard first-pass radionuclide angiography (FPRNA) is:
A.
Tc-99m sestamibi
B.
Tc-99m pertechnetate
C.
Tc-99m diethylamine triamine pentaacetic acid
D.
Tc-99m sulfur colloid
53.
“Evolution” by GE Healthcare, “Astonish” by Philips, and Flash 3D by Siemens are examples of:
A.
Attenuation correction systems
B.
Hybrid systems
C.
Advanced image reconstruction techniques
D.
New camera designs
54.
The PET potential for quantifying myocardial blood flow and blood flow reserve in absolute terms is highly beneficial in patients with:
A.
Balanced ischemia
B.
Myocardial infarction
C.
Hibernating myocardium
D.
Unstable angina
55.
MRI and echocardiography viability studies with dobutamine are based on the evaluation of:
A.
Cell membrane integrity
B.
Contractile reserve
C.
Myocardial perfusion
D.
Scar tissue
56.
Which of the following statements describing the scanning sealed source system used for the attenuation map creation in transmission computed tomography (TCT) is FALSE:
A.
The system requires strict quality control to ensure precise movement of the line source
B.
The flux of X-ray photons from a conventional sealed source is much higher than typical X-ray tube
C.
The scanning line source system is geometrically complex and less sensitive than CT-based techniques
D.
The system requires an electronic window as well as source strength
57.
According to the Lexiscan package insert, nursing women may consider interrupting nursing after regadenoson administration for:
A.
1 h
B.
10 h
C.
24 h
D.
48 h
58.
Research bias, introduced when there is a sufficient time delay between the application of the test, and the reference standard to allow change in the disease state, is called:
A.
Differential verification bias
B.
Disease progression bias
C.
Incorporation bias
D.
Treatment paradox bias
59.
In patients with a normal MPI study, the hard event rate (cardiac death or non-fatal myocardial infarction) occurring during an average follow-up of 2 years is approximately:
A.
0.7 % per year
B.
1.4 % per year
C.
2.3 % per year
D.
3.0 % per year
60.
A deceleration of heart rate following exercise termination is called:
A.
Chronotropic incompetence
B.
Inotropic incompetence
C.
Heart rate recovery
D.
Sinus bradycardia
61.
The transmission-to-cross-talk ratio (TCR) depends on all of the following EXCEPT:
A.
The injected activity
B.
The transmission source strength
C.
The body habitus
D.
The camera sensitivity
62.
Which of the following adenosine receptors stimulation may result in bronchial constriction and peripheral vasodilation?
A.
A1
B.
A2a
C.
A2b
D.
A3
63.
According to the appropriate use criteria (AUC), which of the following tests will be appropriate for an exercising regularly 54-year-old woman presented with atypical chest pain, hx of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and secondary to LVH resting ECG changes?
A.
Cardiac CT
B.
Coronary angiogram
C.
Exercise ECG
D.
Stress radionuclide MPI
64.
The PET perfusion imaging agents: F-18-fluorobenzyl triphenyl phosphonium and F-18 flupiridaz bind to the:
A.
Cell wall
B.
Lysosome
C.
Mitochondria
D.
Nuclear membrane
65.
All of the following response patterns can be observed on echocardiography viability studies with low dose dobutamine infusion EXCEPT:
A.
Biphasic response
B.
Sustained improvement
C.
Triphasic response
D.
Worsening
66.
Patients with inferior wall abnormalities on supine imaging, that were absent on prone imaging, had a risk of subsequent cardiac events that is comparable to the risk in patients with:
A.
Summed stress score more than 25 on supine-only studies
B.
Summed stress score more than 15 on supine-only studies
C.
Summed stress score more than 5 on supine-only studies
D.
Normal supine-only studies
67.
Adenosine produces vasoconstriction in:
A.
Coronary arteries
B.
Coronary veins
C.
Renal afferent arterioles
D.
Pulmonary veins
68.
In patients with coronary artery disease, coronary flow reserve decreases in proportion to the degree of stenosis severity and is exhausted for stenosis:
A.
≥20 %
B.
≥40 %
C.
≥60 %
D.
≥80 %
69.
Which of the following is the energy supplier for the cell?
A.
Lysosome
B.
Mitochondria
C.
Ribosome
D.
Vacuole
70.
All of the following baseline electrocardiographic abnormalities may preclude use of exercise ECG for noninvasive stress testing EXCEPT:
A.
Left bundle branch block
B.
Premature atrial contractions
C.
Permanent ventricular pacing
D.
Ventricular pre-excitation syndrome
71.
High-speed SPECT technology introduces a series of small, pixilated solid-state detector columns equipped with:
A.
NaTI crystals
B.
LYSO crystals
C.
CsI(Tl) crystals
D.
BGO crystals
72.
After an intravenous injection of Tc 99m macroaggregated albumin, an increased portion of perfusion getting into systemic circulation rather than the lungs is referred to as:
A.
Pulmonary hypertension
B.
The percentage R–L shunt
C.
The percentage L–R shunt
D.
Pulmonary embolism
73.
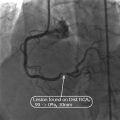
A 79-year-old man presents to ED with complaints of intermittent lightheadedness and dizziness. He has type 2 diabetes and is hypertensive. What are the ECG (Fig. 4.2) findings?
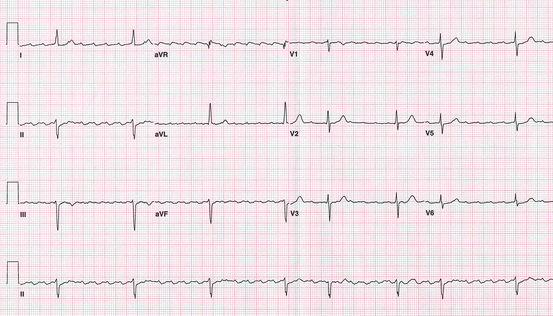

Fig. 4.2
Electrocardiogram
A.
Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
B.
Atrial flutter with variable A–V block
C.
Sinus rhythm with frequent PVCs in a pattern of bigeminy
D.
Sinus tachycardia with frequent PACs
74.
F-18 fluorodexyglucose is transported into the myocyte by the sarcolemmal glucose transporters:
A.
GLUT 3 and GLUT 6
B.
GLUT 2 and GLUT 5
C.
GLUT1 and GLUT 4
D.
GLUT 0 and GLUT 3
75.
The mechanism responsible for a normal MPI study, despite established CAD, involves preserved:
A.
Collagen fibers
B.
Endothelial function
C.
Smooth muscle
D.
Striated muscle
76.
Stress ECG-gated myocardial SPECT imaging with Tc-99m-labeled agents soon after exercise is superior to conventional late imaging in identifying patients with myocardial:
A.
Infarction
B.
Inflammation
C.
Ischemia
D.
Stunning
77.
The ramp filter suppresses the star artifact by controlling:
A.
High frequencies
B.
Low frequencies
C.
Medium frequencies
D.
Noise
78.
Which of the following is currently considered as the gold standard for ventricular volumes and function measurements?
A.
GSPECT
B.
ECHO
C.
MRI
D.
MUGA
79.
Which of the following statements describing radionuclide angiography (RNA) is FALSE?
A.
RNA can be performed with each a planar technique or tomography
B.
RNA can be done at rest or with exercise
C.
RNA-derived EF is based on geometric assumptions
D.
RNA can be completed with first-pass and gated equilibrium approaches
80.
The pulmonary vascular bed can accommodate as much as a/an _________________ increase in cardiac output.
A.
Twofold
B.
Fourfold
C.
Sixfold
D.
Eightfold
81.
The highest spatial frequency that can be encoded in the digital image is called:
A.
Temporal
B.
Nyquist
C.
Fourier
D.
Limited
82.
Administration of dipyridamole, adenosine, or regadenoson results in:
A.
An 8–10 mm Hg increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure and reflex increase in heart rate by 10 and 20 beats/min
B.
A reduction of 8–10 mm Hg in systolic and diastolic blood pressure and reflex increase in heart rate by 10 and 20 beats/min
C.
A reduction of 8–10 mm Hg in systolic and diastolic blood pressure and reflex decrease in heart rate by 10 and 20 beats/min
D.
An 8–10 mm Hg increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure and reflex decrease in heart rate by 10 and 20 beats/min
83.
Which of the following LV function parameters is assessed by evaluating the changes in brightness from the end-diastolic to the end-systolic frame?
A.
Regional wall motion
B.
Systolic wall thickening
C.
Regional EF
D.
Global EF
84.
During the cardiac PET/CT acquisition, the respiratory cycle can be monitored by using all of the following EXCEPT:
A.
A bellows
B.
A chest band
C.
An electrocardiograph
D.
An infrared tracking system
85.
According to the American College of Cardiology guidelines, patients with a 75 % pretest likelihood of CAD are considered to be:
A.
Not at risk for CAD
B.
At low risk for CAD
C.
At moderate risk for CAD
D.
At high risk of CAD
86.
Which of the following statements describing the radiation safety approach in breast-feeding mothers referred for radionuclide imaging is INCORRECT?
A.
The breasts can be pumped before the injection of radioisotope and the milk can be stored in
B.
The refrigerator for 5 days
C.
The breasts can be pumped before the injection of radioisotope and the milk can be frozen for up to 6 month.
D.
After the injection of the radioisotope, the milk can be collected and after allowing appropriate decay can be given to the infant
E.
After the injection of the radioisotope, the milk can be collected and given to the infant
87.
Adenosine is a naturally occurring purine nucleoside that forms from the breakdown of:
A.
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
B.
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
C.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
D.
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)
88.
A phenomenon when dilation of one vascular network “redirects” blood flow from another region within the organ that is already maximally dilated, because of the presence of proximal lesions, is called the coronary:
A.
Collaterals
B.
Steal
C.
Fistula
D.
Atherosclerosis
89.
I-123 mIBG imaging produces a quantitative index called:
A.
Ejection fraction
B.
Heart-to-mediastinum ratio
C.
Lung uptake index
D.
Transient ischemic dilation
90.
Which of the following is the strongest and most consistent prognostic marker identified in exercise testing?
A.
Chest pain
B.
J point depression
C.
Maximum exercise capacity
D.
Premature atrial contractions
91.
Soft tissue attenuation from breasts may produce MPI artifacts in up to:
A.
20 % studies in women
B.
40 % studies in women
C.
60% studies in women
D.
80% studies in women
92.
When performing the first pass study, the integrity of the bolus is assessed by placing a ROI over the:
A.
Inferior vena cava
B.
Right atrium
C.
Right ventricle
D.
Superior vena cava
93.
When cardiac death and nonfatal myocardial infarction are considered as separate endpoints, functional and perfusion data obtained from GSPECT suggests:
A.
Post-stress LVEF is the best predictor of nonfatal infarction, whereas the amount of ischemia is the best predictor of cardiac death
B.
Post-stress LVEF is the best predictor of cardiac death, whereas the amount of ischemia is the best predictor of nonfatal infarction
C.
Post-stress LVEF and the amount of ischemia are the best predictors of nonfatal infarction
D.
Post-stress LVEF and the amount of ischemia are the best predictors of cardiac death
94.
An iterative reconstruction begins with:
A.
Scatter correction
B.
A guess of the image
C.
Simulate scanning
D.
Random correction
95.
The hypothesis stating that accuracy of any test depends on the pretest probability of disease in the patient population being studied is known as:
A.
Bayes’ theorem
B.
Fourier transform
C.
Iterative algorithm
D.
Prevalence rates
96.
The adenosine infusion should be discontinued early under any of the following circumstances EXCEPT:
A.
Diastolic blood pressure >90 mm Hg
B.
Patient’s request to stop
C.
Systolic blood pressure <80 mm Hg
D.
Wheezing
97.
Which of the following algorithms can be used to measure LV diastolic dyssynchrony from gated SPECT MPI?
A.
Global ejection fraction
B.
Phase analysis
C.
Wall motion
D.
Wall thickening
98.
The myocardium of patients with systolic heart failure is characterized by:
A.
A reduction of presynaptic norepinephrine uptake and reduction in postsynaptic β-adrenoceptor density
B.
An increase in presynaptic norepinephrine uptake and increase in postsynaptic β-adrenoceptor density
C.
An increase in presynaptic norepinephrine uptake and reduction in postsynaptic β-adrenoceptor density
D.
A reduction of presynaptic norepinephrine uptake and increase in postsynaptic β-adrenoceptor density
99.
Functional improvement after coronary artery bypass grafting, or percutaneous angioplasty when evaluated by GSPECT, is apparent by an/a:
A.
Increase in the ESV, a decrease in the LVEF
B.
Increase in the LVEF and in the ESV
C.
Decrease in the LVEF and in the ESV
D.
Increase in the LVEF, a decrease in the ESV
100.
Perceived exertion ratings between 18 and 20 on the Borg Scale suggest that physical activity is being performed at:
A.
A light level of intensity
B.
A moderate level of intensity
C.
A very hard level of intensity
D.
A patient’s maximum exercise capacity
101.
Which of the following exercise stress test findings/symptoms indicate a high probability of coronary artery disease (select three)?
A.
Angina like chest pain
B.
Fall in blood pressure
C.
T wave decrease in height
D.
Substantial ST depression at low work rate
E.
Tachycardia
102.
The upright over supine position for performing first-pass radionuclide angiography (FPRNA) is preferred because:
A.
Liver background is reduced in the upright position
B.
Pulmonary background is reduced in the upright position
C.
Liver background is increased in the upright position
D.
Pulmonary background is increased in the upright position
103.
Which of the following variables increase sensitivity of MPI?
A.
Left circumflex coronary stenosis
B.
Branch vessel or distal stenosis
C.
Inadequate heart rate response during exercise
D.
Proximal location of stenosis
104.
Rubidium acts like a microsphere that crosses the capillary membrane and is trapped because of:
A.
Change charge state
B.
Decay process
C.
Its size
D.
Change in shape
105.
Which of the following medications should be stopped a week before treadmill ECG testing?
A.
Aggrenox
B.
Digoxin
C.
Dipyridamole
D.
Warfarin
106.
All of the following are advantages of using CT over the radionuclide-based transmission for attenuation correction of SPECT data EXCEPT:
A.
The CT image has less noise than transmission images acquired using radionuclide source
B.
The CT image can be acquired faster than a transmission image
C.
The CT source decays slower than a radionuclide source
D.
The CT images will not be influenced by cross-talk from the SPECT radionuclide
107.
Figure 4.3 presents a LV volume curve derived from an 8-frame gated myocardial perfusion imaging study using 4D-MSPECT. Calculated ED of LV is approximately:
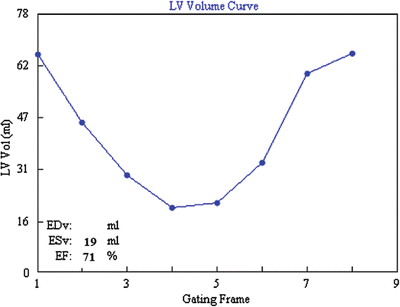

Fig. 4.3
Volume curve
A.
47 %
B.
66 %
C.
71 %
D.
85 %
108.
The risk assessment tool from the Framingham Heart Study is employed to predict a person’s chance of having a heart attack in the next:
A.
Year
B.
2 years
C.
5 years
D.
10 years
109.
Transmission imaging is a mean of creating:
A.
An emission scan
B.
An uniformity correction map
C.
An attenuation map
D.
An attenuation map
110.
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) combines exercise testing with:
A.
Blood chemistry
B.
Electrolyte analysis
C.
Myocardial perfusion imaging
D.
Ventilation gas analysis
111.
The biologic half-life of dipyridamole is:
A.
1–9 min
B.
10–29 min
C.
30–45 min
D.
46–60 min
112.
Which of the following radiopharmaceuticals can be used for detecting and quantifying R–L and L–R shunts?
A.
Tc-99m albumin aggregate
B.
Tc-99m sodium pertechnetate
C.
Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate
D.
Tc-99m dimercaptocuccinic acid
113.
Which of the following statements comparing exercise echocardiography to exercise MPI is INCORRECT?
A.
The diagnostic accuracy of the two techniques is comparable
B.
The prognostic value of the two techniques is comparable
C.
Stress echocardiography is more accurate than stress MPI in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy
D.
Stress echocardiography is more accurate than stress MPI in patients with high body mass index
114.
The two main energetic pathways used by the heart are:
A.
Amino acid and glucose metabolism
B.
Carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism
C.
Lipid and protein metabolism
D.
Fatty acid and fructose metabolism
115.
Which of the following allows dynamic assessment of cardiac function at rest and during exercise or pharmacologic agent administration?
A.
Angiography
B.
Echocardiography
C.
Electrocardiography
D.
Myocardial perfusion imaging
116.
A hypertensive response to exercise is defined as one in which the systolic blood pressure rises to more than:
A.
190 mm Hg
B.
220 mm Hg
C.
250 mm Hg
D.
280 mm Hg
117.
A direct negative chronotropic, dromotropic, and inotropic effect of adenosine on the heart is attributable to:
A.
The A1-receptor agonism
B.
The A1-receptor antagonism
C.
The A2-receptor agonism
D.
The A2-receptor antagonism
118.
Any constellation of clinical findings that the physician feels is consistent with obstructive coronary artery disease is called:
A.
Unstable angina
B.
Ischemic equivalent
C.
Myocardial infarction
D.
Somatopsychic syndrome
119.
Distance (size) in the spatial domain and frequency in the frequency domain are:
A.
Equal
B.
Proportionally related
C.
Inversely related
D.
Independent from each other
120.
Which of the following is considered a relative indication to terminate an exercise stress test?
A.
Difficulties monitoring the ECG
B.
Patient request to stop the test
C.
Shortness of breath
D.
Signs of poor perfusion
121.
Binodenoson and apadenoson are:
A.
Adenosine antagonists
B.
Beta blockers
C.
Calcium channel blockers
D.
Selective A2A receptor agonists
122.
Radionuclide angiography (RNA) can provide information on all of the following EXCEPT:
A.
Intracardiac shunts
B.
Myocardial viability
C.
Pulmonary transit time
D.
Wall motion
123.
The discordance between the times of right ventricular (RV) and left ventricular (LV) contraction is called:
A.
Diastolic incompetence
B.
Intraventricular dyssynchrony
C.
Interventricular dyssynchrony
D.
Systolic incompetence
124.
The extraction of the FDG during a capillary single pass is about:
A.
10 %
B.
40 %
C.
80 %
D.
100 %
125.
Which cell feature is responsible for making proteins?
A.
Lysosomes
B.
Mitochondria
C.
Ribosomes
D.
Vacuoles
126.
The property of a filter that describes how quickly the transition is made between frequencies that are kept and frequencies that are eliminated is called:
A.
Cut-off
B.
Power
C.
Order
D.
Roll-on
127.
With respect to its molecular structure,synaptic uptake and intracellular storage I-123 MIBG resembles the neurotransmitter:
A.
Acetylcholine
B.
Dopamine
C.
Histamine
D.
Norepinephrine
128.
Which of the following occurrences is classified as a “hard event” in risk stratification in stable chest pain syndromes?
A.
Acute chest pain
B.
Heart failure
C.
Nonfatal MI
D.
Unstable angina
129.
According to the current ACC/AHA guidelines for exercise testing, stopping beta-blockers before EST is discouraged to avoid:
A.
Anginal symptoms
B.
Headache
C.
Orthostatic hypotension
D.
Tachycardia
130.
Specificity and sensitivity of exercise testing for the diagnosis of CAD is:
A.
82–92 % and 74–94 % accordingly
B.
61–73 % and 59–81 % accordingly
C.
59–81 % and 61–73 % accordingly
D.
74–94 % and 82–92 % accordingly
131.
Inside the myocardial cell, ammonia is quickly converted to an ammonium ion, which is rapidly converted and trapped as glutamine by the enzyme:
A.
Alanine aminotransferase
B.
Aspartate aminotransferase
C.
Glutamine synthase
D.
Nitrate reductase
132.
A caudal tilt of the LAO view during equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography (ERNA) is helpful to separate:
A.
The atria from the aorta
B.
The atria from the ventricle
C.
The ventricle from the aorta
D.
The ventricles
133.
Diaphragmatic attenuation is estimated to occur in up to:
A.
5 % of myocardial perfusion studies
B.
25 % of myocardial perfusion studies
C.
45 % of myocardial perfusion studies
D.
65 % of myocardial perfusion studies
134.
Which of the following PET tracers has been be used to evaluate the cardiac parasympathetic nervous system?
A.
F-18 fluorodopamine
B.
F-18 fluoroethoxybenzovesamicol
C.
C-11 epinephrine
D.
C-11 phenylephrine
135.
Figure 4.4 presents a screenshot of a standard LAO view MUGA scan. The arrow is pointing to the:
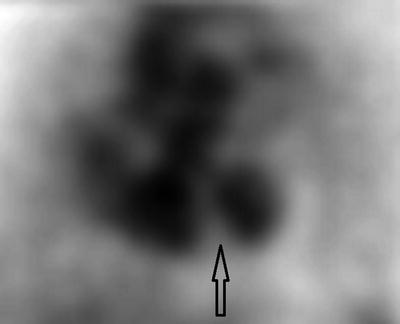

Fig. 4.4
MUGA scan
A.
Interatrial septum
B.
Intraatrial thrombus
C.
Interventricular septum
D.
Intraventricular thrombus
136.
Which of the following baseline ECG findings DOES NOT significantly reduce the accuracy of the EST for the diagnosis of ischemia?
A.
Left bundle branch block
B.
Right bundle branch block
C.
Ventricular pacing
D.
Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome
137.
The method by which an image is transformed into its frequency components is called:
A.
Fourier transform
B.
Fourier space
C.
Inverse Fourier transform
D.
Fourier rebinning
138.
The concept of “normalcy rate” has been developed in an attempt to compensate for:
A.
Age differences
B.
Gender differences
C.
Qualitative bias
D.
Referral bias
139.
The absence of perfusion abnormalities in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy:
A.
Is a false negative finding
B.
Excludes CAD as the cause of the cardiomyopathy
C.
Has a low diagnostic value
D.
Indicates absence of viable myocardium
140.
Low-level exercise, implemented in combination with pharmacologic stress MPI, is performed at:
A.
0 mph, 10 % grade
B.
1.7 mph, 0 % grade
C.
3.5 mph, 10 %
D.
5.0 mph, 0 % grade
141.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

Tc-99m sestamibi accumulates more avidly in tumor cells because tumor cells, when compared to the surrounding normal epithelial cells, have:
A.




A greater lysosomal density
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree