Pulmonary Veins
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Gerald F. Abbott, MD
Terminology
Abbreviations
Secondary pulmonary lobule (SPL)
Overview of Pulmonary Veins
Morphology
Branching tapering tubular structures
Peripheral tributaries anastomose to form central pulmonary veins draining into left atrium
Function
Collection of oxygenated blood from alveolar-capillary membrane
Conduit of oxygenated blood to left atrium for delivery to systemic circulation
Anatomy of Pulmonary Veins
General Concepts
Sources of pulmonary venous drainage
Efferent veins from alveolar capillaries
Bronchial and vascular wall capillary networks
Septal veins of SPL
Veins of visceral pleura
Histology
Mural smooth muscle and elastic lamina
Small pulmonary veins are histologically indistinguishable from small pulmonary arteries
Imaging of Normal Pulmonary Veins
Imaging Anatomy
Pulmonary veins travel in periphery of anatomic lung units
Acinus
Lobule
Segment
Veins of SPL
Drain into interlobular septal pulmonary veins with tributaries from
Alveolar-capillary network
Bronchial artery-derived airway wall (subendothelial) capillary network
Pleura
Each lobular or septal pulmonary vein drains 2 or more adjacent SPLs
Imaging Features
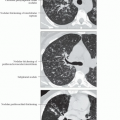
SPL pulmonary veins
May be visible in periphery of normal SPL
Help define SPL boundaries on HRCT
Measure approximately 0.5 mm in diameter
Identified approximately 1-1.5 cm from pleural surfaces
Peripheral pulmonary veins
Periphery of pulmonary subsegments and segments
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree