Chapter 21 Recognizing Abnormalities of Bone Density
Normal Bone Anatomy
Conventional Radiography
 On conventional radiographs, bones consist of a dense cortex of compact bone, which completely envelopes a less dense medullary cavity containing cancellous bone arranged as trabeculae, separated primarily by blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, and fat. The proportions of cortical versus trabecular bone vary in different skeletal sites and even at different locations in the same bone, i.e., the cortex is naturally thicker in some places than in others.
On conventional radiographs, bones consist of a dense cortex of compact bone, which completely envelopes a less dense medullary cavity containing cancellous bone arranged as trabeculae, separated primarily by blood vessels, hematopoietic cells, and fat. The proportions of cortical versus trabecular bone vary in different skeletal sites and even at different locations in the same bone, i.e., the cortex is naturally thicker in some places than in others. When viewed in tangent on conventional radiographs, the cortex produces a smooth white shell of varying thickness that appears as a dense white band along the outer margins of the bone.
When viewed in tangent on conventional radiographs, the cortex produces a smooth white shell of varying thickness that appears as a dense white band along the outer margins of the bone. The medullary cavity on conventional radiographs appears as a core of less dense, grayish material inside the cortical shell, interlaced with a fine network of bony trabecular markings. The corticomedullary junction is the edge between the inner margin of the cortex and the medullary cavity (Fig. 21-1).
The medullary cavity on conventional radiographs appears as a core of less dense, grayish material inside the cortical shell, interlaced with a fine network of bony trabecular markings. The corticomedullary junction is the edge between the inner margin of the cortex and the medullary cavity (Fig. 21-1). It is important to remember that the cortex completely surrounds the entire bone but on conventional radiographs is best seen where it is viewed in profile, i.e., where the x-ray beam passes tangentially to the bone.
It is important to remember that the cortex completely surrounds the entire bone but on conventional radiographs is best seen where it is viewed in profile, i.e., where the x-ray beam passes tangentially to the bone. Almost all examinations of bone start with conventional radiographs obtained with at least two views exposed at a 90° angle to each other (called orthogonal views) so as to localize abnormalities better and to visualize as much of the circumference of the bone as possible.
Almost all examinations of bone start with conventional radiographs obtained with at least two views exposed at a 90° angle to each other (called orthogonal views) so as to localize abnormalities better and to visualize as much of the circumference of the bone as possible.CT and MRI
 CT and MRI are able to demonstrate the entire circumference and internal matrix of bone, including, especially with MRI, surrounding soft tissues not visible on conventional radiographs. This is accomplished by computer-aided reformatting and a superior ability to display more subtle differences in tissue densities (Fig. 21-2).
CT and MRI are able to demonstrate the entire circumference and internal matrix of bone, including, especially with MRI, surrounding soft tissues not visible on conventional radiographs. This is accomplished by computer-aided reformatting and a superior ability to display more subtle differences in tissue densities (Fig. 21-2). In addition to bony trabeculae, the marrow cavity contains red and yellow bone marrow. The red marrow produces the precursors of blood cells. Yellow marrow contains fat. The composition of marrow is different for different bones of the body and changes during life to become less hematopoietically active with age so that, around age 30, most of the appendicular skeleton contains only yellow marrow while most of the red marrow resides in the axial skeleton. Unlike conventional radiography, MRI is an excellent means of studying the components of marrow, a fact that makes MRI so useful in the study of marrow pathology.
In addition to bony trabeculae, the marrow cavity contains red and yellow bone marrow. The red marrow produces the precursors of blood cells. Yellow marrow contains fat. The composition of marrow is different for different bones of the body and changes during life to become less hematopoietically active with age so that, around age 30, most of the appendicular skeleton contains only yellow marrow while most of the red marrow resides in the axial skeleton. Unlike conventional radiography, MRI is an excellent means of studying the components of marrow, a fact that makes MRI so useful in the study of marrow pathology. Whereas the cortex is the part of the bone most easily visualized on conventional radiographs, cortical bone has a very low signal intensity on conventional MRI sequences.
Whereas the cortex is the part of the bone most easily visualized on conventional radiographs, cortical bone has a very low signal intensity on conventional MRI sequences.The Effect of Bone Physiology on Bone Anatomy
 Bones reflect the general metabolic status of the individual. Their composition requires a protein-containing, collagenous matrix (osteoid) upon which bone mineral, principally calcium phosphate, is transformed into cartilage and bone.
Bones reflect the general metabolic status of the individual. Their composition requires a protein-containing, collagenous matrix (osteoid) upon which bone mineral, principally calcium phosphate, is transformed into cartilage and bone. Bones are continuously undergoing remodeling processes that include resorption of old or diseased bone by osteoclasts and formation of new bone by osteoblasts. While osteoblasts are responsible for bone matrix production, osteoclasts resorb both the matrix and mineral.
Bones are continuously undergoing remodeling processes that include resorption of old or diseased bone by osteoclasts and formation of new bone by osteoblasts. While osteoblasts are responsible for bone matrix production, osteoclasts resorb both the matrix and mineral. Both osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity depend on the presence of a viable blood supply to bring those cells to the bone
Both osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity depend on the presence of a viable blood supply to bring those cells to the bone Bones also respond to mechanical forces—for example, the contractions of muscles and tendons, the process of bearing weight, constant use, or prolonged disuse—that help to form or maintain the shape as well as the content of each bone.
Bones also respond to mechanical forces—for example, the contractions of muscles and tendons, the process of bearing weight, constant use, or prolonged disuse—that help to form or maintain the shape as well as the content of each bone. In this chapter, we arbitrarily divide abnormalities of bone density into two major categories based primarily on their appearance on conventional radiographs—those that produce a pattern of either increased or decreased bone density and then subdivide those two patterns by extent of disease: focal versus diffuse (or generalized) changes (Table 21-1).
In this chapter, we arbitrarily divide abnormalities of bone density into two major categories based primarily on their appearance on conventional radiographs—those that produce a pattern of either increased or decreased bone density and then subdivide those two patterns by extent of disease: focal versus diffuse (or generalized) changes (Table 21-1). If MRI were used as the basis for categorization, bone (marrow) disorders could be divided into four other categories:
If MRI were used as the basis for categorization, bone (marrow) disorders could be divided into four other categories:TABLE 21-1 CHANGES IN BONE DENSITY
| Density | Extent | Examples Used in this Chapter |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Density ↑ | Diffuse | Diffuse osteoblastic metastases |
| Osteopetrosis (rare) | ||
| Focal | Localized osteoblastic metastases | |
| Avascular necrosis of bone | ||
| Paget disease | ||
| Decreased Density ↓ | Diffuse | Osteoporosis |
| Hyperparathyroidism | ||
| Rickets and osteomalacia | ||
| Focal | Localized osteolytic metastases | |
| Multiple myeloma | ||
| Osteomyelitis |
Recognizing a Generalized Increase in Bone Density
 On conventional radiographs and CT, there will be an overall whiteness (sclerosis) to all or most of the bones.
On conventional radiographs and CT, there will be an overall whiteness (sclerosis) to all or most of the bones. This leads to a diffuse loss of visualization of the normal network of bony trabeculae in the medullary cavity because of replacement of the normal intertrabecular fatty marrow by bone-producing elements.
This leads to a diffuse loss of visualization of the normal network of bony trabeculae in the medullary cavity because of replacement of the normal intertrabecular fatty marrow by bone-producing elements. There is also a loss of visualization of the normal corticomedullary junction because of the abnormally increased density of the medullary cavity relative to the cortex (Fig. 21-3).
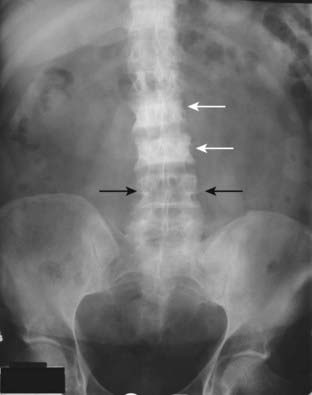
There is also a loss of visualization of the normal corticomedullary junction because of the abnormally increased density of the medullary cavity relative to the cortex (Fig. 21-3).
Figure 21-3 Diffuse metastatic disease from carcinoma of the prostate.
The bones are diffusely sclerotic. You can no longer see the normal trabeculae or the junction between the medullary cavity and the cortex as the medullary cavities have been filled in with osteoblastic metastatic disease that obscures these normal boundaries and increases the overall bone density. Contrast this picture with that of Paget disease of the pelvis (see Fig. 21-12).
Carcinoma of the Prostate
 Diffuse, blood-borne, metastatic disease from carcinoma of the prostate is the prototype for generalized increase in bone density. Osteoblastic activity occurs beyond the control of normal physiologic constraints.
Diffuse, blood-borne, metastatic disease from carcinoma of the prostate is the prototype for generalized increase in bone density. Osteoblastic activity occurs beyond the control of normal physiologic constraints. Metastatic disease to bone occurs in over 80% of autopsied patients with carcinoma of the prostate. Multiple bone metastases from carcinoma of the prostate occur much more frequently than do solitary bone lesions.
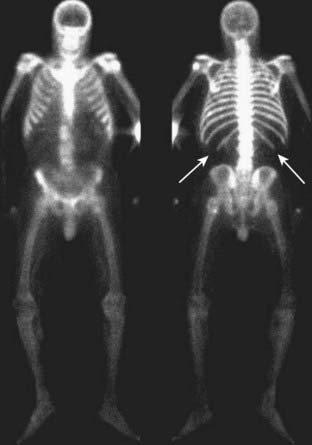
Metastatic disease to bone occurs in over 80% of autopsied patients with carcinoma of the prostate. Multiple bone metastases from carcinoma of the prostate occur much more frequently than do solitary bone lesions. With diffuse bone metastases, a so-called superscan may be seen on radionuclide bone scan. The superscan demonstrates high radiotracer uptake throughout the skeleton, with poor or absent renal excretion of the radiotracer (Fig. 21-4).
With diffuse bone metastases, a so-called superscan may be seen on radionuclide bone scan. The superscan demonstrates high radiotracer uptake throughout the skeleton, with poor or absent renal excretion of the radiotracer (Fig. 21-4).Osteopetrosis
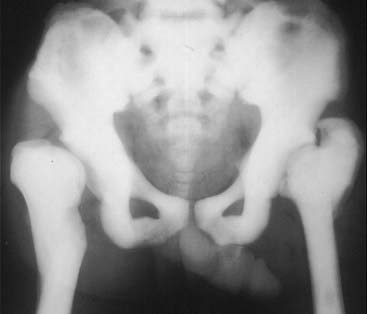
 Osteopetrosis (also called marble bone disease for obvious reasons) is a rare hereditary defect in osteoclastic activity that ultimately results in an increase in bone density affecting the entire skeleton (Fig. 21-5).
Osteopetrosis (also called marble bone disease for obvious reasons) is a rare hereditary defect in osteoclastic activity that ultimately results in an increase in bone density affecting the entire skeleton (Fig. 21-5). Although the bones are increased in density, they are mechanically inferior to normal bone and are more prone to pathologic fractures.
Although the bones are increased in density, they are mechanically inferior to normal bone and are more prone to pathologic fractures. In the infantile form of this disease, the defective osseous material can replace normal bone marrow leading to anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia (pancytopenia).
In the infantile form of this disease, the defective osseous material can replace normal bone marrow leading to anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia (pancytopenia).Recognizing a Focal Increase in Bone Density
![]() Focal sclerotic lesions can affect the cortex and medullary cavity. Those that affect the cortex will usually produce periosteal new-bone formation (periosteal reaction), which leads to an appearance of thickening of the cortex. Those that affect the medullary cavity will result in punctate, amorphous sclerotic lesions surrounded by the normal medullary cavity (Fig. 21-6).
Focal sclerotic lesions can affect the cortex and medullary cavity. Those that affect the cortex will usually produce periosteal new-bone formation (periosteal reaction), which leads to an appearance of thickening of the cortex. Those that affect the medullary cavity will result in punctate, amorphous sclerotic lesions surrounded by the normal medullary cavity (Fig. 21-6).
Carcinoma of the Prostate
 A substance secreted by tumor cells from metastatic carcinoma of the prostate may stimulate osteoblastic activity and produce focal areas of localized increased density, i.e., sclerotic bone lesions. The lesions may also be diffuse. These lesions are most often seen in the vertebrae, ribs, pelvis, humeri, and femora (Fig. 21-7).
A substance secreted by tumor cells from metastatic carcinoma of the prostate may stimulate osteoblastic activity and produce focal areas of localized increased density, i.e., sclerotic bone lesions. The lesions may also be diffuse. These lesions are most often seen in the vertebrae, ribs, pelvis, humeri, and femora (Fig. 21-7). The radionuclide bone scan is currently the study of choice for detecting skeletal metastases, regardless of the suspected primary (Box 21-3).
The radionuclide bone scan is currently the study of choice for detecting skeletal metastases, regardless of the suspected primary (Box 21-3).Box 21-3 Finding Metastases to Bone—Bone Scan
Avascular Necrosis of Bone
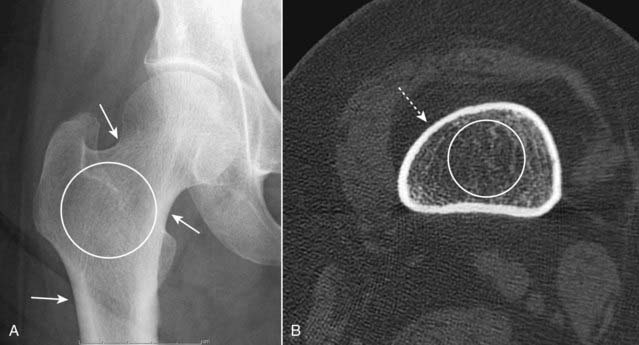
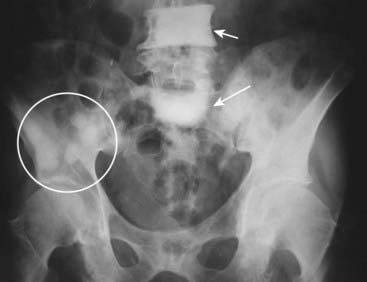
 Avascular necrosis (AVN) of bone (also called ischemic necrosis, aseptic necrosis, osteonecrosis) results from cellular death and leads to collapse of the affected bone. It usually involves those bones that have a relatively poor collateral blood supply (e.g., scaphoid in the wrist or the head of the femur) and tends to affect the hematopoietic elements of marrow earliest so that MRI is the most sensitive modality for detecting AVN.
Avascular necrosis (AVN) of bone (also called ischemic necrosis, aseptic necrosis, osteonecrosis) results from cellular death and leads to collapse of the affected bone. It usually involves those bones that have a relatively poor collateral blood supply (e.g., scaphoid in the wrist or the head of the femur) and tends to affect the hematopoietic elements of marrow earliest so that MRI is the most sensitive modality for detecting AVN. There are a myriad of causes of avascular necrosis. Some of the more common are shown in Table 21-2.
There are a myriad of causes of avascular necrosis. Some of the more common are shown in Table 21-2. On conventional radiographs, the region of avascular necrosis appears denser than the surrounding bone. On MRI, there is usually a decrease from the normal high signal produced by fatty marrow (Fig. 21-8).
On conventional radiographs, the region of avascular necrosis appears denser than the surrounding bone. On MRI, there is usually a decrease from the normal high signal produced by fatty marrow (Fig. 21-8).