3 The approximate expected number of cancers that should be found in 1,000 initial screening mammograms is
A. 1 to 2
B. 6 to 10
C. 11 to 14
D. 15 to 19
E. 20 to 24
4 Over a year, 100 cancers are identified; 94 of these were identified based on biopsy recommendations from a screening mammogram and an additional 6 cancers developed after a negative mammogram. What is the sensitivity in this population?
A. 6%
B. 88%
C. 90%
D. 94%
E. 96%
5 When assessing for accurate positioning on mediolateral oblique (MLO) view, which of the following is correct?
A. A large amount of the upper abdomen should be visible.
B. The breast should be pulled out and down.
C. The pectoral muscle should widen at the axilla and extend to the nipple, and the anterior margin should be convex.
D. The inframammary fold should be neutral in position.
6 A patient has a negative screening mammogram study and 8 months later develops a palpable mass that is biopsied to reveal invasive ductal carcinoma. This is termed a
A. False negative
B. False positive
C. True positive
D. True negative
7 Which of the following quality control tests are performed weekly for filmscreen mammography?
A. Darkroom cleanliness
B. Processor quality control
C. Screen cleanliness
D. Viewbox cleanliness
E. Fixer retention
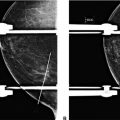
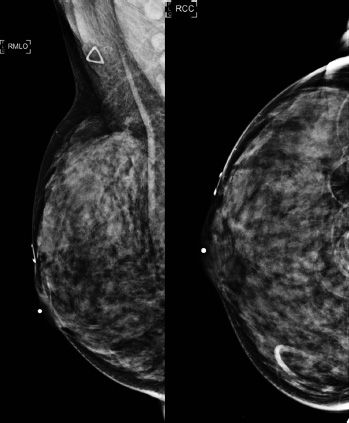
8a An 85-year-old female with history of left mastectomy. The patient presented for a screening mammogram of the right breast. A radiopaque marker was placed on the nipple. Images are provided below.
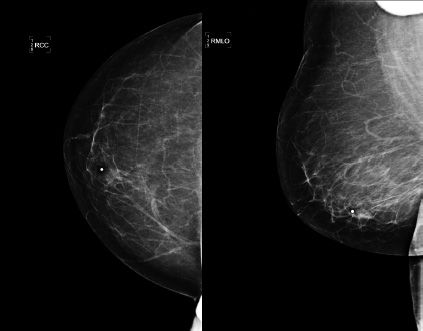
Based on the screening mammogram images, what is the most appropriate BI-RADS assessment?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 1
C. BI-RADS 2
D. BI-RADS 3
E. BI-RADS 4
8b The patient is called back for a repeat mediolateral oblique (MLO) image of the right breast (see below):
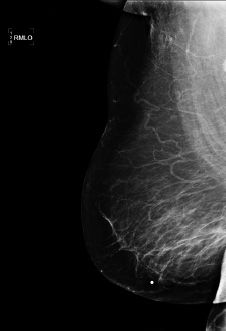
The reason the mediolateral oblique view was repeated was because of
A. Hair artifact
B. Motion artifact
C. Chin artifact
D. Deodorant artifact
E. Skin artifact
9 The posterior nipple line measures 13 cm on the mediolateral oblique (MLO) view. What is an acceptable posterior nipple line measurement on the craniocaudal (CC) view?
A. 8 cm
B. 9 cm
C. 10 cm
D. 11 cm
E. 12 cm
10 In order to meet MQSA requirements, all mammography facilities must review medical outcomes audit data for the aggregate of interpreting physicians as well as data for each individual interpreting physician at that facility. How often must the medical outcomes audit data be reviewed?
A. 3 months
B. 6 months
C. 12 months
D. 24 months
11 Prior to independently interpreting any new mammographic modality the interpreting physician must first obtain and document additional training in this modality. How many hours of training are required?
A. 4 hours
B. 6 hours
C. 8 hours
D. 12 hours
12 A screening mammogram contains significant motion artifact on one view. Which member of the team is responsible for assuring appropriate corrective action is taken?
A. Interpreting physician
B. Radiologic technologist
C. Medical physicist
D. Equipment vendor
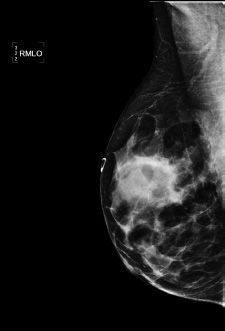
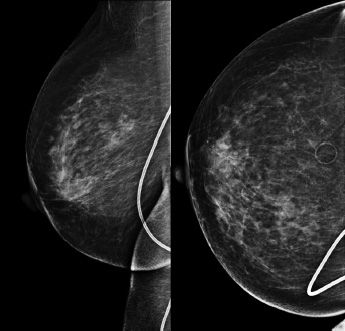
13a A 41-year-old female with history of a palpable lump in the right breast. Images are provided below.
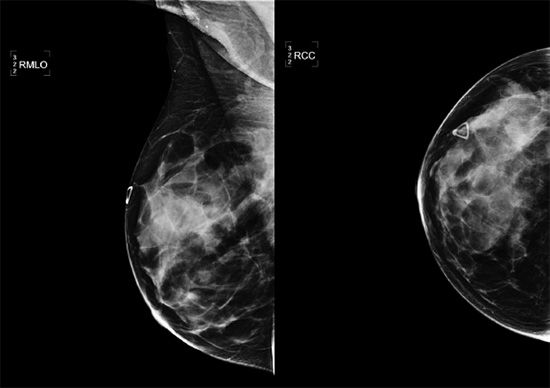
Based on the diagnostic mammogram images provided, what is the most appropriate next step?
A. Repeat MLO view due to possible artifact.
B. Proceed to a targeted right breast ultrasound of area that is palpable.
C. Request rolled craniocaudal views of the right breast.
D. Recommend return to annual screening mammography.
E. Refer the patient to see a breast surgeon.
13b The patient is called back for a repeat mediolateral oblique (MLO) image of the right breast (see below).
The reason the mediolateral oblique view was repeated was because of
A. Hair artifact
B. Chin artifact
C. Deodorant artifact
D. Suboptimal patient positioning
E. Motion artifact
14 Which of the following is correct regarding screening mammography guidelines as recommended by American College of Radiology?
A. Annual mammograms starting at age 40 until 80
B. Biannual mammograms starting at age 35 and annual after age 40
C. Annual mammograms starting at age 50
D. Biannual mammograms starting at age 40 and annual after age 50
E. Annual mammograms starting at age 40 until the individual’s overall health allows
15 Which of the following is correct regarding proper positioning of breasts in mammography?
A. The craniocaudal (CC) view is a projection parallel to the pectoralis major muscle.
B. On the CC view, the pectoralis major muscle is seen approximately 75% of the time.
C. On the mediolateral oblique (MLO) view, the pectoralis major should be concave anteriorly.
D. On the MLO view, the pectoralis major muscle should be seen above the level of the axis of the nipple.
E. The nipple should be in profile on at least one view.
16 Federal regulations require that follow-up on surgical and/or pathology results be performed for patients with positive mammograms. How frequently are facilities required to conduct this follow-up?
A. Daily
B. Weekly
C. Monthly
D. Yearly
17 Failure to inform patients of their results in a timely manner is considered a significant violation. What is the time limit set by the FDA to provide lay summaries to all patients?
A. 7 days
B. 14 days
C. 30 days
D. 60 days
18 Which organization regulates mammography quality standards in the United States?
A. Food and Drug Administration
B. American College of Radiology
C. Department of Health and Human Services
D. Regulated by each state independently without federal involvement
19 Ghosting artifact on MRI is caused by:
A. Wrong frequency-encoding direction
B. Wrong phase-encoding direction
C. Poor shimming
D. Patient motion
20 The definition of positive predictive value 1 (PPV1) is:
A. Percentage of examinations with an abnormal final interpretation that result in a tissue diagnosis of cancer within 1 year
B. Percentage of examinations with a normal initial interpretation that result in a tissue diagnosis of cancer within 1 year
C. Percentage of examinations with an abnormal initial interpretation that result in a tissue diagnosis of cancer within 1 year
D. Percentage of examinations with an abnormal final interpretation where it is known that a biopsy was performed as a result of the abnormal diagnostic examination that result in tissue diagnosis of cancer within 1 year
21 Which of the following statements concerning BRCA-1 mutation carrier is correct?
A. It is autosomal recessive.
B. It is a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17.
C. Lifetime risk of breast cancer is 25% to 35% with the carrier.
D. It is also associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.
22 What is the benchmark for the Cancer Detection Rate (CDR) according to the fourth edition of BI-RADS?
A. 1–5/1,000
B. 1–10/1,000
C. 2–10/1,000
D. >2.5/1,000
E. >5/1,000
23 What is the benchmark for the recall rate in screening mammography according to the fourth edition of BI-RADS ?
A. <10%
B. <20%
C. 10% to 15%
D. 5% to 12%
E. 5% to 15%
24 Which of the following is a requirement for continuing education in mammography?
A. Interpretation of at least 960 mammograms per year
B. 15 hours of CME that are breast specific per year
C. Performance of at least 36 breast biopsies in 36 months
D. Interpretation of at least 100 breast ultrasound examinations in 1 year
25 Which of the following describes the appropriate positioning for the MLO and CC views on a screening mammogram?
A. The pectoralis muscle must always be present on both the MLO and CC projections.
B. The pectoralis muscle must only be present on the CC projection.
C. The difference between the line from the nipple to the back of the film on CC and the line from the nipple to the pectoralis muscle on MLO is 2 cm.
D. The difference between the line from the nipple to the back of the film on CC and the line from the nipple to the pectoralis muscle on MLO is 1 cm.
26 Regarding compression plate and imaging receptor, which of the following is necessary?
A. Both 18 × 24 cm and 12 × 18 cm sizes are required.
B. Collimation to the breast contour
C. Compression force of 45 to 60 pounds.
D. A fixed grid is required for each receptor size.
E. Paddle advanced by a foot motor with hand compression adjustment
27 The following study was performed to evaluate for silicone breast implant rupture.
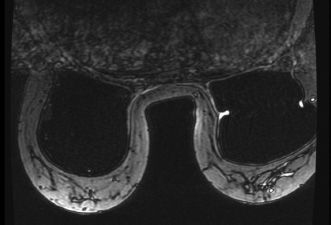
This image depicts which artifact?
A. Susceptibility artifact
B. Wrap/aliasing artifact
C. Radiofrequency (RF) interference artifact
D. Silicone saturation artifact
28 This table demonstrates data obtained from a breast care center of a community hospital in a 12-month period.
28a What is the screening abnormal interpretation rate at this center?
A. 4%
B. 5%
C. 6%
D. 8%
E. 12%
28b What is the cancer detection rate?
A. 4/1,000
B. 5/1,000
C. 6/1,000
D. 8/1,000
E. 12/1,000
29 The following image from a contrast-enhanced breast MR examination demonstrates which artifact?
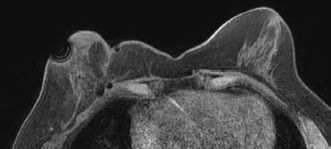
A. Chemical shift artifact
B. Wrap/Aliasing artifact
C. Susceptibility artifact
D. Motion artifact
30 Regarding standardized film labeling for mammogram images, which of the following is correct?
A. Either the patient’s full name or a unique patient identification number needs to be on the film.
B. The name and address of the facility is needed when a patient requests films for other facilities.
C. Arabic number indicating the cassette should be on every image.
D. View and laterality placed near the nipple
E. The technologist’s employee number should be included.
31 A 55-year-old woman is placed into a BI-RADS 3 category after a diagnostic workup. According to the BI-RADS lexicon, a BI-RADS 3 finding has less than what percent chance of malignancy?
A. 1%
B. 2%
C. 3%
D. 4%
E. 5%
32 A 60-year-old female presents with a finding which is placed into a BI-RADS 5 category. According to the BI-RADS lexicon, a BI-RADS 5 lesion has greater than or equal to what percent chance of malignancy?
A. 90%
B. 93%
C. 95%
D. 97%
E. 99%
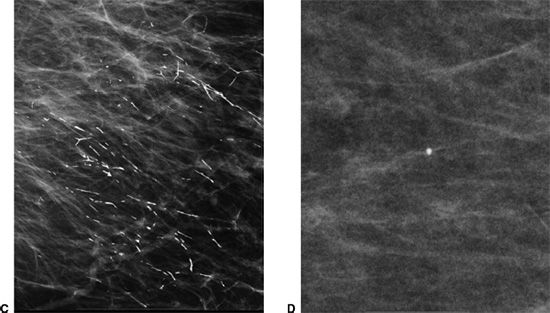
33 What artifact is noted on this study?
A. Hair artifact
B. Deodorant
C. VP shunt catheter
D. Jewelry
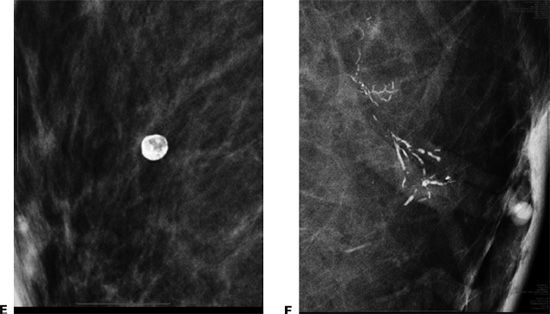
34 What artifact is noted on this study?
A. Hair artifact
B. Deodorant
C. VP shunt catheter
D. Jewelry
35 According to the American College of Radiology and the American Cancer Society, contrast-enhanced screening breast MRI is recommended for women at what percentage lifetime risk of developing breast cancer?
A. >10%
B. >20%
C. >50%
D. >75%
36 What artifact is noted on this study?
A. Static artifact
B. Gridlines artifact
C. Hair artifact
D. Roller artifact
37 A premenopausal woman requires a breast MRI with contrast. Which week of the menstrual cycle is the best choice to perform the MRI?
A. Days 1 to 6
B. Days 7 to 14
C. Days 15 to 21
D. Days 22 to 28
38 Which of the following is a clinical indicator of breast cancer risk according to the 2007 American Cancer Society (ACS) recommendations for performing a screening breast MRI as an adjunct to mammography?
A. Hodgkin disease with mantle field radiation
B. History of neurofibromatosis type 1
C. Lifetime risk of breast cancer of 10% or more using standard risk assessment models
D. Breast density > 50%
39 A phantom image obtained during a weekly check should show which of the following to meet minimum acceptable criteria?
A. Two fibers, two microcalcification clusters, and two masses
B. One fiber, two microcalcification clusters, and one mass
C. Three fibers, three calcification clusters, and three masses
D. Four fibers, three calcification clusters, and three masses
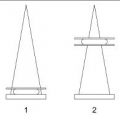
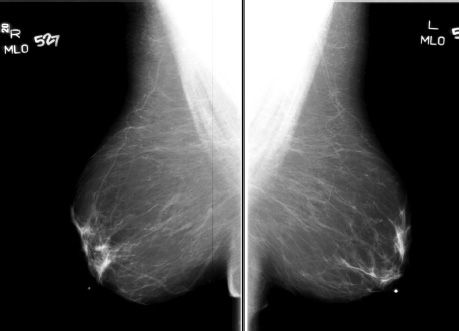
40 The view shown in the image below is suboptimal for evaluating which portion of the breast?
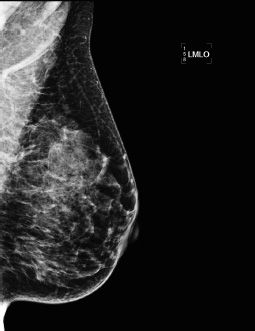
A. Inferior
B. Lateral
C. Medial
D. Superior
41 Regarding contrast-enhanced breast MRI for the detection of breast cancer, which one of the following statements is correct?
A. Cancer is excluded if a mass has hyperintense/fluid signal on the T2-weighted sequence.
B. Breast MRI is optimally performed in week 4 of a patient’s menstrual cycle.
C. T1-weighted non–fat saturation is the best sequence for identification of a fat-containing mass.
D. A body coil is the optimal radiofrequency receiver coil for the exam.
E. An equivalent dose of a gadolinium-based contrast agent is used for breast MR patients.
42a The following image from a contrast-enhanced breast MR examination demonstrates which artifact?
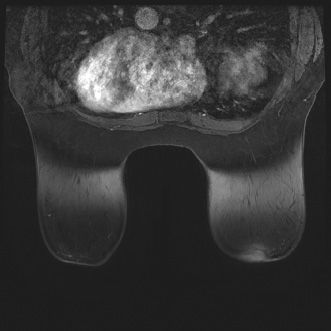
A. Chemical shift artifact
B. Wrap/aliasing artifact
C. Susceptibility artifact
D. Patient motion/ghosting artifact
E. Inhomogeneous fat saturation artifact
42b What can reduce inhomogeneous fat saturation artifact on breast MRI?
A. Enlarging the field of view
B. Reducing patient motion
C. Shimming the magnet frequently
D. Increasing the bandwidth
E. Check for a leak in the radiofrequency (RF) shield
43 The following image from a contrast-enhanced breast MR examination demonstrates which artifact?
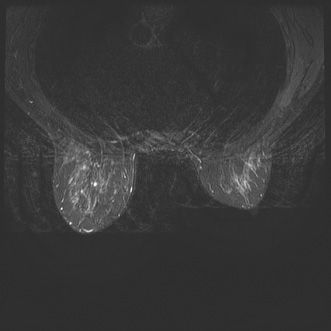
A. Chemical shift artifact
B. Wrap/aliasing artifact
C. Susceptibility artifact
D. Patient motion/ghosting artifact
E. Inhomogeneous fat saturation artifact
44 Which one of the following artifacts is present on the axial postcontrast T1-weighted fat-saturated MR image seen below?
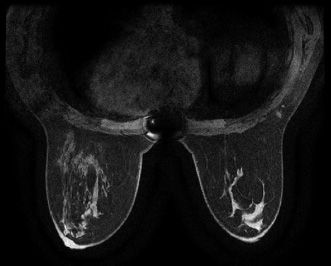
A. Chemical shift artifact
B. Wrap/aliasing artifact
C. Susceptibility artifact
D. Patient motion/ghosting artifact
E. Inhomogeneous fat saturation artifact
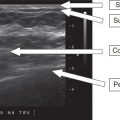
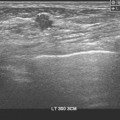
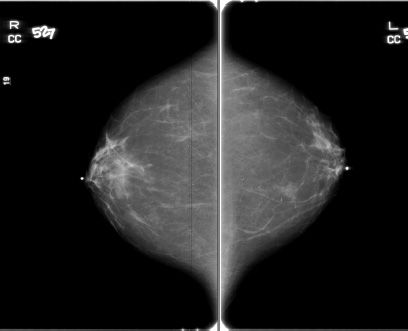
45 Based on the images, which one of the following breast imaging ultrasound lexicon terminologies best describes the finding?
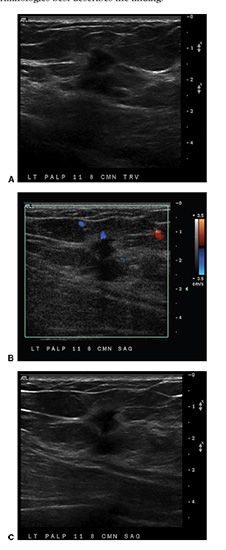
A. Oval isoechoic mass with a circumscribed margin
B. Lobular hypoechoic mass with associated skin thickening
C. Round, anechoic mass with posterior acoustic enhancement
D. Irregular hypoechoic mass with angular margins
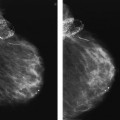
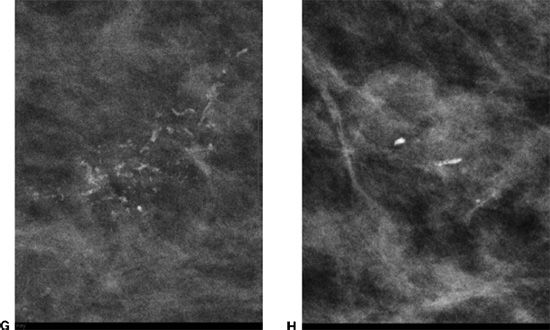
46 You are shown a left mediolateral oblique (MLO) and craniocaudal (CC) (zoomed) mammogram images (Figures A and B). What is the MOST descriptive of the calcifications?
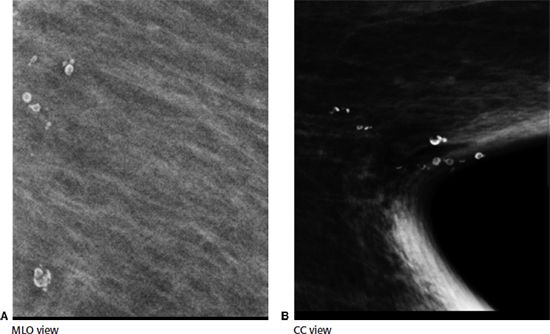
A. Amorphous
B. Pleomorphic
C. Punctate
D. Lucent centered
E. Dystrophic
47 In a well-positioned mammogram, which of the following statements is correct?
A. The pectoralis muscle should be convex on the mediolateral oblique (MLO) view.
B. The pectoralis muscle should extend inferior to the posterior nipple line on the MLO view.
C. The pectoralis muscle thickness should be >1 cm on the craniocaudal (CC) view.
D. The CC view should be exaggerated to include the axillary tail.
E. The length of the posterior nipple line on the CC view should be 1 cm greater than on the MLO view.
48 The mediolateral oblique (MLO) image taken during a screening mammogram examination demonstrates which type of digital mammogram artifact?
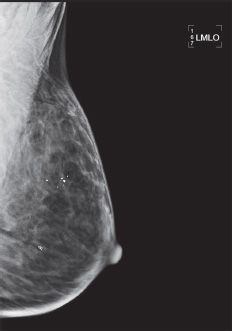
A. Motion artifact
B. Ghost image
C. Grid lines
D. Deodorant artifact
49 The below mediolateral oblique (MLO) image was taken during a screening mammogram examination demonstrates which type of digital mammogram artifact?
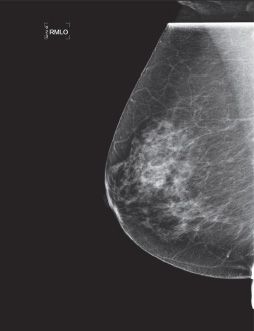
A. Dirt or dust on compression paddle
B. Ghost image
C. Readout failure
D. Dead pixels
E. Gridlines
50 What is the artifact present on the following mediolateral oblique (MLO) image? The second image denotes a part of the MLO view magnified.
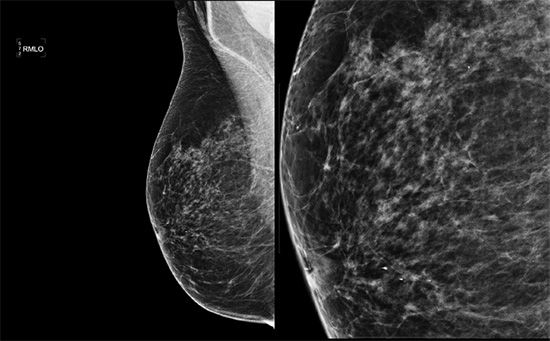
A. Motion
B. Gridlines
C. Deodorant
D. Filtration artifact
51 The universal amount of intravenous gadolinium used for contrast enhancement in breast MR imaging is:
A. 0.1 mmol/kg
B. 0.2 mmol/kg
C. 0.3 mmol/kg
D. 0.4 mmol/kg
E. 0.5 mmol/kg
52 In order to ensure the quality of the mammographic images, the posterior nipple line on MLO and CC projections should be within
A. 0.5 cm
B. 1.0 cm
C. 1.5 cm
D. 2.0 cm
E. It should be equal.
53a Which one of the following artifacts is present on the T1-weighted non–fat-saturated localizer image?
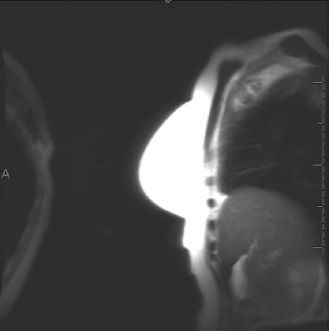
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree