KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Abnormal direct communication between artery and vein
Imaging
- •
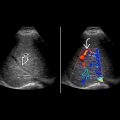
Usually in renal parenchyma; may be extrarenal
- •
Not usually visible when small
- •
Large arteriovenous fistulas: Dilated serpiginous vessels
- •
Feeding artery shows high-velocity, low-resistance waveform with spectral broadening
- •
Pulsatile arterialized flow in draining vein when large
- •
Perivascular tissue vibration producing color in adjacent tissues on color Doppler
- •
Catheter angiography is gold standard for diagnosis, allows endovascular treatment
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Pseudoaneurysm
- •
Renal artery stenosis
Pathology
- •
Complication of percutaneous transplant biopsy or insertion of nephrostomy
Clinical Issues
- •
Postbiopsy incidence: 1-18%
- •
Most asymptomatic or present with hematuria
- •
50% disappear within 48 hours; 70% resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years
- •
30% symptomatic and persistent
- •
Observation in majority with serial ultrasound
- •
Treated with superselective embolization of feeding artery if hematuria persists or renal function impaired
Scanning Tips
- •
Look for arteriovenous fistula when patients develop hematuria after renal transplant biopsy
- •
Best detected when background normal color flow is suppressed by using higher Doppler scale