NORMAL ANATOMY AND SONOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
Testis
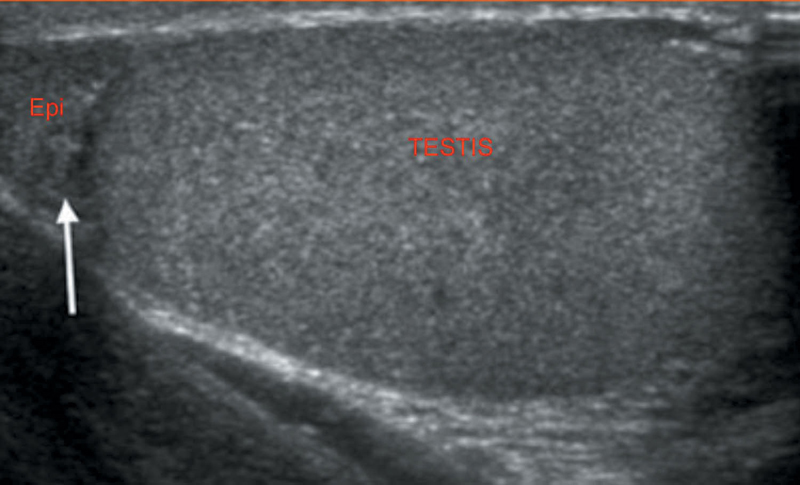
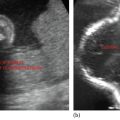
Symmetrical ovoid structure; homogeneous echotexture (Figure 42.1).
Length—3–5 centimeters; width 2–4 centimeters; anteroposterior (AP) diameter 3 centimeters.
Surrounded by dense white fibrous capsule (Tunica albuginea).
Epididymis
Elongated crescent-shaped structure.
Length—6–7 centimeters; has head, body, and tail.
Located superolaterally over posterior aspect of testis, iso/hypoechoic relative to testicle.
Tunica vaginalis
Parietal layer → Lines the scrotal wall.
Visceral layer → Envelopes the testis, epididymis, and proximal spermatic cord. Covers the entire testis except small area posteriorly called mediastinum testis (where spermatic cord and its contents join the testicle and seen as a linear echogenic band).
Blood supply
Arterial
• Testicular artery
• Deferential artery
• Cremasteric artery
Venous
Pampiniform plexus—Testicular vein drains into the inferior vena cava (IVC) on the right side and left renal vein on the left side.
Figure 42.1 Normal scrotal echotexture.
Spermatic cord: Heterogeneous structure (echogenic) in close proximity to the head of epididymis. Color Doppler shows the presence of vessels in it.
Supine position with patient’s scrotum supported by towels/sheet.
High frequency (7.5–15 MHz) linear array transducer used.
Scanning—Transverse and sagittal planes.
Valsalva maneuver—For evaluation of varicocele.
Indications for Scrotal USG
1. Evaluation of acute scrotal disorder—Torsion, Inflammation, and trauma
2. Evaluation of scrotal fluid collection
• Hydrocele
• Pyocele/Hematocele
3. Evaluation of scrotal mass
• Extratesticular
• Intratesticular
4. Evaluation of metastatic disease
• Retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy
• Testicular involvement—Lymphoma, leukemia
5. Evaluation of varicocele in infertile men
6. Evaluation of undescended testis
Discovered incidentally
Cyst of Tunica albuginea—Mean age 40 years. Usually solitary and unilocular
Cyst of Tunica vaginalis—Rare; anechoic ± septations. Echoes d/t. Hemorrhage may be seen
Intratesticular cyst—Simple, well-defined cyst with posterior acoustic enhancement
1. Tubular ectasia of rete testis:
Idiopathic, benign condition
Partial/complete obstruction of efferent ductules leading to cystic dilation
B/L and asymmetrical
USG findings:
Peripheral elongated structure containing multiple small cystic structures. No calcification, no solid component, and no flow on color Doppler.
2. Epidermoid cysts
Benign, well circumscribed.
Second to fourth decade.
USG findings:
Alternating rings of hyperechogenicity and hypoechogenicity leading to characteristic ONION RING SIGN (Whorled appearance)
No flow on Doppler imaging (c.f. testicular masses)
3. Abscess—Complication of epididymo-orchitis usually
Infectious causes → Mumps, small pox, influenza, and typhoid.
Noninfectious → Testicular torsion, infected tumor
USG findings:
Enlarged testicle containing cystic mass with hypoechoic/mixed echogenic areas
4. Scrotal tuberculosis:
On USG:
Enlarged hypoechoic, heterogeneous epididymis with or without calcifications.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree