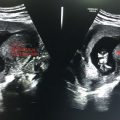
1. Gestational age estimation: Based on biparietal diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), femur length (FL), and abdominal circumference (AC) by comparing these parameters to the reference curves. If difference between maternal age (MA) and gestational age (GA) >2 weeks, pregnancy should be redated.
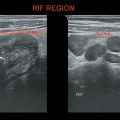
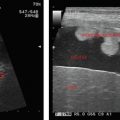
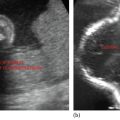
BPD: Measured in the transverse plane from the outer edge of the near temporoparietal bone to the inner edge of the far temporoparietal bone. Thalamus should be visualized at this level (Figure 18.1).
HC: Outer-to-outer diameter is measured at the same level (Figure 18.1).
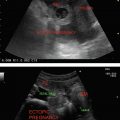
AC: Measured in the transverse plane at the fetal liver with the umbilical portion of left portal vein in the center of the abdomen (Figures 18.1 and 18.2).
Normal heart rate should always be measured (Figure 18.2).
2. Fetal morphology assessment: Requires systematic scanning.
3. Amniotic fluid volume
By measuring the deepest pocket fluid in each of the four quadrants and adding the four values.
If >20 centimeters—Polyhydramnios
<5 centimeters—Oligohydramnios
4. Placenta:
Location of placenta
Umbilical cord evaluation
Distance of placenta to internal os
5. Presentation and cardiac activity of fetus
6. For invasive procedures
Level-1 examination: Standard or routine obstetric ultrasound—Includes evaluation of the maternal uterus, cervix, adnexa, placenta, and fetal anatomy.
Level-2 examination: Specialized/targeted obstetric ultrasound—Detailed fetal anatomic survey that should be done by an expert in obstetric imaging.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree