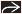Sinonasal Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Michelle A. Michel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
NHL-SN: Extranodal lymphoproliferative malignancy
Imaging
Appearance can mimic variety of neoplasms & aggressive inflammatory disorders
Predilection for nasal cavity > sinuses
CT: Homogeneous mass ± bone remodeling or destruction
May be hyperdense due to high N:C ratio
MR: ↓ T2 signal
Variable homogeneous enhancement
Imaging modality of choice: Multiplanar MR with post-contrast fat suppression
Top Differential Diagnoses
Sinonasal Wegener granulomatosis
Sinonasal adenocarcinoma
Esthesioneuroblastoma
Sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma
Pathology
3 pathologic subgroups
B-cell (Western) phenotype
T-cell (Asian) phenotype
NKTL (Asian): Subtype of T cell
Clinical Issues
Male patient in 6th decade with nonspecific symptoms of nasal obstruction & discharge
Local radiotherapy (XRT) is primary treatment ± combination chemotherapy
Diagnostic Checklist
NHL could be included in DDx for almost any aggressive adult nasal soft tissue mass
Imaging clue to diagnosis: Presence of enlarged cervical nodes & Waldeyer lymphatic mass
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Sinonasal non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL-SN)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
Natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (NKTL)
Definitions
NHL-SN: Extranodal lymphoproliferative malignancy most often of B-cell, T-cell, or NK/T-cell origin
NKTL: Subtype of peripheral T-cell lymphoma
NKTL previously called lethal midline granuloma, polymorphic reticulosis, angiocentric T-cell malignant lymphoma
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
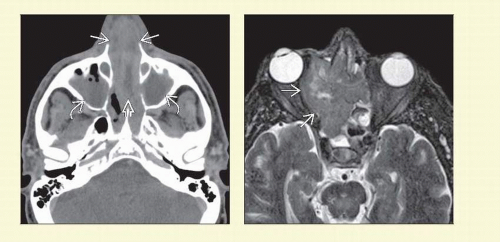
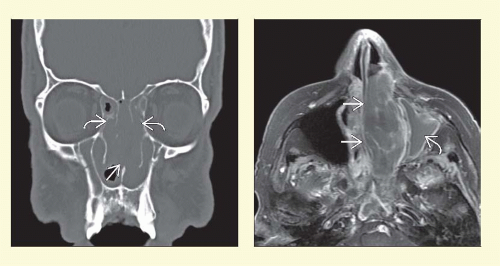
Homogeneous soft tissue mass with predilection for nasal cavity ± bone destruction
Very nonspecific imaging features
NHL-SN can mimic variety of neoplasms & aggressive inflammatory disorders
Location
Nasal cavity > maxillary > ethmoid > frontal sinuses
NKTL may have simultaneous involvement of nasopharynx & oropharynx in addition to sinonasal cavities
Size
Usually between 2-5 cm
Morphology
Variable: Diffusely infiltrative & ill-defined, nodular, or bulky mass
CT Findings
NECT
Bulky, lobular, soft tissue mass in nasal cavity ± sinuses
May be hyperdense compared to soft tissue due to high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic (N:C) ratio
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree