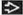Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Michelle A. Michel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant epithelial tumor with squamous cell or epidermoid differentiation
Imaging
Location: Maxillary antrum involved > 80%
CT findings
Soft tissue density mass with irregular margins
Aggressive bone destruction
MR findings
↓ T2 signal due to ↑ N:C ratio
Enhances to lesser degree than other sinonasal malignancies
Multiplanar enhanced MR optimal for tumor mapping, detection of PNTS & nodes
Top Differential Diagnoses
Sinonasal adenocarcinoma
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC)
Invasive fungal sinusitis
Sinonasal non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Wegener granulomatosis
Pathology
Risk factors: Inhaled wood dust, metallic particles, chemicals, HPV, inverted papilloma
Formaldehyde & asbestos exposure may ↑ risk
Human papilloma virus, pre- or coexisting inverted papilloma ↑ risk
Clinical Issues
Symptoms mimic chronic sinusitis & delay diagnosis
Age at presentation: 50-70 years old
Most common malignancy of sinonasal area
15% maxillary sinus SCCa have malignant adenopathy
Overall 5-year survival: 60%
Combined surgery & XRT most common treatment
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCCa)
Synonyms
Epidermoid carcinoma, transitional carcinoma, nonkeratinizing carcinoma, respiratory mucosal carcinoma
Definitions
Malignant epithelial tumor growing from sinus surface epithelium into sinus lumen with squamous cell or epidermoid differentiation
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
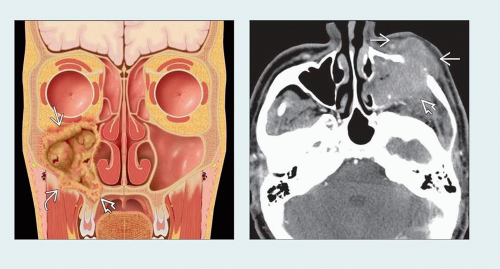
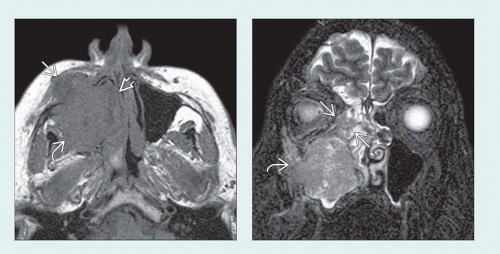
Aggressive antral soft tissue mass with invasion & destruction of sinus walls
Location
75% arise in sinuses; 30% arise primarily in nose
Maxillary antrum (85%), ethmoid (10%), frontal/sphenoid (< 5%)
Radiologist creates presurgical tumor map of spread
Medial: Nasal cavity → ethmoid sinuses
Anterior: Subcutaneous tissues of cheek
Posterior: Retroantral fat pad, pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) & masticator space
Lateral: Malar eminence & subcutaneous tissues
Superior: Through orbital floor into orbit proper or via PPF → inferior orbital fissure → orbit
Perineural tumor spread (PNTS): Inferior orbital nerve or PPF → V2 (foramen rotundum) → cavernous sinus
Size
Usually fills maxillary antrum
Morphology
Well defined to poorly defined with irregular, spiculated margins
CT Findings
CECT
Solid, moderately enhancing mass with aggressive bone destruction
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree