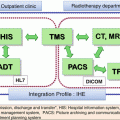
Authors
N
Median dose
Median f/u (year)
Local control rate (%)
3-year
5-year
10-year
Photon
Catton et al. [12]
24
50
5.2
23
15
Romero et al. [13]
18
50
3.1
17
Forsyth et al. [14]
39
50
8.3
39
31
Magrini et al. [15]
12
58
6
25
25
Proton (± photon)
Munzenrider et al. [2]
169
66–83
3.4
73
54
Noel et al. [4]
100
67
2.6
86 (2 year)
54 (4 year)
Igaki et al. [5]
13
72
5.8
67
46
Ares et al. [6]
42
73.5
3.2 (mean)
81
Helium
Castro et al. [16]
53
65
4.3
63
Carbon
Shults-Ertner et al. [11]
96
60
2.6 (mean)
81
70
NIRS
47
60.8
4.5
91
82
18.5.2 Chondrosarcoma
Twelve patients with chondrosarcoma were treated with C-ion RT at our institute. The 5-year actuarial local control rate and overall survival rate were 86 and 63 %, respectively. In Germany, Schulz-Ertner et al. employed C-ion RT for the treatment of 54 patients with low- and intermediate-grade chondrosarcoma of the skull base [17]. The median total dose administered was 60 CGE in 20 fractions over 3 weeks. The median follow-up was 33 months. The 4-year actuarial local control rate and 5-year overall survival rate were 89.8 and 98.2 %, respectively. Grade 3 late toxicity occurred in one patient only.
18.5.3 Other Tumors
Nine patients with olfactory neuroblastoma were treated with C-ion RT, and their 5-year actuarial local control rate and overall survival rate were 100 and 56 %, respectively. In 7 patients with skull base meningioma, the 5-year actuarial local control rate and overall survival rate were 80 and 86 %, respectively.
18.6 Case Study
18.6.1 Case 1 (Chordoma of the Skull Base)
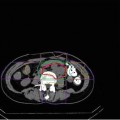
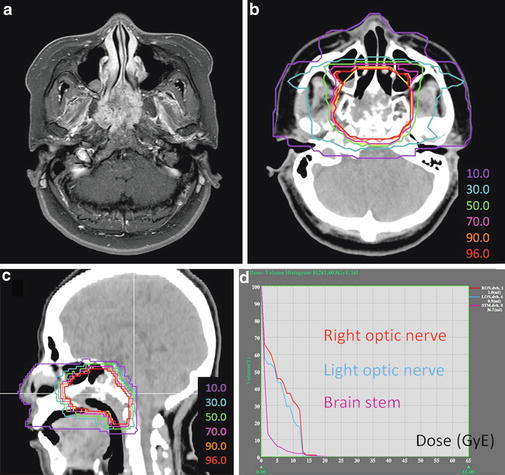
A 61-year-old woman presented with nasal septum tumor and bilateral nasal obstructions. An incisional biopsy revealed chordoma of the skull base. MRI examination revealed a lesion in the clivus invading the nasal septum, sphenoid sinus, and anterior vertebral muscle (Fig. 18.1a). C-ion RT was delivered at 60.8 GyE/16 fractions. Determination of the GTV was based on T1-weighted and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted and T2-weighted MRI obtained using image fusion technique. The CTV had minimum margins of 8 mm added to the GTV. The margin to the brain stem was reduced to meet the dose constraint for the brain stem. Three portals, one vertical and two horizontal, were used to spare the temporal lobes. The vertical beam direction should not be parallel to the nasal septum, because the beam targeted at the nasal septum may reach the brain stem, even if there is a small setup error. This patient was rotated 10° from the supine position when the vertical beam was used (Fig. 18.1b, c). The dose constraint of the optic nerves and brain stem were accomplished (Fig. 18.1d). The patient recovered well and is without any disease 2 years later.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

Fig. 18.1
(a) Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance axial image obtained before carbon ion radiotherapy. (b) and (c




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree