Small Bowel Carcinoma
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Imaging
Most commonly in jejunum, within 30 cm of ligament of Treitz
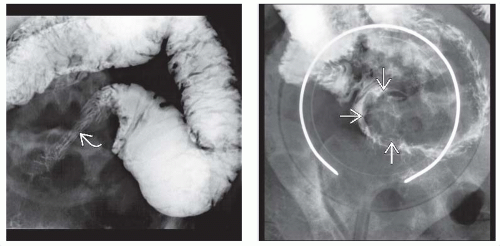
Infiltrating tumor: “Apple core” or annular lesion
Short, well-demarcated, circumferential narrowing
Irregular lumen, overhanging edges, ± ulceration
Narrow, rigid stricture with prestenotic dilatation
Polypoid sessile tumor: Small plaque-like growth
Often presents with intussusception
± enlarged mesenteric nodes; perivascular invasion
± metastases: Liver, peritoneal surfaces, ovaries
Top Differential Diagnoses
Intestinal metastases and lymphoma
NHL: Bulky mass, luminal narrowing or aneurysmal dilation
Usually with large mesenteric nodes
Metastases: Multiple, from colon or melanoma
Intestinal GIST
Usually larger, more exophytic mass
May cavitate, ± aneurysmal dilation of lumen
Carcinoid tumor
Hypervascular submucosal mass, mesenteric invasion
Primary often difficult to detect; metastases more obvious
Mesenteric mass: Ca++ and desmoplastic reaction
Crohn disease
Pathology
Adult celiac disease, Crohn disease, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, familial polyposis syndromes
All associated with ↑ prevalence of SBC
Clinical Issues
Malignant tumors of SB are < 2% of all GI tumors
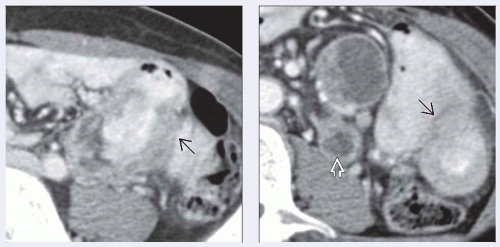 (Left) Axial CECT shows a jejunal mass
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree


|