| SKULL BASE REGION | Cerebellopontine angle/internal auditory canal |
| HISTOPATHOLOGY | N/A |
| PRIOR SURGICAL RESECTION | Surgical exploration only |
| PERTINENT LABORATORY FINDINGS | Pretreatment audiogram: Class D hearing in left ear with word recognition at 35%; right sensorineural hearing loss with word recognition at 100% |
Case description
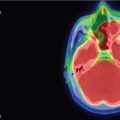
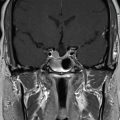
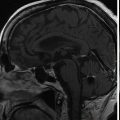
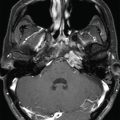
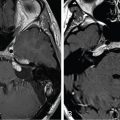
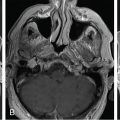
The patient presented at 64 years of age with imbalance and dizziness associated with tinnitus and decline in left-sided hearing. A workup led to the discovery of a left-sided homogeneously enhancing tumor in the cerebellopontine angle (CPA) ( Figure 8.41.1 ), which demonstrated growth over time ( Figure 8.41.2 ). A craniotomy for resection was recommended. She underwent a translabyrinthine craniotomy due to her baseline hearing loss ( Figure 8.41.3 ). During bone removal over the internal auditory canal (IAC), the facial nerve became irritable on running electromyographic monitoring. The dura was opened, and the tumor at cranial nerve VII-VIII complex was identified. The facial nerve fired at 0.3 mA stimulation of the tumor capsule, signifying that this was likely a facial nerve schwannoma (FNS) rather than a vestibular schwannoma (VS). The operation was halted in order to preserve her normal facial nerve function. Three months later, the tumor again demonstrated growth ( Figure 8.41.4 ). A repeat audiogram confirmed complete left-sided deafness ( Figure 8.41.5 ). Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS) was recommended and was performed the following year ( Figure 8.41.6 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | Gamma Knife – Perfexion |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) |
|
| Number of Fractions | 1 |