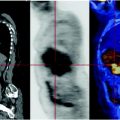
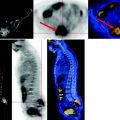
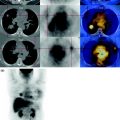
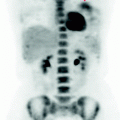
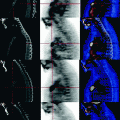
Fig. 5.1
Satellite lesion
5.4 Conclusions
The FDG PET shows high concentration of the subglottic cancer. Absence of lesions characterized by abnormal metabolism in the remaining parts of the body examined.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree