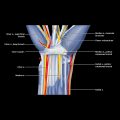
Synovial Swelling
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
 Knees, hips, hands, & feet
Knees, hips, hands, & feet
 Increasing age, trauma, excessive physical use, genetics, & obesity are all predisposing factors
Increasing age, trauma, excessive physical use, genetics, & obesity are all predisposing factors
 Variable synovial inflammation is more common in osteoarthritis than previously thought
Variable synovial inflammation is more common in osteoarthritis than previously thought
 Tends to occur close to areas of pathologically damaged bone & cartilage
Tends to occur close to areas of pathologically damaged bone & cartilage
 Only modest correlation between severity of osteoarthritis & degree of synovitis
Only modest correlation between severity of osteoarthritis & degree of synovitis
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
 Now known as giant cell tumor of tendon sheath
Now known as giant cell tumor of tendon sheath
 Benign proliferative synovial disorder
Benign proliferative synovial disorder
 Knee > hip > ankle > shoulder
Knee > hip > ankle > shoulder
 Joint involvement is diffuse though may predominate in 1 or several areas of joint
Joint involvement is diffuse though may predominate in 1 or several areas of joint
 Usually moderate to high degree of hyperemia
Usually moderate to high degree of hyperemia
 Characteristic MR pattern on gradient echo imaging due to paramagnetic effect of hemosiderin
Characteristic MR pattern on gradient echo imaging due to paramagnetic effect of hemosiderin
 Localized to single area of synovium
Localized to single area of synovium
 Proliferation & metaplastic transformation of synovium
Proliferation & metaplastic transformation of synovium
 Affects any synovium, including synovium-lined joint, bursa, or tendon
Affects any synovium, including synovium-lined joint, bursa, or tendon
 Active synovial proliferation & cartilaginous metaplasia → inactive phase
Active synovial proliferation & cartilaginous metaplasia → inactive phase
 Mineralized nodules are hyperechoic; cartilage nodules are hypoechoic
Mineralized nodules are hyperechoic; cartilage nodules are hypoechoic
 Variable-sized joint effusion
Variable-sized joint effusion
 ± erosion of adjacent cartilage & bone
± erosion of adjacent cartilage & bone
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree